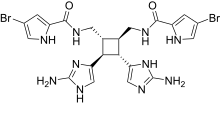
Sceptrin
Sceptrin is a bioactive marine isolate.[1] It has been isolated from the marine sponge Agelas conifera and appears to have affinity for the bacterial actin equivalent MreB.[2] As such, this compound possess antibiotic potential.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
N,N′-{[(1R,2R,3S,4S)-3,4-Bis(2-amino-1H-imidazol-5-yl)cyclobutane-1,2-diyl]bis(methylene)}bis(4-bromopyrrole-2-carboxamide) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H24Br2N10O2 | |
| Molar mass | 620.310 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Cipres, A; O'Malley, DP; Li, K; Finlay, D; Baran, PS; Vuori, K (2010). "Sceptrin, a marine natural compound, inhibits cell motility in a variety of cancer cell lines". ACS Chemical Biology. 5 (2): 195–202. doi:10.1021/cb900240k. PMC 2825093. PMID 20030414.
- Rodriguez, AD; Lear, MJ; La Clair, JJ (2008). "Identification of the binding of sceptrin to MreB via a bidirectional affinity protocol". J Am Chem Soc. 130 (23): 7256–7258. doi:10.1021/ja7114019. PMID 18479102.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.