Lung infarction
Lung infarction occurs when an artery to the lung becomes blocked and part of the lung dies.[1] It is most often caused by pulmonary embolism.
| Lung Infarction | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Pulmonary infarction |
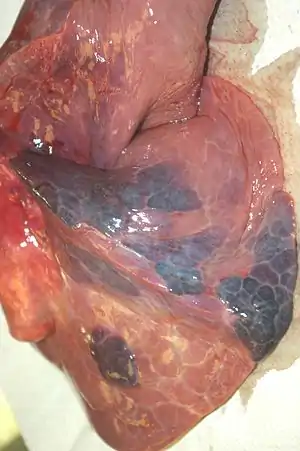 | |
| Pulmonary infarcts found on autopsy | |
| Specialty | Pulmonology, cardiology |
Because of the dual blood supply to the lungs from both the bronchial circulation and the pulmonary circulation, this tissue is more resistant to infarction. An occlusion of the bronchial circulation does not cause infarction, but it can still occur in pulmonary embolism when the pulmonary circulation is blocked and the bronchial circulation cannot fully compensate for it.[2]
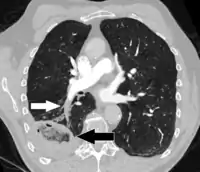 CT scan of a lung infarction because of chronic pulmonary embolism (white arrow). The infarcted area (black arrow) has a reverse halo sign.
CT scan of a lung infarction because of chronic pulmonary embolism (white arrow). The infarcted area (black arrow) has a reverse halo sign.
References
- Philip T. Cagle (2008). Color atlas and text of pulmonary pathology (2 ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 291. ISBN 9780781782081.
- Thomas H. McConnell (2007). The Nature of Disease: Pathology for the Health Professions. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 81–. ISBN 978-0-7817-5317-3.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.