Propionyl chloride
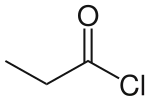
Propionyl chloride (also propanoyl chloride) is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH2C(O)Cl. It is the acyl chloride derivative of propionic acid. It undergoes the characteristic reactions of acyl chlorides.[1] It is a colorless, corrosive, volatile liquid.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propanoyl chloride | |
| Other names
Propionic chloride; propionic acid chloride (1:1) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.064 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H5ClO | |
| Molar mass | 92.52 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.0646 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −94 °C (−137 °F; 179 K) |
| Boiling point | 80 °C (176 °F; 353 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Corrosive, flammable; highly toxic |
| Flash point | 54 °C (129 °F; 327 K) |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose) |
100 mg/kg (rat, oral) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It is used as a reagent for organic synthesis. In derived chiral amides and esters, the methylene protons are diastereotopic.[2]
Synthesis
Propionyl chloride is industrially produced by chlorination of propionic acid with phosgene:[3]
- CH3CH2CO2H + COCl2 → CH3CH2COCl + HCl + CO2
References
- Michael B Smith (22 November 2016). Organic Synthesis. Elsevier Science. p. 165. ISBN 978-0-12-800807-2.
- Gage, James R.; Evans, David A. (1990). "Diastereoselective Aldol Condensation Using a Chiral Oxazolidinone Auxiliary: (2S,3S)-3-Hydroxy-3-phenyl-2-methylpropanoic Acid". Org. Synth. 68: 83. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.068.0083.
- Samel, Ulf-Rainer; Kohler, Walter; Gamer, Armin Otto; Keuser, Ullrich (2005). "Propionic acid and derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a22_223.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.