Traverse Mountains
The Traverse Mountains, or sometimes Traverse Range,[1] are an anomalous, geologically complex, east-trending range that separates Salt Lake Valley and Utah Valley in Salt Lake and Utah counties in the U.S. State of Utah.
| Traverse Mountains | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 5,410 ft (1,650 m) |
| Coordinates | 40°28′19″N 111°52′59″W |
| Geography | |
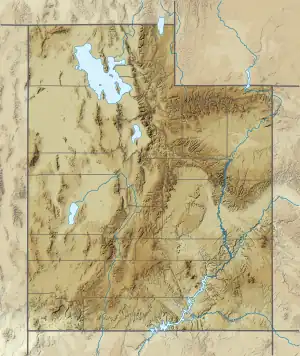 Traverse Mountains Location of the Traverse Mountains within the State of Utah | |
| Country | United States |
| State | Utah |
Point of the Mountain is colloquially used to refer to the part of this range that separates the Salt Lake City and Provo metropolitan areas, as well as the mountain pass at 40°27′13″N 111°54′38″W,[2] used by the highways and rail arteries that connect the two areas.
Description


The Traverse Mountains mark the boundary between the Salt Lake and Provo segments of the Wasatch Fault, and they are much faulted and locally involved in landslides. Lake Bonneville once covered Salt Lake and Utah Valleys, and shorelines and deposits from the ice age lake are now etched into the flanks of the Traverse Mountains.
The eastern section of the range (often called Traverse Mountain) is split up between the cities of Lehi and Draper. The Draper portion contains the Suncrest community, while the Lehi portion contains the Traverse Mountain community. Between the two communities, the Flight Park State Recreation Area (state park) sit atop the range. The western section of the range is part of the Camp Williams National Guard Training Site.
Two locations on the far west end of the eastern section of the range are Point of the Mountain and Steep Mountain, 6,160 feet (1,878 m).[3]
East Traverse Mountains Mega-landslide
New research suggests that the entirety of the East Traverse Mountains, from the Point of the Mountain to Corner Canyon, is a single mega-landslide, 57 km2 in area, that was emplaced in a landslide event between 6.5 to 6.1 million years ago.[4][5] The East Traverse Mountains previously included the upper portion of the mountains to the south of Little Cottonwood Canyon, overlying the 30.5-26 million year old granitic intrusive rocks of the Little Cottonwood stock. A catastrophic landslide event, perhaps triggered by an earthquake along the adjacent Wasatch Fault, displaced the Paleozoic sedimentary rocks about 16-17 kilometers (~10 miles) west to its current location.[6]
There are several lines of evidence that support this idea. Pseudotachylyte zones in the area, caused by intense frictional heat, mark the landslide's path.[7] Extensive brecciation of bedrock throughout the East Traverse Mountains are evidence of an extremely damaging event that affected the whole mountain.[7] Additionally, a brecciated remnant of the landslide was preserved near Box Elder Peak.[8] Finally, there are pebble dikes on the East Traverse Mountains, which include pieces of igneous rock that match those in pebble dikes from the Little Cottonwood stock in age, texture, and mineralogy. Thus, the pebble dikes in Little Cottonwood Canyon represent the lower half of the hydrothermal system, while the upper half of the system is represented by the pebble dikes that are lodged in the rocks that now make up the East Traverse Mountains before the landslide. Several million years later, the landslide occurred, carrying the upper half of the granite-bearing pebble dikes with it. The slide probably occurred in this area due to hydrothermal alteration caused by the Little Cottonwood intrusion that weakened the overlying rocks.[6]
References
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Traverse Mountains
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Point of the Mountain
- Utah Atlas & Gazetteer, DeLorme, 9th ed., 2014, p. 24-25 ISBN 0899332552
- Keith, Jeffrey (2017). "PROPOSED MEGA-LANDSLIDE ORIGIN FOR THE EAST TRAVERSE MOUNTAINS, UTAH – EVIDENCE FROM PEBBLE DIKES". GSA Conference Abstracts.
- Jordan, Lars (2018). "The age of the East Traverse Mountain landslide, Utah: disruption of Miocene lake sediments and U-Pb ages of fracture-hosted opal". GSA Conference Abstracts.
- Jensen, Collin (2019). Multi-Stage Construction of the Little Cottonwood Stock, Utah: Origin, Intrusion, Venting, Mineralization, and Mass Movement (MS thesis). Brigham Young University. hdl:1877/etd10951.
- Chadburn, Ryan (2018). "NEW EVIDENCE FOR A MEGA-LANDSLIDE ORIGIN FOR THE EAST TRAVERSE MOUNTAINS, UTAH". GSA Conference Abstracts.
- Kindred, Thane (2018). "PSEUDOTACHYLYTE--CATACLASITE IN THE DAMAGE ZONE LOCATED NORTH OF BOX ELDER PEAK, WASATCH MOUNTAINS, UTAH, ASSOCIATED WITH THE 57 KM2 TRAVERSE MOUNTAIN LANDSLIDE". GSA Conference Abstracts.
External links
 Media related to Traverse Mountains at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Traverse Mountains at Wikimedia Commons