Rogletimide
Rogletimide, also known as pyridoglutethimide, is a medication which was never marketed.[1] It is related in chemical structure to the sedative/hypnotic drug glutethimide, but instead has pharmacological activity as a selective aromatase inhibitor similar to the related drug aminoglutethimide and has no significant sedative-hypnotic effect.[2] This makes it potentially useful in the treatment of breast cancer, and with fewer side effects than aminoglutethimide, but its lower potency caused it to be unsuccessful in clinical trials.[1][3]
| Generation | Medication | Dosage | % inhibitiona | Classb | IC50c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| First | Testolactone | 250 mg 4x/day p.o. | ? | Type I | ? |
| 100 mg 3x/week i.m. | ? | ||||
| Rogletimide | 200 mg 2x/day p.o. 400 mg 2x/day p.o. 800 mg 2x/day p.o. | 50.6% 63.5% 73.8% | Type II | ? | |
| Aminoglutethimide | 250 mg mg 4x/day p.o. | 90.6% | Type II | 4,500 nM | |
| Second | Formestane | 125 mg 1x/day p.o. 125 mg 2x/day p.o. 250 mg 1x/day p.o. | 72.3% 70.0% 57.3% | Type I | 30 nM |
| 250 mg 1x/2 weeks i.m. 500 mg 1x/2 weeks i.m. 500 mg 1x/1 week i.m. | 84.8% 91.9% 92.5% | ||||
| Fadrozole | 1 mg 1x/day p.o. 2 mg 2x/day p.o. | 82.4% 92.6% | Type II | ? | |
| Third | Exemestane | 25 mg 1x/day p.o. | 97.9% | Type I | 15 nM |
| Anastrozole | 1 mg 1x/day p.o. 10 mg 1x/day p.o. | 96.7–97.3% 98.1% | Type II | 10 nM | |
| Letrozole | 0.5 mg 1x/day p.o. 2.5 mg 1x/day p.o. | 98.4% 98.9%–>99.1% | Type II | 2.5 nM | |
| Footnotes: a = In postmenopausal women. b = Type I: Steroidal, irreversible (substrate-binding site). Type II: Nonsteroidal, reversible (binding to and interference with the cytochrome P450 heme moiety). c = In breast cancer homogenates. Sources: See template. | |||||
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Roglethimide; Pyridoglutethimide |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Aromatase inhibitor |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H14N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 218.256 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Synthesis
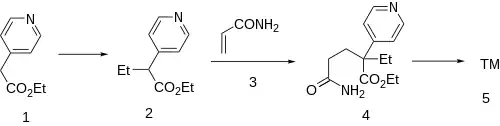
Base catalyzed alkylation of ethyl 4-pyridylacetate [54401-85-3] (1) with iodoethane gives ethyl 2-(4-pyridyl)butyrate [76766-56-8] (2). Base catalyzed conjugate addition of the carbanion to acrylamide (3) gives (4). The last step is an intramolecular cyclization to rogletimide (5).
References
- Frederick A. Luzzio (17 May 2019). Imides: Medicinal, Agricultural, Synthetic Applications and Natural Products Chemistry. Elsevier Science. pp. 361–. ISBN 978-0-12-815676-6.
- Vanden Bossche HV, Moereels H, Koymans LM (1994). "Aromatase inhibitors--mechanisms for non-steroidal inhibitors". Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 30 (1): 43–55. doi:10.1007/bf00682740. PMID 7949204. S2CID 24414161.
- MacNeill FA, Jones AL, Jacobs S, Lønning PE, Powles TJ, Dowsett M (October 1992). "The influence of aminoglutethimide and its analogue rogletimide on peripheral aromatisation in breast cancer". British Journal of Cancer. 66 (4): 692–7. doi:10.1038/bjc.1992.339. PMC 1977412. PMID 1419608.
- Boss, Aileen M.; W. Clissold, Derek; Mann, John; Markson, Andrew J.; Thickitt, Christopher P. (1989). "A concise synthesis of racemic pyridoglutethimide and its resolution using chiral stationary phase HPLC". Tetrahedron. 45 (18): 6011–6016. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)89128-6.
- Derek W. Clissold, John Mann, Christopher P. Thickitt, US5112976 (1992 to National Research Development Corporation).