Borders of Poland
The Borders of Poland are 3,511 km (2,182 mi)[1] or 3,582 km (2,226 mi) long.[2] The neighboring countries are Germany to the west, the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south, Ukraine and Belarus to the east, and Lithuania and the Russian province of Kaliningrad Oblast to the northeast. To the north, Poland is bordered by the Baltic Sea.

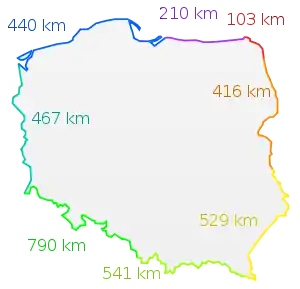

Breakdown of border lengths per entity:
- Czech Republic–Poland border: 796 km (495 mi)[1] or 790 km (490 mi)[2]
- Poland–Slovakia border: 541 km (336 mi)[1] or 539 km (335 mi)[2]
- Poland–Ukraine border: 535 km (332 mi)[1] or 529 km (329 mi)[2]
- Germany–Poland border: 467 km (290 mi)[2][1]
- Belarus–Poland border: 418 km (260 mi)[1] or 416 km (258 mi)[2]
- Poland–Russia border (Kaliningrad Oblast): 210 km (130 mi)[2][1]
- Lithuania–Poland border: 104 km (65 mi)[1] or 103 km (64 mi)[2]
- sea (Baltic Sea): 440 km (270 mi)[1] or 528 km (328 mi)[2]
The Polish coastline is 770 km (480 mi) long.[1]
History
The borders of modern Poland were defined in the aftermath of the Second World War and the establishment of the People's Republic of Poland. They were agreed in the field of international law by the Yalta Agreement of February 11, 1945 and the Potsdam Agreement of August 2, 1945. These agreements generally defined the course of borders, without setting them out in detail. Their specification and then demarcation in the field had to be normalized in bilateral agreements between the states concerned.
Major border crossings
After accession of Poland to the European Union in 2004, border crossings with EU states (Germany, Czech Republic, Slovakia and Lithuania) were made redundant. Infrastructure remains in place, but its systematic use and the controls are no longer allowed by the Schengen agreement.[3]
Former
with Germany
with the Czech Republic
- Jakuszyce (district of Szklarska Poręba)
- Kudowa-Słone
- Chałupki
- Cieszyn
with Slovakia
with Lithuania
Historically, Poland also had borders (and border crossings) with former countries, or with countries that no longer share a common border with Poland:
- former countries: Czechoslovakia, Soviet Union, East Germany
- countries which once shared a common border with Poland: Romania, Hungary, Latvia
See also
References
- "WARUNKI NATURALNE I OCHRONA ŚRODOWISKA (ENVIRONMENT AND ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION)". MAŁY ROCZNIK STATYSTYCZNY POLSKI 2013 (CONCISE STATISTICAL YEARBOOK OF POLAND 2013). 2013. p. 26. ISSN 1640-3630.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - (in Polish) Informacje o Polsce - informacje ogólne Archived June 25, 2009, at the Wayback Machine (archive.org Archived 2005-02-22 at the Wayback Machine ). Page gives Polish PWN Encyklopedia as reference.
- Ustawa z dnia 29 czerwca 2007 r. o zmianie ustawy o ochronie granicy państwowej oraz ustawy o zmianie ustawy o Straży Granicznej oraz niektórych innych ustaw. Dziennik Ustaw, 2007, numer 140. pozycja 982