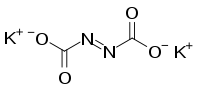
Potassium azodicarboxylate
Potassium azodicarboxylate is chemical compound that used as a precursor to diimide. It can be synthesized by the reaction of potassium hydroxide with azodicarbonamide and it reacts with carboxylic acids to form diimide.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2K2N2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 194.229 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow crystals |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Pasto, Daniel J. (2001). "Potassium Azodicarboxylate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. doi:10.1002/047084289x.rp195. ISBN 9780470842898.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.