Reutericyclin
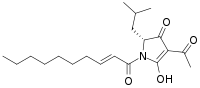
Reutericyclin is a bacteriocin produced by the bacterium Lactobacillus reuteri that has potential use as a food preservative.[1] Reutericyclin is a hydrophobic, negatively charged molecule with the molecular formula C20H31NO4.[1][2] Reutericyclin disrupts the cell membrane of sensitive bacteria by acting as a proton ionophore.[2] Reutericyclin has a broad spectrum of activity against Gram-positive bacteria, but has no effect on Gram-negative bacteria because the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria prevents access by hydrophobic compounds.[1][2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R)-4-Acetyl-1-[(E)-dec-2-enoyl]-3-hydroxy-2-(2-methylpropyl)-2H-pyrrol-5-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Gänzle MG (2004). "Reutericyclin: biological activity, mode of action, and potential applications". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 64 (3): 326–332. doi:10.1007/s00253-003-1536-8. PMID 14735324.
- Engevik MA, Versalovic J (2017). "Biochemical Features of Beneficial Microbes: Foundations for Therapeutic Microbiology". Microbiology Spectrum. 5 (5): 3–47. doi:10.1128/microbiolspec.BAD-0012-2016. ISBN 9781555819699. PMC 5873327. PMID 28984235.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.