Retinyl acetate
Retinyl acetate (retinol acetate, vitamin A acetate) is a natural form of vitamin A which is the acetate ester of retinol. It has potential antineoplastic and chemopreventive activities.[2][3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
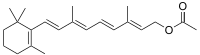
| IUPAC name
(2E,4E,6E,8E)-3,7-Dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl)nona-2,4,6,8-tetraen-1-yl acetate | |
| Other names
Retinol acetate; Vitamin A acetate; Vitamin A1 acetate; Acetylretinol; all-trans-Retinol acetate; all-trans-Retinyl acetate; all-trans-Vitamin A acetate; | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 1915439 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.405 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H32O2 | |
| Molar mass | 328.496 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 57 to 58 °C (135 to 136 °F; 330 to 331 K)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  | |
| Warning | |
| H315, H361, H413 | |
| P201, P202, P264, P273, P280, P281, P302+P352, P308+P313, P321, P332+P313, P362, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
In the United States, retinyl acetate is classified generally recognized as safe (GRAS) in the amounts used to fortify foods with vitamin A.[4][5]
Toxicology
World Health Organization recommendation on Maternal Supplementation During Pregnancy states that "health benefits are expected for the mother and her developing fetus with little risk of detriment to either, from a daily supplement not exceeding 10,000 IU vitamin A (3000mcg RE) at any time during pregnancy." Preformed Vitamin A refers to retinyl palmitate and retinyl acetate.[6]
References
- Retinyl acetate from Sigma-Aldrich
- Moon, Richard C.; Grubbs, Clinton J.; Sporn, Michael B.; Goodman, Dawn G. (1977). "Retinyl acetate inhibits mammary carcinogenesis induced by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea". Nature. 267 (5612): 620–1. Bibcode:1977Natur.267..620M. doi:10.1038/267620a0. PMID 876383. S2CID 4211886.
- Retinyl acetate, National Cancer Institute Drug Dictionary
- Select Committee on GRAS Substances (SCOGS) Opinion: Vitamin A, United States Food and Drug Administration
- 21 CFR 184.1930
- World Health Organization Nutrition Unit (1998). Safe vitamin A dosage during pregnancy and lactation. World Health Organization. hdl:10665/63838.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
