Sōya (PL107)
Sōya (宗谷) is a Japanese icebreaker that serves as a museum ship in Tokyo after a long and storied service spanning some of the 20th century's historic events. It is named for Sōya Subprefecture in Hokkaido.
 Sōya at the Museum of Maritime Science, Tokyo | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name |
|
| Namesake | Sōya Subprefecture |
| Owner |
|
| Ordered | 1936 |
| Builder | Koyagi/Kawaminami/Matsuo |
| Laid down | 31 October 1936 |
| Launched | 16 February 1938 |
| Completed | 10 June 1938 |
| Maiden voyage | possibly 1939 |
| Nickname(s) |
|
| Status | Museum ship |
| General characteristics | |
| Type | Icebreaker / Patrol Vessel / Research Vessel |
| Displacement | 3,800t(1944)/4,100t(1978) |
| Length |
|
| Beam |
|
| Propulsion | VTE steam engine, 2 boilers, 1 shaft. / Diesel engines |
| Speed | 12.4 knots (23.0 km/h; 14.3 mph) |
Construction
The vessel was built as Volochaevets, commissioned by the Soviets in 1936 from the Matsuo shipyard, on Nagasaki's Koyagi Island, as partial payment for Japan's construction of the South Manchuria Railway (also known as the Chinese Eastern Railway). Two other ice-strengthened cargo ships were ordered at the same time, Bolshevik and Komsomolets. All three were built, but owing to the worsening state of Japan-Soviet relations by that time, the ships were never delivered. Volochaevets was launched from the now-renamed Kawaminami Shipyard in February 1938. She was completed as an ice-breaking cargo freighter for the Tatsunan Kisen Co. and was renamed Chiryō Maru. Bolshevik and Komsomolets were renamed Minryo Maru (民領丸) and Tenryo Maru (地領丸).[1][2][3][4]
War role
In November 1939, the Imperial Japanese Navy requisitioned Chiryo Maru for national service. In February 1940, she was renamed Sōya, a name previously held by the former Varyag, an armoured cruiser seized from Imperial Russia, but which Japan returned in 1916. The icebreaker Sōya was assigned duties as an auxiliary ammunition supply and survey vessel. In May 1942, she participated in the Battle of Midway (Operation "MI"), where she was assigned to Miyamoto Sadachika's 16th Minesweeper Unit (along with auxiliary minesweepers Showa Maru No. 8, Tama Maru No. 3, Tama Maru No. 5, Showa Maru No. 7; submarine chasers CH-16, CH-17, and CH-18; cargo ships Meiyo Maru and Yamafuku Maru).[5] She survived the Second World War, albeit with multiple close calls. In January 1943 Sōya was attacked by USS Greenling. The torpedoes either missed or proved to be duds: Sōya's crew hoisted one undetonated torpedo onto the deck in celebration. In the February 1944 Operation Hailstone, aircraft from TF58 attacked the Japanese anchorage at Truk, sinking 41 Japanese vessels. Sōya escaped, but ran aground as she did so; 10 crewmembers were killed.[2] On 26 June 1945 the submarine USS Parche attacked a convoy escorting Sōya and other transport ships from Yokohama to Hakodate, sinking an escort vessel and disabling one transport ship. On 9 August 1945, Sōya was at anchor in Onagawa Bay as part of a flotilla with other vessels when British bombers attacked from the air, sinking at least two of them.[2]
Postwar
After the war, with Japan in defeat and needing to repatriate millions of individuals from its former colonies, Sōya was removed from the navy list and was assigned duties with the nation's repatriation fleet. Modifications at this time included removal of her guns and the installation of facilities for passengers, such as toilets in what had been her large forward and aft cargo holds. Spacious wooden accommodations were also built on deck. She undertook numerous missions embarking troops and passengers, including calls at Shanghai, Tinian, and Guam. In light of her ice-breaking ability, she was also assigned northerly missions, and by 1948, had made 14 voyages to and from Sakhalin (the former Karafuto), evacuating citizens by agreement with the new authorities from what had become part of the Soviet Union.[6]
(Sōya should not be confused during this period with Soya Maru, one of three ice-strengthened passenger ferries that operated on the Japan National Railways maritime Chihaku Line between Odomari, the present-day Korsakov in Sakhalin, and Wakkanai in Hokkaido from 1923 to August 1945.)[7]
In 1949, her repatriation duties ceased and Sōya was transferred to the Maritime Safety Agency, the precursor to the Japan Coast Guard. In a new role supplying remote lighthouses, she is reputed to have become known in some circles as the Santa Claus of the Sea.[2]
Antarctic research vessel
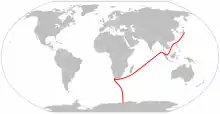
In 1950, the ship received a comprehensive refit in preparation for service as Japan's first dedicated Antarctic research ship. In 1956, her further modifications included the replacement of her steam engine with twin diesel engines and the installation of a helicopter deck with the ability to store light helicopters for voyage. In 1957, her forward gunwale was built up and 1958, a further refit added a second, larger helicopter deck above the earlier one, which became a vast new storage space. Between 1956 and 1962, Sōya undertook missions to the Antarctic. Her second voyage, in 1958, made headlines worldwide when she rescued personnel stranded at the Showa research station in the face of approaching winter. The evacuation did not extend to the mission's dogs, and 15 Karafuto-Ken huskies were abandoned to fend for themselves on the ice. The following spring, the ship returned to find two dogs still alive. The mutts, named Taro and Jiro, became bywords in Japan for fortitude. The story travelled worldwide due in part to two movies: Nankyoku Monogatari (South Pole Story; released in the U.S. as Antarctica) and a treatment by Disney in the Hollywood film Eight Below.[2] Sōya herself experienced hardship during her time in the Antarctic, including becoming stuck in the ice and needing assistance from the nearby Russian icebreaker Ob.[8]
Icebreaking rescue vessel
When retired from Antarctic duties, Sōya became an ice-breaking rescue ship for Japan's Maritime Safety Agency. Sōya was based during this period in Hokkaido.[2]
Museum ship
Sōya was fully decommissioned in 1978. Her last mission was a farewell tour to communities she had served, including the port of Hakodate, and photographs exist from this period of well-wishers swarming the ship before her departure. In 1979, Sōya was moored alongside at the Museum of Maritime Science, Tokyo, and remains open to the public as a museum ship, open daily and generally closed only when typhoons threaten Tokyo. She remains in largely original condition. Her propellers have been removed and placed on deck, but her interior is largely intact from Antarctic exploration days. As a result of modifications made in the 1950s, though, her superstructure has changed considerably from her appearance during World War II. Gone are the tall funnel and aft crane assembly, while the addition of a helicopter landing deck and higher forward gunwales give her a beefier appearance than the cargo ship she started out as.[1][2][9]
References
- "Home :: -Museum of Maritime Science- ::". Archived from the original on 26 January 2012. Retrieved 24 January 2012.
- Hackett, Bob; Kingsepp, Sander; Cundall, Peter (2007). "IJN Soya: Tabular Record of Movement". combinedfleet.com. Retrieved 13 February 2009.
- Nagasawa, Fumio (1998). "天領丸型 TENRYO MARU Class 3隻 (1938)". Nostalgic Japanese Steamships (in Japanese).
- ""地領丸"の時代 (The era of "Jiryomaru")". The Nippon Foundation Library (in Japanese). Retrieved 6 February 2021.
- Hackett, Bob; Kingsepp, Sander (2012). "IJN SOYA". combinedfleet.com. Retrieved 4 November 2019.
- Soya, Historic Ships Study Guide #3, published by Museum of Maritime Science, Tokyo, 2003
- 稚泊連絡船史 (in Japanese)
- Information from a video display at the Funenokagakukan museum in Tokyo.
- "Soya / Guide in Facilities / Home - :: -Museum of Maritime Science- ::". Archived from the original on 30 November 2009. Retrieved 5 February 2009.