Propanephosphonic acid anhydride
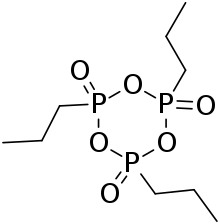
Propanephosphonic acid anhydride (PPAA, T3P) is an anhydride of propanephosphonic acid. Its structure is a cyclic trimer, with a phosphorus–oxygen core and propyl groups and additional oxygens attached.[1] The chemical is a useful reagent for peptide synthesis reactions, where it activates the carboxylic acid partner for subsequent reaction with amines. It is commercially available as 50 % solution in DMF or ethyl acetate as a slightly yellow mixture.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,4,6-Tripropyl-1,3,5,2λ5,4λ5,6λ5-trioxatriphosphinane-2,4,6-trione | |
| Other names
PPACA; PPAA; T3P; Propylphosphonic anhydride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.102.078 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H21O6P3 | |
| Molar mass | 318.182 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H290, H314 | |
| P234, P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P390, P404, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.