Piroctone olamine
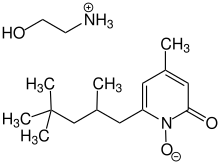
Piroctone olamine (INN; also known as piroctone ethanolamine) is a compound sometimes used in the treatment of fungal infections.[1] Piroctone olamine is the ethanolamine salt of the hydroxamic acid derivative piroctone was first synthesized in 1979 by Schwarzkopf-Henkel (Germany).
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.065.957 |
| MeSH | Piroctone+olamine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H30N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 298.421 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It is often used in anti-dandruff shampoo as a replacement for the commonly used compound zinc pyrithione which was banned in the EU in 2021 due to potentially DNA-damaging effects. In addition to reducing the prevalence of dandruff through actively decreasing sebum production, Piroctone Olamine has been found to improve hair shaft diameter and reduce hair fall, while providing hair conditioning advantages.
It is structurally similar to ciclopirox and pyrithione, containing a substituted pyridine (pyridinone) group which inhibits ergosterol synthesis.
References
- Dubini F, Bellotti MG, Frangi A, Monti D, Saccomani L (2005). "In vitro antimycotic activity and nail permeation models of a piroctone olamine containing transungual water soluble technology". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 55 (8): 478–83. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1296892. PMID 16149717.