Regio I Porta Capena
The Regio I Porta Capena is the first regio of imperial Rome, under Augustus's administrative reform. Regio I took its name from the Porta Capena ("Gate to Capua"), a gate of the Servian Walls, through which the Appian Way entered the city prior to the construction of the Aurelian Walls.
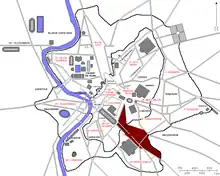
Geographic extent and important features
Bordered to the north by the Via Appia as it passed between the Palatine Hill and the Caelian Hill, Regio I stretched through the ancient Porta Capena either to at least the boundary of the future Aurelian Walls, and possibly originally beyond the Porta Appia.[1] Including areas that were traversed by the Via Appia and the Via Latina, the boundary eventually turned back towards the ancient city until it returned back to the Caelian Hill. Prior to the construction of the Aurelian Walls, it is unclear how far along the Via Appia Regio I continued.[2] A measurement taken at the end of the 4th century recorded that the perimeter of the region was 12,219 Roman feet (approximately 3.61km).[3]

Within this region lay a spring and a grove once sacred to the nymph Egeria, a divine consort and counsellor of Numa Pompilius, the second king of Rome. A brook called the Almo was nearby; this was where annually, on 27 March, the sacred black stone of the Magna Mater was brought from her temple on the Palatine Hill to where the brook crossed the Via Appia south of the Porta Capena, for the ceremony of lavatio (washing). Also present was the oldest temple to Mars in Rome, "Templum Martis in Clivo". Built near the first miliarium of the Via Appia, it was where, in Republican times, the legions gathered prior to their allotted campaign, and where they returned to lay down their arms before re-entering the city.[4] Along with the Temple of Mars, this region also had a temple dedicated to Minerva and one to the Tempestas.
Between the Servian and Aurelian Walls stood three Triumphal arches that spanned the via Appia: the Arch of Drusus, the Arch of Lucius Verus and Marcus Aurelius (for the Parthian triumph of 166 CE) and the Arch of Trajan. Neither of the first two arches are extant; however, the so-called Arch of Drusus that is still standing in the former Regio I is most likely the remains of the Arch of Trajan.[5]
Regio I also included the Baths of Commodus and the Septizodium. Finally, it also contained the Mutatorium Caesaris. This was an area reserved for the Imperial family where their private transport could be housed and held for use whenever they returned to the capital from the Via Appia. At the turn of the 5th century, the Regio contained ten aediculae (shrines), 120 domūs (patrician houses), 26 horrea (warehouses), 86 balneae (bath houses) and 87 loci (fountains).[6]
If the region extended beyond the Aurelian Wall, the region will also have included the Circus of Maxentius and the Tomb of Caecilia Metella.[7]
Subdivisions
At the turn of the 5th century, the Regio was divided into ten vici (districts) and 3,250 insulae (blocks). It had two curators and was served by 48 Roman magistrates.[8]
See also
Notes
- Gregorovius, pg. 29
- Gregorovius, pg. 31
- Notitia, REGIO I PORTA CAPENA
- "Templum Martis in Clivo".
- Richardson, L. A New Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome (1992), pgs. 30-31
- Notitia, REGIO I PORTA CAPENA
- Gregorovius, pg. 30
- Notitia, REGIO I PORTA CAPENA
References
- Platner, Samuel Ball, A Topographical Dictionary of Ancient Rome, Oxford University Press (1929) (online version)
- Gregorovius, Ferdinand, History of the City of Rome in the Middle Ages, Vol. 1, (1894)
- DISCRIPTIO XIIII REGIONVM VRBIS ROMÆ, Curiosum - Notitia. 4th-century descriptions of the regions of Rome and their main buildings. Archived from the original on 8 June 2019.