Polyvinyl ether
Polyvinyl ethers are a class of organic polymers derived from vinyl ethers. Common monomers include methyl vinyl ether and ethyl vinyl ether, the polymer having the formula [CH2CH(OR)]n (R = methyl, ethyl). Commercial interest has also focused on polymers derived from ethyl, isobutyl, octadecyl substituents in place of methyl. Like other vinyl polymers, the polymers exhibit tacticity. Polymerization is typically initiated with Lewis acids such as boron trifluoride.[1]
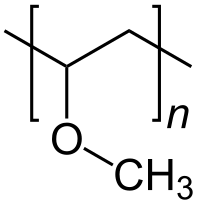
Polyvinylmethylether.
References
- Gerd Schröder (2012). "Poly(Vinyl Ethers)". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_011.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.