Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico
The Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico (Spanish: Asamblea Legislativa de Puerto Rico) is the territorial legislature of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, responsible for the legislative branch of the government of Puerto Rico. The Assembly is a bicameral legislature consisting of an upper house, the Senate (Spanish: Senado) normally composed of 27 senators,[lower-alpha 1] and the lower house, the House of Representatives (Spanish: Cámara de Representantes) normally consisting of 51 representatives.[lower-alpha 1] Eleven members of each house are elected at-large rather than from a specific legislative district with all members being elected for a four-year term without term limits.
Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico Asamblea Legislativa de Puerto Rico | |
|---|---|
| 19th Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Senate House of Representatives |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 27 Senators 51 Representatives |
 | |
Senate political groups | PPD (12) PNP (10) MVC (2) PIP (1) PD (1) Independent (1) |
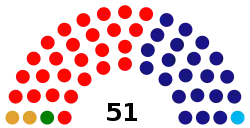 | |
House of Representatives political groups | PPD (25) PNP (21) MVC (2) PIP (1) PD (1) Independent (1) |
| Elections | |
Senate voting system | plurality-at-large for 16 electoral districts seats and single non-transferable vote for 11 at-large seats |
House of Representatives voting system | first-past-the-post for 40 electoral districts seats and single non-transferable vote for 11 at-large seats |
Last Senate election | November 3, 2020 |
Last House of Representatives election | November 3, 2020 |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Capitol of Puerto Rico, San Juan | |
The structure and responsibilities of the Legislative Assembly are defined in Article III of the Constitution of Puerto Rico which vests all legislative power in the Legislative Assembly. Every bill must be passed by both houses and signed by the Governor of Puerto Rico to become law. Each house has its unique powers. The constitution also states that each house shall be the unique judge on the legal capacity of its members. The constitution also grants parliamentary immunity to all elected members of the Legislative Assembly.
The assembly currently in session is the 19th Legislative Assembly of Puerto Rico, composed of the 27th Senate and the 31st House of Representatives.
The Legislative Assembly convenes at the Capitol in San Juan.
History
The House of Representatives is the oldest legislative body in Puerto Rico. It was formed on November 25, 1897, when the Spanish government of Prime Minister Práxedes Mateo Sagasta granted autonomy to the archipelago, creating a House that was composed of 32 members.[2] Beside the House there was also an Administrative Council of 15 members, eight of whom were elected by a "Colegio de Compromisarios" and the other seven were named by the Governor General in representation of the Spanish monarch.
After Puerto Rico was ceded to the United States on July 25, 1898, as part of the Spanish–American War, a military government was imposed archipelago.[3] This was until April 12, 1900, when the U.S. Congress approved the first civil government for Puerto Rico under the federal Foraker Act. The act granted the archipelago with a civil governor (named by the U.S. President) and a House of Delegates composed of 35 members elected by the people of Puerto Rico, as well as an Executive Council of 11 members, designated all by the U.S. president, and six sitting members consisting of the governor's cabinet.[4]
The political arrangement under the Foraker Act continued until 1917. On March 2 of that year, president Woodrow Wilson approved the Jones–Shafroth Act (Pub. L.Tooltip Public Law (United States) 64–368, 39 Stat. 951, enacted March 2, 1917), which provided for the creation of an completely separate legislative branch with regards to the Executive branch in sections 25-39 of the statute.[5] It established a House of Representatives with 39 members and a Senate of 19 members, all elected directly by the people of the unincorporated territory. Puerto Rico was then divided into 7 senatorial districts and 35 house districts. The first Senate of Puerto Rico was elected in July 1917.[6]
 |
|---|
The unincorporated territory is divided into 8 senatorial and 40 House districts. On July 25, 1952, the Constitution of Puerto Rico was formally adopted, establishing the current House of Representantes and Senate as the bicameral houses of the Legislative Assembly (as stated in Article III).
Powers
The Constitution of Puerto Rico vests all legislative powers in the Legislative Assembly. Each house has the sole power to be the judge of the legal capacities of its members. The members of both houses are protected by parliamentary immunity, which Article III, Section 14 states "no member of the Legislative Assembly shall be imprisoned...", they also shall not be held accountable for anything said in the floor.
Each House holds exclusive powers that are not given to the other. The House of Representatives has the exclusive power to initiate an impeachment process and the Senate the exclusive power to pass judgement. All laws dealing with the commonwealth budget or taxes must originate in the House of Representatives. The Senate retains the exclusive power to extend its consent to appointments to government offices made by the governor (judges, cabinet secretaries and others) as stated by law or Constitution.
The Legislative Assembly, with the consent of two-thirds of each chamber may propose amendments to the constitution. Proposed amendments are then subject to approval by the people of Puerto Rico in a referendum. It also has the power to consolidate or create municipalities.
Qualifications
Under Article III, Sections 5 and 6, members of the Legislative Assembly must be fluent in either Spanish or English, must be a citizen of the United States and Puerto Rico, and have resided in Puerto Rico for at least two years prior to their election. Senators must be at least 30 years old, while House representatives must be at least 25 years old. Both Senators and Representatives (except those elected at-large) must reside in their constituent district at least one year prior to their election.
Sessions
The following is a list of legislative assemblies, with a count starting on the legislature elected in the 1948 Puerto Rican general election, following the enactment of the Puerto Rico Elective Governor Act of 1947 by president Harry S. Truman.
Moves to unicameralism
Act No. 477 of September 23, 2004 provided for a referendum to be held on July 10, 2005, in which Puerto Rican voters were to indicate if they favored changing the Legislative Assembly to a single house, or maintain the bicameral legislature established by the 1917 Jones Act, which had been retained (with modifications) by the 1952 Constitution of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico. A vote for unicameralism would constitute a mandate for the Legislative Assembly to hold a second referendum on July 9, 2007, on the constitutional amendment that would establish a unicameral legislature by 2009.
In the unicameral referendum held on July 10, 2005, Puerto Rican voters approved a mandate for the Legislative Assembly to hold a second referendum on the constitutional amendment that would establish unicameral legislature by 456,267 votes in favor, versus 88,720 against; voter turnout was only 22.6%, the lowest turnout figure in Puerto Rico's electoral history, vastly below the 81.7% that had gone to the polls just a few months earlier for the general election.[7][8][9] Another referendum was scheduled for July 2007 to approve the specific amendments to the Constitution of Puerto Rico that are required for the change. However, the Supreme Court of Puerto Rico ruled in June that it could not force the Legislative Assembly to initiate a constitutional amendment process to become a single chamber legislature.[10] Further moves to unicameralism have been tabled.
Agencies
Agencies of the legislative branch include:
- Commission on Civil Rights
- Comptroller
- Office of Legislative Services
- Ombudsman
- Superintendency of the Capitol
Notes
- Each house can increase its number of legislators when in a general election more than two-thirds of the members of either house are elected from one political party or from a single ticket.[1]
References
- "Article III, Section 7,". Constitution of Puerto Rico. July 25, 1952. Retrieved August 6, 2013.
- "Carta Autonómica de 1897 de Puerto Rico". www.lexjuris.com. Retrieved December 6, 2020.
- "Military Government in Puerto Rico - The World of 1898: The Spanish-American War (Hispanic Division, Library of Congress)". www.loc.gov. Library of Congress. Retrieved May 11, 2022.
- Maldonado, Yanelba Mota. "Ocupación Militar y la ley Foraker". Enciclopedia PR (in Spanish). Fundación Puertorriqueña de las Humanidades (FPH). Retrieved February 19, 2019.
- "1917 Jones Act [(H.R. 9533), Pub. L. No. 64-368] · PRCAP (PR Citizenship Archives Project)". www.scholarscollaborative.org. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- Nolla Acosta, Juan José (January 25, 2013). Puerto Rico Election Results, 1899-2012. Lulu.com. ISBN 978-1-300-67141-1. Retrieved December 30, 2022.
- María Vera. "Trabajan borrador unicameralidad". El Vocero. Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved October 2, 2006.
- Elections in Puerto Rico:No Unicameralism Referendum on July 9, 2007
- "La Participación Ciudadana en los Procesos Electorales en Puerto Rico" (PDF). Oficina de Asuntos Legales. Comisión Estatal de Elecciones de Puerto Rico (CEEPUR) / State Electoral Commission. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 4, 2006. Retrieved October 2, 2006. (via "Comisión Estatal de Elecciones". Archived from the original on December 6, 2004. Retrieved March 17, 2007.)
- José Córdova Iturregui y Otros vs. Cámara de Representantes del Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, 2007 TSPR 133
External links
- House of Representatives of Puerto Rico (in Spanish)
- Senate of Puerto Rico (in Spanish)
- Elected Senators 1917
- Senatorial Districts 1917-2011
.svg.png.webp)