Phosphine-borane
In chemistry, phosphine-boranes are organophosphorus compounds with the formula R3−nHnPBH3. They are Lewis acid-Lewis base adducts derived from organophosphines (PR3−nHn) and borane (BH3). They are generally colorless or white solids. Since these adducts are air-stable, they represent a protected form of the parent organophosphine.[1][2]
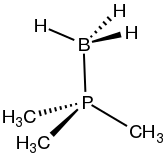
Structure of Me3PBH3, a phosphine-borane.
Formation and decomplexation
Typically phosphine-boranes are produced by treating the parent phosphine with a source of borane:
- PR3−nHn + BH3 → R3−nHnPBH3
Because borane solutions are expensive or dangerous, the borane is often generated in situ, e.g., by oxidation of borohydride with iodine.[3]
Deprotection to liberate the phosphine is often achieved by treatment with a tertiary amine:[2]
- R3−nHnPBH3 + R'3N → R'3NBH3 + R3−nHnP
See also
- Frustrated Lewis pair, where the borane is often tris(pentafluorophenyl)borane
- Ammonia borane, related to phosphine-borane but with ammonia or amines in place of organophosphines
References
- Alayrac, Carole; Lakhdar, Sami; Abdellah, Ibrahim; Gaumont, Annie-Claude (2014). "Recent Advances in Synthesis of P-BH3 Compounds". Phosphorus Chemistry II. Topics in Current Chemistry. Vol. 361. pp. 1–82. doi:10.1007/128_2014_565. ISBN 978-3-319-15511-1. PMID 25504072.
- Brunel, Jean Michel; Faure, Bruno; Maffei, Michel (1998). "Phosphane–Boranes: Synthesis, Characterization and Synthetic Applications". Coordination Chemistry Reviews. 178–180: 665–698. doi:10.1016/S0010-8545(98)00072-1.
- Mathur, M. A.; Myers, W. H.; Sisler, H. H.; Ryschkewitsch, G. E. (2007). "Methyldiphenylphosphine-Borane and Dimethylphenylphosphine-Borane". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 15. pp. 128–133. doi:10.1002/9780470132463.ch29. ISBN 9780470132463.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.