Portal:Writing
Welcome to the writing portal
Introduction

Writing is a cognitive and social activity involving neuropsychological and physical processes and the use of writing systems to create persistent representations of human language. A system of writing relies on many of the same semantic structures as the language it represents, such as lexicon and syntax, with the added dependency of a system of symbols representing that language's phonology and morphology. Nevertheless, written language may take on characteristics distinctive from any available in spoken language.
The outcome of this activity, also called "writing", and sometimes a "text", is a series of physically inscribed, mechanically transferred, or digitally represented linguistic symbols. The interpreter or activator of a text is called a "reader".
Writing systems do not themselves constitute languages (with the debatable exception of computer languages); they are a means of rendering language into a form that can be read and reconstructed by other humans separated by time and/or space. While not all languages use a writing system, those that do can complement and extend the capacities of spoken language by creating durable forms of language that can be transmitted across space (e.g. written correspondence) and stored over time (e.g. libraries or other public records). Writing can also have knowledge-transforming effects, since it allows humans to externalize their thinking in forms that are easier to reflect on, elaborate on, reconsider, and revise. (Full article...)
Selected article
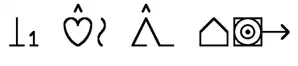
Blissymbolics or Blissymbols were conceived of as an ideographic writing system consisting of several hundred basic symbols, each representing a concept, which can be composed together to generate new symbols that represent new concepts. Blissymbols differ from all the world's major writing systems in that the characters do not correspond at all to the sounds of any spoken language.
They were invented by Charles K. Bliss (1897-1985) after the Second World War. Bliss wanted to create an easy-to-learn international auxiliary language to allow communication between people who do not speak the same language. He was inspired by Chinese ideograms, with which Bliss became familiar while in Shanghai as a refugee from Nazi anti-semitic persecution. His system World Writing was explained in his work Semantography (1949). This work laid out the language structure and vocabulary for his utopian vision of easy communication, but it failed to gain popularity. However, since the 1960s, Blissymbols have become popular as a method of augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) for non-speaking people with cerebral palsy or other disorders, for whom it can be impossible to otherwise communicate with spoken language. (Full article...)
Selected picture

Selected biography

Andrew Robinson was educated at the Dragon School, Eton College where he was a King's Scholar, University College, Oxford where he read Chemistry and finally the School of Oriental and African Studies in London. He is the son of Neville Robinson, an Oxford physicist. He is based in London and is currently a full-time writer.
Robinson has written several books about the history of writing, including:
- The Story of Writing: Alphabets, Hieroglyphs and Pictograms. Thames and Hudson (2000). ISBN 0-500-28156-4.[4]
- Lost Languages: The Enigma of the World's Great Undeciphered Scripts. McGraw-Hill (2002). ISBN 0-07-135743-2.[5][6]
- Writing and Script. Oxford University Press (2009). ISBN 9780199567782.[3][7][8] (Full article...)
Did you know...
Categories
Writing • Calligraphy • Penmanship • Writing implements • Inks • Alphabetic writing systems • Abjad • Abugida • Kanji • Logographic writing systems • Writing systems • Cyrillic alphabets • Hellenic scripts • Script typefaces
Major topics
• Calligraphy •
Western calligraphy • Islamic calligraphy • Indian calligraphy • Chinese calligraphy • Korean calligraphy • Japanese calligraphy • Persian calligraphy • Manuscript
• Writing instruments •
Pen • Ink brushes • Inks • Ink stone • Qalam • Quill • Dip pen • Nib • Paper • Writing slate • Pencil • Typewriter • Word processor • Dry erase marker • Touchscreen
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
WikiProjects
- WikiProject Writing systems
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
 Commons
Commons
Free media repository -
 Wikibooks
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
 Wikidata
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
 Wikinews
Wikinews
Free-content news -
 Wikiquote
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
 Wikisource
Wikisource
Free-content library -
 Wikispecies
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
 Wikiversity
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
 Wikivoyage
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
 Wiktionary
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
References
- Andrew Robinson (1), LibraryThing.
- Books by Andrew Robinson, Alibris.
- Mark Twaite, Interview with Andrew Robinson, The Book Depository, 2009.
- Andrew Robinson, Andrew Robinson on the story of writing. The Times, 29 September 2007.
- James McConnachie, Lost Languages: The Enigma of the World's Undeciphered Scripts by Andrew Robinson. The Sunday Times, 8 March 2009.
- Andrew Robinson, Decoding antiquity: Eight scripts that still can't be read. New Scientist, 27 May 2009.
- Steven Poole, Writing and Script by Andrew Robinson. The Guardian, 19 September 2009.
- Greg Neale, "Book reviews: Writing and Script". Oxford Today, 22(2):37, 2010.