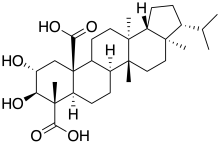
Retigeric acid B
Retigeric acid B is a hopanoids chemical compound isolated from Lobaria.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2α,3β-Dihydroxy-13,17-dimethyl-26,28-dinor-8α,13α,14β,17α,18β-hopane-23,25-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3R,3aR,5aR,5bR,7aR,8S,9R,10R,11aR,13aS,13bR)-9,10-Dihydroxy-3a,5a,8,13a-tetramethyl-3-(propan-2-yl)-1,2,3,3a,4,5,5a,5b,6,7,7a,8,9,10,11,13,13a,13b-octadecahydro-11aH-cyclopenta[a]chrysene-8,11a-dicarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H46O6 | |
| Molar mass | 502.692 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Zhang HJ, Ou Y, Lou HX (June 2007). "[Studies on chemical constituents of Lobaria kurokawae yoshim]". Zhong Yao Cai (in Chinese). 30 (6): 651–5. PMID 17918430.
- Liu H, Liu YQ, Liu YQ, et al. (December 2010). "A novel anticancer agent, retigeric acid B, displays proliferation inhibition, S phase arrest and apoptosis activation in human prostate cancer cells". Chemico-Biological Interactions. 188 (3): 598–606. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2010.07.024. PMID 20692244.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.