Rosin (chemical)
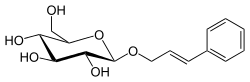
Rosin is a glycoside ester of Cinnamyl alcohol and a constituent of Rhodiola rosea.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2E)-3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-yl β-D-glucopyranoside | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-2-(Hydroxymethyl)-6-{[(2E)-3-phenylprop-2-en-1-yl]oxy}oxane-3,4,5-triol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H20O6 | |
| Molar mass | 296.32 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Related compounds
The three cinnamyl alcohol-vicianosides of rhodiola rosea commonly referred to as "rosavins" are rosin and the structurally related disaccharide Rosavin which is the arabinose ester of rosin, and Rosarin, the arabinofuranose ester of rosin. Salidroside, common in rhodiola spp. and occurring in Rhodiola rosea is not a cinnamyl alcohol glycoside, but a glycoside of tyrosol.[1]
Sources
The cinnamyl alcohol glycosides rosin, rosavin and rosarin occur in the context of rhodiola species, only in Rhodiola rosea.[1]
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.