Plastic hinge
In the structural engineering beam theory, the term "plastic hinge" is used to describe the deformation of a section of a beam where plastic bending occurs.[1] In earthquake engineering plastic hinge is also a type of energy damping device allowing plastic rotation [deformation] of an otherwise rigid column connection.[2]
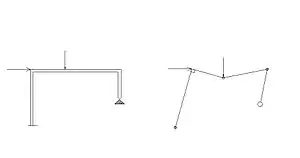

Plastic behaviour
In plastic limit analysis of structural members subjected to bending, it is assumed that an abrupt transition from elastic to ideally plastic behaviour occurs at a certain value of moment, known as plastic moment (Mp). Member behaviour between Myp and Mp is considered to be elastic. When Mp is reached, a plastic hinge is formed in the member. In contrast to a frictionless hinge permitting free rotation, it is postulated that the plastic hinge allows large rotations to occur at constant plastic moment Mp.
Plastic hinges extend along short lengths of beams. Actual values of these lengths depend on cross-sections and load distributions.[3] But detailed analyses have shown that it is sufficiently accurate to consider beams rigid-plastic, with plasticity confined to plastic hinges at points. While this assumption is sufficient for limit state analysis, finite element formulations are available to account for the spread of plasticity along plastic hinge lengths.[4]
By inserting a plastic hinge at a plastic limit load into a statically determinate beam, a kinematic mechanism permitting an unbounded displacement of the system can be formed. It is known as the collapse mechanism. For each degree of static indeterminacy of the beam, an additional plastic hinge must be added to form a collapse mechanism.
Sufficient number of plastic hinges(N) required to make a collapse mechanism (unstable structure):
N=Degree of static indeterminacy + 1
References
- Megson, T.H.G. (2005-04-29). Structural and Stress Analysis, Second Edition (2 ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-6221-2.
- Analysis of Rotational Column with Plastic Hinge Michael Long and Corey Bergad, retrieved November 5, 2006
- Megalooikonomou, Konstantinos G.; Tastani, Souzana P.; Pantazopoulou, Stavroula J. (2018). "Effect of Yield Penetration on Column Plastic Hinge Length". Engineering Structures. 156: 161–174. Bibcode:2018EngSt.156..161M. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2017.11.003.
- Scott, Michael H.; Fenves, Gregory L. (2006). "Plastic Hinge Integration Methods for Force-Based Beam–Column Elements". Journal of Structural Engineering. 132 (2): 244–252. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9445(2006)132:2(244).