Pitfall trap
A pitfall trap is a trapping pit for small animals, such as insects, amphibians and reptiles. Pitfall traps are a sampling technique, mainly used for ecology studies and ecologic pest control.[1] Animals that enter a pitfall trap are unable to escape. This is a form of passive collection, as opposed to active collection where the collector catches each animal (by hand or with a device such as a butterfly net). Active collection may be difficult or time-consuming, especially in habitats where it is hard to see the animals such as thick grass.

Structure and composition
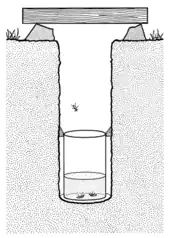
Pitfall traps come in a variety of sizes and designs. They come in two main forms: dry and wet pitfall traps. Dry pitfall traps consist of a container (tin, jar or drum) buried in the ground with its rim at surface level used to trap mobile animals that fall into it. Wet pitfall traps are basically the same, but contain a solution designed to kill and preserve the trapped animals. The fluids that can be used in these traps include formalin (10% formaldehyde), methylated spirits, alcohol, ethylene glycol, trisodium phosphate, picric acid or even (with daily checked traps) plain water. A little detergent is usually added to break the surface tension of the liquid to promote quick drowning. The opening is usually covered by a sloped stone or lid or some other object. This is done to reduce the amount of rain and debris entering the trap, and to prevent animals in dry traps from drowning (when it rains) or overheating (during the day) as well as to keep out predators.
One or more fence-lines of some sort may be added to channel targets into the trap.[2]
Traps may also be baited. Lures or baits of varying specificity can be used to increase the capture rate of a certain target species or group by placing them in, above or near the trap. Examples of baits include meat, dung, fruit and pheromones.
Uses
Pitfall traps can be used for various purposes:
- During the mating seasons of toads, frogs and salamanders in temperate climates, these animals often have to cross busy roads on their way from wintering grounds to breeding ponds.[3] To prevent them from being killed, volunteers may place low fences along roads which the animals have to cross. On short distances, dry pitfall traps are then placed along the fences to collect the animals, which subsequently are manually transferred to the other side of the road, thus preventing massive roadkill.
- Collectors and researchers of various ground-dwelling arthropod species may use pitfall traps to collect the animals they are interested in. This can be done without bait (for example ground beetles and spiders) or with bait (for example dung beetles).
- When used in series, these traps may also be used to estimate species richness (number of species present) and abundances (number of individuals), and this combined information may be used to calculate biodiversity indices (e.g. the Shannon index).
Disadvantages of pitfalls
There are inevitably biases in pitfall sampling when it comes to comparison of different groups of animals and different habitats in which the trapping occurs. An animal's trappability depends on the structure of its habitat (e.g. density of vegetation, type of substrate). Gullan and Cranston (2005) recommend measuring and controlling for such variations. Intrinsic properties of the animal itself also affect its trappability: some taxa are more active than others (e.g. higher physiological activity or ranging over a wider area), more likely to avoid the trap, less likely to be found on the ground (e.g. tree-dwelling species that occasionally move across the terrain), or too large to be trapped (or large enough to escape if trapped). Trappability can also be affected by conditions such as temperature or rain, which may alter the animal's behaviour. The capture rate is therefore proportional not only to how abundant a given type of animal is (which is often the factor of interest), but how easily they are trapped. Comparisons between different groups must therefore take into account variation in habitat structure and complexity, changes in ecological conditions over time and the innate differences in species.[4]
See also
References
- Pitfall traps description
- Ellis, M.V. (2013). "Impacts of pit size, drift fence material and fence configuration on capture rates of small reptiles and mammals in the New South Wales rangelands". Australian Zoologist. 36 (4): 404–412. doi:10.7882/AZ.2013.005.
- "City of Chilliwack".
- Ellis, M. V.; Bedward, M. (2014). "A simulation study to quantify drift fence configuration and spacing effects when sampling mobile animals". Ecosphere. 5 (5): art55. doi:10.1890/ES14-00078.1.
Further reading
- Gullan, P. J. and Cranston, P. S. (2005). The Insects: An Outline of Entomology. Malden, MA. Blackwell Publishing.
