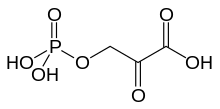
Phosphohydroxypyruvic acid
Phosphohydroxypyruvic acid is an organic acid most widely known as an intermediate in the synthesis of serine.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Oxo-3-(phosphonooxy)propanoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.559 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Phosphohydroxypyruvic+acid |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H5O7P | |
| Molar mass | 184.040 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Chemical properties
Phosphohydroxypyruvic acid is a moderately weak acid.
References
- Igamberdiev, Abir U.; Kleczkowski, Leszek A. (2018). "The Glycerate and Phosphorylated Pathways of Serine Synthesis in Plants: The Branches of Plant Glycolysis Linking Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism". Frontiers in Plant Science. 9: 318. doi:10.3389/fpls.2018.00318. PMC 5861185. PMID 29593770.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.