Danaus chrysippus
Danaus chrysippus, also known as the plain tiger,[1][2] African queen,[2] or African monarch, is a medium-sized butterfly widespread in Asia, Australia and Africa.[2] It belongs to the Danainae subfamily of the brush-footed butterfly family Nymphalidae. Danainae primarily consume plants in the genus Asclepias, more commonly called milkweed. Milkweed contains toxic compounds, cardenolides, which are often consumed and stored by many butterflies. Because of their emetic properties, the plain tiger is unpalatable to most predators. As a result, its coloration is widely mimicked by other species of butterflies. The plain tiger inhabits a wide variety of habitats, although it is less likely to thrive in jungle-like conditions and is most often found in drier, wide-open areas.[3]
| Plain tiger[1][2] African queen[2] | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Upperside | |
| Male underside both D. c. chrysippus, Kerala, India | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Lepidoptera |
| Family: | Nymphalidae |
| Genus: | Danaus |
| Species: | D. chrysippus |
| Binomial name | |
| Danaus chrysippus | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
| |

D. chrysippus encompasses three main subspecies: D. c. alcippus, D. c. chrysippus, and D. c. orientis. These subspecies are found concentrated in specific regions within the larger range of the entire species.[4]
The plain tiger is believed to be one of the first butterflies depicted in art. A 3,500-year-old ancient Egyptian fresco in Luxor features the oldest known illustration of this species.
Description
D. chrysippus is a medium-sized butterfly with a wingspan of about 7–8 cm (2.8–3.1 in). The body is black with white spots. The wings are a brownish orange, the upper side brighter and richer than the underside. The apical half of the forewing is black with a white band. The hindwing has three black spots in the center. The wings are bordered in black and outlined with semicircular white spots.[5] This species exhibits slight sexual dimorphism, as the Male has large scent glands on his hindwings, which the female lacks. They appear as a large black spot with a white centre if viewed from the underside
D. chrysippus is a polymorphic species, so the exact coloring and patterning vary within and between populations.[6][7]
It is similar in appearance to the Indian fritillary (Argynnis hyperbius), which may coexist with it.[8][9]
 Close-up of the wing scales of a male Danaus chrysippus
Close-up of the wing scales of a male Danaus chrysippus Male showing the pheromone pouch and brush-like organ in Kerala
Male showing the pheromone pouch and brush-like organ in Kerala
Geographic range
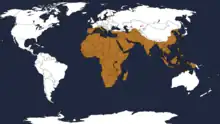
The plain tiger is found across the entirety of Africa, where the predominant subspecies is D. c. alcippus. Its range extends across the majority of Asia throughout Indian subcontinent,[1] as well as many south Pacific islands. The plain tiger is even present in parts of Australia.[3] D. c. chrysippus is most common throughout Asia and in some select regions in Africa, while D. c. orientis is present in more tropical African regions as well as some African islands, including Madagascar and the Seychelles.[5][2] It is also found in Southern Europe and Kuwait. These insects are considered bioinvaders in North America.
Habitat
The plain tiger prefers arid, open areas, and is found in a variety of habitats, including deserts, mountains, deciduous forests, and human-tended gardens in cities and parks. It is comfortable at altitudes ranging from sea level to around 1,500 m (4,900 ft).[3]
Food resources
Larval food plants
The plain tiger's larval host plants are from several families, most importantly Asclepiadoideae (Apocynaceae):[10]
- Asclepias – milkweeds (recorded on A. cancellata, A. coarctata, A. curassavica, A. fulva, A. kaessneri, A. lineolata, A. physocarpa, A. reflexa, A. scabrifolia, A. semilunata, A. stenophylla, A. swynnertonii, A.syriaca)
- Aspidoglossum interruptum
- Calotropis – mudar (recorded on C. gigantea, C. procera)
- Caralluma burchardii (recorded from Canary Islands/Spain)
- Ceropegia dichotoma (recorded from Canary Islands/Spain)
- Cryptolepis buchananii
- Cynanchum (recorded on C. abyssinicum, C. acutum, C. altiscandens, C. amplexicaule, C. carnosum, C. floribundum, C. sublanceolatum)
- Gomphocarpus fruticosus
- Kanahia laniflora
- Leichardtia australis
- Leptadenia hastata
- Marsdenia leichhardtiana
- Metaplexis japonica
- Orbea variegata (recorded from Canary Islands/Spain)
- Oxystelma pulchellum
- Pentatropis (recorded on P. atropurpurea, P. quinquepartita)
- Pergularia daemia
- Periploca linearifolia
- Pleurostelma cernuum
- Secamone (recorded on S. afzelii, S. parvifolia, S. platystigma)
- Stapelia gigantea
- Stathmostelma (recorded on S. gigantiflorum, S. pedunculatum)
- Vincetoxicum (recorded on V. tanakae, V. sylvaticum)
Host plants from other families include Dyerophytum indicum (Plumbaginaceae), Ficus (Moraceae; recorded on F. laevis, F. racemosa), Ipomoea (Convolvulaceae; recorded on I. alba, I. bona-nox), Lepisanthes rubiginosa (Sapindaceae) as well as some Euphorbiaceae, Malvaceae, Poaceae, Rosaceae and Scrophulariaceae.
Adult food plants
Adult plain tiger butterflies obtain nectar from various flowering plants. The particular plants available vary depending on the geographic range of the butterfly population and the season, as certain plants do not flower throughout the entire year.[11][12]
India
- Catharanthus roseus
- Lantana camara
- Vernonia cinerea
- Tridax procumbens
- Asystasia gangetica
- Antigonon leptopus, January through April and August through December
- Tecoma stans, May through December[11]
- Heliotropium indicum
Australia
- Goodenia maidenian
- Eucalyptus conglobata
- E. oleosa
- Ptilotis obovata
- Asclepias
- Lantana
- Leucopogon
- Daviesia
In addition to nectar, adult plain tigers obtain pyrrolizidine alkaloids from the dead stems of different plant types. In Australia, the following plants have been identified as sources of pyrrolizidine alkaloids for D. chrysippus:[12]
- Parsonsia eucalyptophylla
- P. straminea
- Echium plantogineum
- Senecio pterophorus
- Heliotropium amplexicaule
Parental care
Oviposition
Females lay eggs singly on the underside of the leaves of a larval food plant.[11] The eggs are most often laid close to the ground.
Life history
Egg
The egg of the plain tiger is about 1.7 mm (0.067 in) long and 0.5 mm (0.020 in) across. When first laid it is white, but gradually turns brown over time. The egg is ridged and dome-shaped. Depending on temperature, the egg is typically hatched in 3–5 days.[11]
 Egg at Tamil Nadu, India
Egg at Tamil Nadu, India At Mananpur, Mumbai, Maharashtra
At Mananpur, Mumbai, Maharashtra
Caterpillar
The larvae of D. chrysippus proceeds through five instar stages. The first instar is about 4 mm (0.16 in) long, and its body is white while the head is black. The second instar is about 8 mm (0.31 in) long, and its body is primarily gray with yellow and black horizontal stripes. This coloration remains for the final three instar stages. The third instar is about 14 mm (0.55 in) long, the fourth about 25 mm (0.98 in) long, and the fifth about 36 mm (1.4 in) long. Depending on temperature, the larval stage can last from 12 to 20 days.[11]
 Larva eating its own eggshell
Larva eating its own eggshell Caterpillar making "moat" to feed during the first instar
Caterpillar making "moat" to feed during the first instar Second instar
Second instar Mature caterpillar
Mature caterpillar_caterpillar_on_a_Calotropis_(Milkweed)_species_in_Hyderabad%252C_AP_W_IMG_7970.jpg.webp) Older caterpillar
Older caterpillar
Prepupal and pupal stages
Before pupation, the caterpillar will become motionless and cease feeding. Its color shifts slightly from gray to brown, and it may lose a small amount of body mass. The prepupal stage lasts 1–3 days depending on temperature. The pupal stage lasts 9–15 days depending on temperature, and the pupa changes color over this period from a pale green to dark brown. Pupae are about 17 mm (0.67 in) tall and 8 mm (0.31 in) wide.[11]
 Pupa
Pupa Fresh pupa at Bandra Kurla Complex, Mumbai
Fresh pupa at Bandra Kurla Complex, Mumbai Pink pupa due to pupation among inanimate objects
Pink pupa due to pupation among inanimate objects
Adult
Male and female D. chrysippus butterflies look very similar and are also similar in size. Adult butterflies typically have a wingspan of 75 mm (3.0 in). The bodies of adult plain tigers are about 23 mm (0.91 in) long, and their antennae are about 12 mm (0.47 in) long. Depending on temperature, males live about 10–15 days and females live about 7–12 days.[11]
 A newly emerged plain tiger female in captivity
A newly emerged plain tiger female in captivity Male D. c. chrysippus, recently emerged from chrysalis
Male D. c. chrysippus, recently emerged from chrysalis
-_mud-puddling_in_Hyderabad%252C_AP_W_IMG_9741.jpg.webp) Mud-puddling
Mud-puddling%252C_Bangalore%252C_India.jpg.webp) Resting with its wings closed
Resting with its wings closed Basking
Basking
Enemies
Egg and larval predators
Most predators of the early developmental stages of D. chrysippus are arthropods. Such potential predators include various kinds of spiders, assassin bugs, cockroaches, ladybugs, ants, and mantises. The caterpillars will even cannibalize each other. Egg and larval mortality is often high; as many as 84% of eggs may be lost to predation and up to 97% of larvae can be lost by the fifth instar, although most larval deaths occur during the third instar.[13]
Adult predators
The most common predators of adult plain tigers are birds. In eastern Africa, the most common predator is the fiscal shrike L. c. humeralis.[14]
Parasites
There are several organisms which parasitize the larvae of D. chrysippus. The fly S. flavohalterata of the Family Tachinidae is responsible for small amounts of parasitization in D. chrysippus populations. It is unclear whether the fly oviposits on the eggs of D. chrysippus or whether the fly oviposits on leaves which are then consumed by D. chrysippus larvae. S. flavohalterata does not kill the larvae, and development is normal until the pupal stage, when larvae dies and the parasite emerges from the pupa instead. A. chrysippi, a parasitic wasp of the family Braconidae, oviposits on larvae early in their development and then kills them in the later stages. As many as fifty wasps may emerge from one large caterpillar, and they then pupate on the deceased host. Parasitic wasps of the genus Charops also infest plain tiger populations, likely during the egg or first instar stage, and then kill the larvae in a later instar stage.[15]
Sturmia convergens is also a parasitoid of D. chrysippus.[16]
Diseases
The plain tiger is infected by a male-killing bacterium called Spiroplasma. Male-killing bacteria are transmitted vertically, from mother to offspring. Female plain tigers infected with Spiroplasma will produce all-female broods, because the bacteria kills infected male offspring during either their embryonic or first larval instar stage. Although male-killing bacteria are uncommon in species which lay eggs singly. Experimentally treating infected females with antibiotics restored an even sex ratio to their subsequent broods, thus indicating that it is indeed Spiroplasma which is responsible for all-female broods in D. chrysippus. However, the prevalence of this bacteria in the plain tiger seems to be restricted to east African populations.[17]
Protective coloration and behavior
The plain tiger is mimicked by several species due to its unpalatability to potential predators. Previously, it was thought that cardenolides obtained from food sources during the larval stage were responsible for the aversive nature of adult D. chrysippus, but many larval food sources lack cardenolides, and some adult West African populations of D. chrysippus do not store cardenolides well, yet still repel predators. More recently, pyrrolizidine alkaloids have been proposed to be responsible for the unpalatability of D. chrysippus. Adult male danaines often feed on plants containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids, and although females rarely do, they may be protected simply through their resemblance to males of the same species. The ability of D. chrysippus to store cardenolides varies across populations, so likely both cardenolides and pyrrolizidine alkaloids contribute to the unpalatability of D. chrysippus to different extents depending on the population.[18]
Because the plain tiger is unpalatable (also called inedible), they are aposematic - their bright coloration serves as a warning to predators that they are either distasteful or toxic. Consequently, once a predator has made the mistake of attempting to eat a plain tiger, they will refrain in the future from attacking similarly colored butterflies. This has led to the evolution of a number of other species which mimic the plain tiger in order to co-opt the protection conferred by such bright coloration.[19]
Batesian mimicry
Batesian mimics are palatable species which mimic unpalatable species, and D. chrysippus is a model for several Batesian mimics, including H. misippus, P. poggei, M. marshalli, and P. dardanus in east Africa. Batesian mimicry is only effective so long as the mimic is less common than the model, or predators will learn that the mimics are in fact edible and then attempt to eat the similar-looking unpalatable butterflies.[19]
Müllerian mimicry
Müllerian mimicry occurs when multiple species which are all unpalatable evolve to resemble one another. In this case, the relative abundance of each species does not have a deleterious effect on any others, because a predator which eats any one of them will be deterred from eating any similar-looking butterflies. In Uganda, D. chrysippus has several Müllerian mimics, including A. encedon and A. encedana.[19]
Genetics
Subspecies
Despite the external similarity, the common tiger (D. genutia) is not closely related to the plain tiger. Three subspecies were considered valid in a 2005 review:[20]
- Danaus chrysippus chrysippus
- Asia, Mediterranean region, northern tropical Africa
- Danaus chrysippus alcippus (Cramer, 1777) - formerly D. c. aegyptius
- From the Cape Verde Islands through tropical Africa to Yemen and Oman. Browner with broader white forewing spots.
- Danaus chrysippus orientis (Aurivillius, 1909) - formerly D. c. liboria
- Saint Helena, southern tropical Africa to South Africa, Madagascar, Comoros, Seychelles and Mascarenes. Small white forewing spots.
D. c. alcippus is well on the way of becoming a distinct species.[20]
On the other hand, the former subspecies petilia, nowadays is recognized as a good species, the lesser wanderer (D. petilia). More enigmatic[20] is the status of the former subspecies (or forms) dorippus and bataviana. These are tentatively also regarded as a distinct species, the dorippus tiger (D. dorippus).
However, it appears (from analysis of mtDNA sequences, which are only inherited from the mother) that the dorippus tiger is the product of an ancient lineage of Danaus hybridizing with plain tiger females[20] As the plain tiger is known to be parasitized at least occasionally by Spiroplasma bacteria which selectively kill off male hosts,[21] a subsequent scarcity of plain tiger males might have led to this hybridization and the evolution of the dorippus tiger. From the colour pattern of this species, it can be assumed that the ancient lineage had no black apex on the forewings, as this characteristic is still absent in D. dorippus.
The presumed subspecies cratippus most likely belongs to either the lesser wanderer or the dorippus tiger, but confirmation of its taxonomic status requires more research. In any case, these three species are closely related; their closest relatives, in turn, might be the soldier (D. eresimus) and queen (D. gilippus) butterflies.[20]
Several local forms have been described from Asia:
- Danaus chrysippus chrysippus f. alcippoides
- The upper hindwing is more or less very white; about half of the individuals have a second submarginal spot in the forewing. Occasionally found in South-East Asia, very rarely in India.
- Danaus chrysippus chrysippus f. gelderi
- The upper hindwing has white markings. Occasionally found on Sulawesi.
- Danaus chrysippus chrysippus f. bowringi
- The upper hindwing has a subapical band composed of somewhat larger spots, and an additional forewing spot as in f. alcippoides is always present. Found throughout the eastern parts of this subspecies' range.
On the other hand, the plethora of named taxa from Africa are apparently F1 or F2 hybrids between the plain tiger subspecies (the contact zone of which is in the general area of Uganda) and/or D. dorippus:
- Danaus chrysippus × alcippoides
- is D. c. chrysippus × D. c. alcippus
- Danaus × transiens, Danaus × klugii, Danaus × albinus and Danaus × semialbinus
- are D. c. alcippus × D. dorippus
Genomes
When D. chrysippus was analyzed via a sample from Kampala, Uganda, it was found that the population was undergoing a significant level of evolutionary change. Three loci were examined, and genotypic frequency differences found at two of the three suggested that opposing selective forces, likely pertaining to Mullerian and Batesian mimicry, acting on males and females is contributing to a balanced polymorphism.[19]
Courtship and mating

_mating_in_Hyderabad%252C_AP_W_IMG_9493.jpg.webp)
In addition to conferring protection from predators, pyrrolizidine alkaloids are necessary in the mating ritual of D. chrysippus. Male plain tigers use the alkaloids to synthesize pheromones which are stored in hair-pencils sheathed in alar organs, which are specialized scales on top of the hindwing. The hair-pencils are fanned out during courtship to release these pheromones, and this appears to be necessary for attracting females. Males deprived of pyrrolizidine alkaloids in their diet are considerably less successful in mating; mating appears to occur preferentially between butterflies of the same subspecies, so coloration is likely also an important signal in the mating process. Female plain tigers have been recorded as mating up to four times.[12]
See also
References
- Varshney, R.K.; Smetacek, Peter (2015). A Synoptic Catalogue of the Butterflies of India. New Delhi: Butterfly Research Centre, Bhimtal & Indinov Publishing, New Delhi. doi:10.13140/RG.2.1.3966.2164. ISBN 978-81-929826-4-9.
- Savela, Markku. "Danaus chrysippus (Linnaeus, 1758)". Lepidoptera and Some Other Life Forms. Retrieved July 1, 2018.
- "Butterflies of Africa - Danaus chrysippus". www.learnaboutbutterflies.com. Retrieved 2017-10-22.
- Smith, David a. S.; Lushai, Gugs; Allen, John A. (2005-06-01). "A classification of Danaus butterflies (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae) based upon data from morphology and DNA". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 144 (2): 191–212. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2005.00169.x. ISSN 0024-4082.
- "Plain tiger videos, photos and facts - Danaus chrysippus". Arkive. Archived from the original on 2017-10-25. Retrieved 2017-10-22.
- Bingham, Charles Thomas (1907). Fauna of British India. Butterflies Vol. 2. London, Calcutta, Simla ...: London, Taylor and Francis; Thacker, Spink, & Co.; [etc.,etc.] pp. 11–13.
- Moore, Frederic (1890–1892). Lepidoptera Indica. Vol. I. Vol. 1. London: Lovell Reeve and Co. pp. 36–41.
- Aamir, Moh'd; Salman, Nour (2020-02-29). "Himalayan butterfly found in Fujairah". Dubai: WAM. Retrieved 2020-03-01.
- Duncan, Gillian (2020-03-01). "Himalayan butterflies found for first time in UAE". The National. Retrieved 2020-03-01.
- Robinson, Dr Gaden S. "Caterpillar Hostplants Database - The Natural History Museum". www.nhm.ac.uk. Retrieved 2017-12-01.
- Golestaneh, S. R.; Askary, H.; Farar, N.; Dousti, A. (2009). "The life cycle of Danaus chrysippus Linnaeus (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae) on Calotropis procera in Bushehr-Iran". Munis Entomology & Zoology. 4 (2): 451–456.
- R. L., Kitching (1999). Biology of Australian Butterflies. Scheermeyer, E.; Jones, R. E.; Pierce, N. E. Melbourne: CSIRO Publishing. ISBN 9780643105140. OCLC 769343248.
- Zalucki, M. P.; Kitching, R. L. (1982-01-01). "Temporal and spatial variation of mortality in field populations of Danaus plexippus L. and D. chrysippus L. Larvae (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae)". Oecologia. 53 (2): 201–207. Bibcode:1982Oecol..53..201Z. doi:10.1007/bf00545664. ISSN 0029-8549. PMID 28311110. S2CID 6102209.
- Brower, Lincoln P.; Gibson, D. O.; Moffitt, C. M.; Panchen, A. L. (1978-06-01). "Cardenolide content of Danaus chrysippus butterflies from three areas of East Africa". Biological Journal of the Linnean Society. 10 (2): 251–273. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8312.1978.tb00015.x. ISSN 0024-4066.
- Edmunds, Malcolm (1976-03-01). "Larval mortality and population regulation in the butterfly Danaus chrysippus in Ghana". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 58 (2): 129–145. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1976.tb00823.x. ISSN 0024-4082.
- "CAB Direct". www.cabdirect.org. Retrieved 2017-11-01.
- Jiggins, F. M.; Hurst, G. D.; Jiggins, C. D.; v. d. Schulenburg, J. H.; Majerus, M. E. (May 2000). "The butterfly Danaus chrysippus is infected by a male-killing Spiroplasma bacterium". Parasitology. 120 (5): 439–446. doi:10.1017/s0031182099005867. ISSN 0031-1820. PMID 10840973. S2CID 34436795.
- Edgar, J. A.; Cockrum, P. A.; Frahn, J. L. (1976-12-01). "Pyrrolizidine alkaloids inDanaus plexippus L. and Danaus chrysippus L.". Experientia. 32 (12): 1535–1537. doi:10.1007/bf01924437. ISSN 0014-4754. S2CID 27664625.
- Smith, David A. S.; Owen, Denis F.; Gordon, Ian J.; Owiny, Agoroachai M. (September 1993). "Heredity - Abstract of article: Polymorphism and evolution in the butterfly Danaus chrysippus (L.) (Lepidoptera: Danainae)". Heredity. 71 (3): 242–251. doi:10.1038/hdy.1993.132. ISSN 0018-067X.
- Smith et al. (2005)
- Jiggins et al. (2000)
- Agius, J (2014). "Danaus chrysippus form alcippoides (Linnaeus, 1758) a new form for the Maltese Islands". SHILAP Revista de Lepidopterología. 42 (167): 429–432.
- Evans, W.H. (1932). The Identification of Indian Butterflies (2nd ed.). Mumbai, India: Bombay Natural History Society.
- Gaonkar, Harish (1996). Butterflies of the Western Ghats, India (including Sri Lanka) - A Biodiversity Assessment of a Threatened Mountain System. Bangalore, India: Centre for Ecological Sciences.
- Gay, Thomas; Kehimkar, Isaac David; Punetha, Jagdish Chandra (1992). Common Butterflies of India. Nature Guides. Bombay, India: World Wide Fund for Nature-India by Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0195631647.
- Gil-T., Felipe (2006): A new hostplant for Danaus plexippus L. in Europe. A study of cryptic preimaginal polymorphism within Danaus chrysippus L. in southern Spain (Andalusia) (Lepidoptera, Nymphalidae, Danainae). ISSN 0171-0079 | Atalanta 37 (1/2): 143–149, 279. Full article: .
- HOSTS (2007): A Database of the World's Lepidopteran Hostplants. Retrieved 2007-AUG-01.
- Jiggins, F.M.; Hurst, G.D.D.; Jiggins, C.D.; Schulenburg, J.H.G.; Majerus, M.E.N. (2000). "The butterfly Danaus chrysippus is infected by a male-killing Spiroplasma bacterium". Parasitology. 120 (5): 439–446. doi:10.1017/S0031182099005867. PMID 10840973. S2CID 34436795.
- Kunte, Krushnamegh (2000). Butterflies of Peninsular India. India, A Lifescape. Hyderabad, India: Universities Press. ISBN 978-8173713545.
- Larsen, Torben (1994): Butterflies of Egypt. Saudi Aramco World, issue 5 (September/October): 24–27.
- Smith, David A.S.; Lushai, Gugs; Allen, John A. (2005). "A classification of Danaus butterflies (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae) based upon data from morphology and DNA". Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 144 (2): 191–212. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2005.00169.x.
- Wynter-Blyth, Mark Alexander (1957). Butterflies of the Indian Region. Bombay, India: Bombay Natural History Society. ISBN 978-8170192329.
- van der Heyden, T (2010). "Orbea variegata (L.) Haworth, 1812 (Apocynaceae, Asclepiadoideae) als Futterpflanze der Larven von Danaus chrysippus (Linnaeus, 1758) auf den Kanarischen Inseln (Spanien) (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae, Danainae)". SHILAP Revista de Lepidopterología. 38 (149): 107–110.
_male_underside.jpg.webp)
