Hyuga fanray
The Hyuga fanray (Platyrhina hyugaensis) is a type of ray of the family Platyrhinidae. It is an endemic species of southern Japan and inhabits shallow region at the depths of 1–50 m (3 ft 3 in – 164 ft 1 in).[2] The population of this ray are decreasing due to continuous human exploitation.[1][3]
| Hyuga fanray | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Superorder: | Batoidea |
| Order: | Torpediniformes |
| Family: | Platyrhinidae |
| Genus: | Platyrhina |
| Species: | P. hyugaensis |
| Binomial name | |
| Platyrhina hyugaensis Iwatsuki, Miyamoto & Nakaya, 2011[2] | |
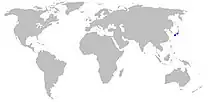 | |
| Range of Hyuga fanray | |
Description
The Hyuga fanray can be differentiated from its congeners because of numerous characteristics, including a pair of thorns on anterior part of scapular section, a row of thorns on mid-dorsum of tail, and dermal denticles of uniform size and shape covering the dorsal surface.[2]
Habitat and distribution
This species is known to live in the continental shelf at depths of 1–50 m (3 ft 3 in – 164 ft 1 in). Its endemic and common habitat is Hyūga Sea in southern Miyazaki Prefecture, although there have also been several discoveries in Kagoshima and Mie Prefectures.[1][2]
The Hyuga fanray experiences a decline in population because it is often taken as bycatch with gillnets or trawls, and probably is used for human consumption.[1] It is predicted that the ray has undergone a population depletion of up to 49% over the past 21 years.[1]
References
- Rigby, C.L.; Derrick, D.; Tanaka, S.; Yamaguchi, A. (2021). "Platyrhina hyugaensis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T169234837A169234849. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T169234837A169234849.en.
- Iwatsuki, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Nakaya, K.; Zhang, J. (2011). "A review of the genus Platyrhina (Chondrichthys: Platyrhinidae) from the northwestern Pacific, with descriptions of two new species". Zootaxa. 2738: 26–40. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.2738.1.2.
- "WoRMS - World Register of Marine Species - Platyrhina hyugaensis Iwatsuki, Miyamoto & Nakaya, 2011". www.marinespecies.org. Retrieved 2023-03-15.
