SOAT1
Sterol O-acyltransferase (acyl-Coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase) 1, also known as SOAT1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SOAT1 gene.[5]
Function
Acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase (EC 2.3.1.26) is an intracellular protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum that forms cholesterol esters from cholesterol. Accumulation of cholesterol esters as cytoplasmic lipid droplets within macrophages and smooth muscle cells is a characteristic feature of the early stages of atherosclerotic plaques (Cadigan et al., 1988).[5]
Structure and biogenesis
SOAT1 is a polytopic integral membrane protein belonging to the membrane-bound O-acyltransferase (MBOAT) superfamily. The structure of SOAT1 has not yet been solved but that of DltB, a bacterial MBOAT, suggests a complex arrangement of multiple transmembrane domains (TMDs).[6] Primary sequences of predicted SOAT1 TMDs indicate many unusual TMD features such as the presence of multiple charged residues within the lipid bilayer.[7] These features can render challenging the integration of a TMD into the hydrophobic phase of the membrane and might therefore require specialised chaperones. A first hint of such a chaperone assisting SOAT1 biogenesis has been the recognition of the involvement of the ER membrane protein complex (EMC), a molecular chaperone and insertase for integral membrane proteins, in maintaining SOAT1 stability.[8]
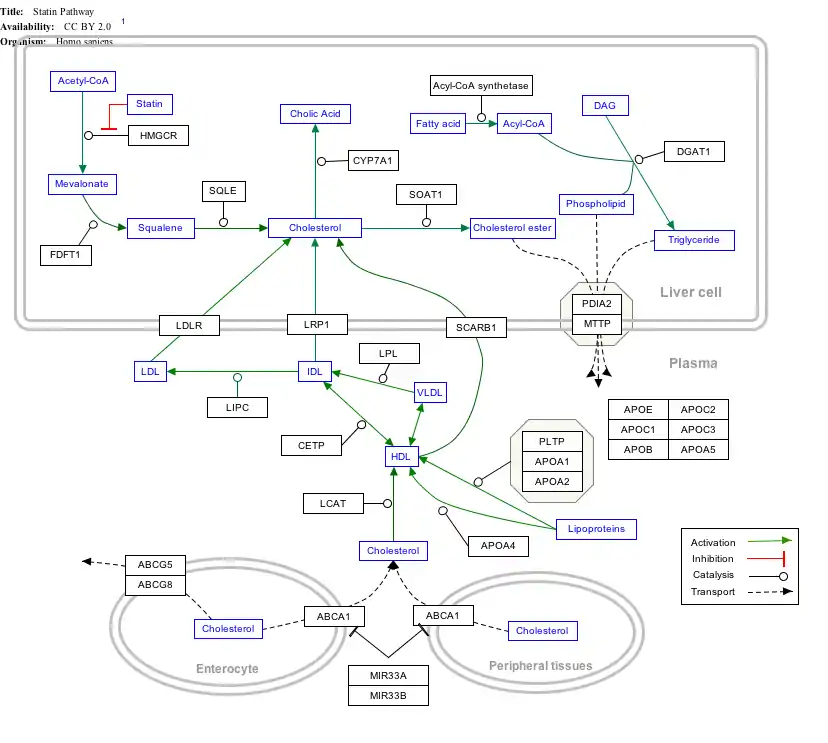
Interactive pathway map
Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "Statin_Pathway_WP430".
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000057252 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026600 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Entrez Gene: SOAT1 sterol O-acyltransferase (acyl-Coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase) 1".
- Ma D, Wang Z, Merrikh CN, Lang KS, Lu P, Li X, Merrikh H, Rao Z, Xu W (October 2018). "Crystal structure of a membrane-bound O-acyltransferase". Nature. 562 (7726): 286–290. Bibcode:2018Natur.562..286M. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0568-2. PMC 6529733. PMID 30283133.
- Lin S, Cheng D, Liu MS, Chen J, Chang TY (August 1999). "Human acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase-1 in the endoplasmic reticulum contains seven transmembrane domains". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (33): 23276–85. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.33.23276. PMID 10438503.
- Volkmar N, Thezenas ML, Louie SM, Juszkiewicz S, Nomura DK, Hegde RS, Kessler BM, Christianson JC (January 2019). "The ER membrane protein complex promotes biogenesis of sterol-related enzymes maintaining cholesterol homeostasis". Journal of Cell Science. 132 (2): jcs223453. doi:10.1242/jcs.223453. PMC 6362398. PMID 30578317.
Further reading
- Chang TY, Chang CC, Lin S, Yu C, Li BL, Miyazaki A (June 2001). "Roles of acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase-1 and -2". Current Opinion in Lipidology. 12 (3): 289–96. doi:10.1097/00041433-200106000-00008. PMID 11353332. S2CID 7310225.
- Chang CC, Noll WW, Nutile-McMenemy N, Lindsay EA, Baldini A, Chang W, Chang TY (January 1994). "Localization of acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase gene to human chromosome 1q25". Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics. 20 (1): 71–4. doi:10.1007/BF02257489. PMID 8197480. S2CID 20146117.
- Chang CC, Huh HY, Cadigan KM, Chang TY (October 1993). "Molecular cloning and functional expression of human acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase cDNA in mutant Chinese hamster ovary cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 268 (28): 20747–55. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.52.35132. PMID 8407899.
- Chang CC, Huh HY, Cadigan KM, Chang TY (October 1993). "Molecular cloning and functional expression of human acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase cDNA in mutant Chinese hamster ovary cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 268 (28): 20747–55. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.52.35132. PMID 8407899.
- Oelkers P, Behari A, Cromley D, Billheimer JT, Sturley SL (October 1998). "Characterization of two human genes encoding acyl coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase-related enzymes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (41): 26765–71. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.41.26765. PMID 9756920.
- Li BL, Li XL, Duan ZJ, Lee O, Lin S, Ma ZM, Chang CC, Yang XY, Park JP, Mohandas TK, Noll W, Chan L, Chang TY (April 1999). "Human acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase-1 (ACAT-1) gene organization and evidence that the 4.3-kilobase ACAT-1 mRNA is produced from two different chromosomes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (16): 11060–71. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.16.11060. PMID 10196189.
- Lin S, Cheng D, Liu MS, Chen J, Chang TY (August 1999). "Human acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase-1 in the endoplasmic reticulum contains seven transmembrane domains". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (33): 23276–85. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.33.23276. PMID 10438503.
- Sakashita N, Miyazaki A, Takeya M, Horiuchi S, Chang CC, Chang TY, Takahashi K (January 2000). "Localization of human acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase-1 (ACAT-1) in macrophages and in various tissues". The American Journal of Pathology. 156 (1): 227–36. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64723-2. PMC 1868616. PMID 10623671.
- Guo Z, Cromley D, Billheimer JT, Sturley SL (August 2001). "Identification of potential substrate-binding sites in yeast and human acyl-CoA sterol acyltransferases by mutagenesis of conserved sequences". Journal of Lipid Research. 42 (8): 1282–91. doi:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)31579-0. PMID 11483630.
- Zhang Y, Yu C, Liu J, Spencer TA, Chang CC, Chang TY (March 2003). "Cholesterol is superior to 7-ketocholesterol or 7 alpha-hydroxycholesterol as an allosteric activator for acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase 1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (13): 11642–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M211559200. PMID 12533546.
- Wollmer MA, Streffer JR, Tsolaki M, Grimaldi LM, Lütjohann D, Thal D, von Bergmann K, Nitsch RM, Hock C, Papassotiropoulos A (June 2003). "Genetic association of acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase with cerebrospinal fluid cholesterol levels, brain amyloid load, and risk for Alzheimer's disease". Molecular Psychiatry. 8 (6): 635–8. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001296. PMID 12851640.
- Smith JL, Rangaraj K, Simpson R, Maclean DJ, Nathanson LK, Stuart KA, Scott SP, Ramm GA, de Jersey J (April 2004). "Quantitative analysis of the expression of ACAT genes in human tissues by real-time PCR". Journal of Lipid Research. 45 (4): 686–96. doi:10.1194/jlr.M300365-JLR200. PMID 14729857.
- Hori M, Miyazaki A, Tamagawa H, Satoh M, Furukawa K, Hakamata H, Sasaki Y, Horiuchi S (July 2004). "Up-regulation of acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase-1 by transforming growth factor-beta1 during differentiation of human monocytes into macrophages" (PDF). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 320 (2): 501–5. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.05.190. PMID 15219857.
- Yang L, Chen J, Chang CC, Yang XY, Wang ZZ, Chang TY, Li BL (April 2004). "A stable upstream stem-loop structure enhances selection of the first 5'-ORF-AUG as a main start codon for translation initiation of human ACAT1 mRNA". Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica. 36 (4): 259–68. doi:10.1093/abbs/36.4.259. PMID 15253151.
- Liang JJ, Oelkers P, Guo C, Chu PC, Dixon JL, Ginsberg HN, Sturley SL (October 2004). "Overexpression of human diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1, acyl-coa:cholesterol acyltransferase 1, or acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase 2 stimulates secretion of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in McA-RH7777 cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (43): 44938–44. doi:10.1074/jbc.M408507200. PMID 15308631.
- Yang L, Lee O, Chen J, Chen J, Chang CC, Zhou P, Wang ZZ, Ma HH, Sha HF, Feng JX, Wang Y, Yang XY, Wang L, Dong R, Ornvold K, Li BL, Chang TY (October 2004). "Human acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase 1 (acat1) sequences located in two different chromosomes (7 and 1) are required to produce a novel ACAT1 isoenzyme with additional sequence at the N terminus". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (44): 46253–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.M408155200. PMID 15319423.
- Yang L, Yang JB, Chen J, Yu GY, Zhou P, Lei L, Wang ZZ, Cy Chang C, Yang XY, Chang TY, Li BL (August 2004). "Enhancement of human ACAT1 gene expression to promote the macrophage-derived foam cell formation by dexamethasone". Cell Research. 14 (4): 315–23. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7290231. PMID 15353128.
- Bertram L, Hsiao M, Mullin K, Parkinson M, Menon R, Moscarillo TJ, Blacker D, Tanzi RE (June 2005). "ACAT1 is not associated with Alzheimer's disease in two independent family-based samples". Molecular Psychiatry. 10 (6): 522–4. doi:10.1038/sj.mp.4001646. PMID 15768051.