Deoxyschizandrin
Deoxyschizandrin is a bio-active isolate of Schisandra chinensis.[1]
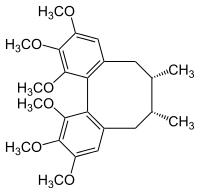 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(6R,7S)-1,2,3,10,11,12-Hexamethoxy-6,7-dimethyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrodibenzo[a,c][8]annulene | |
| Other names
Schizandrin A; Schisandrin A; Dimethylgomisin J | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H32O6 | |
| Molar mass | 416.514 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Deoxyschizandrin has been found to act as an agonist of the adiponectin receptor 2 (AdipoR2).[2]
References
- Chang, R; Li, Y; Yang, X; Yue, Y; Dou, L; Wang, Y; Zhang, W; Li, X (2013). Ma, Xin-Liang (ed.). "Protective role of deoxyschizandrin and schisantherin a against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats". PLOS ONE. 8 (4): e61590. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...861590C. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061590. PMC 3631228. PMID 23620773.
- Sun Y, Zang Z, Zhong L, Wu M, Su Q, Gao X, Zan W, Lin D, Zhao Y, Zhang Z (2013). "Identification of adiponectin receptor agonist utilizing a fluorescence polarization based high throughput assay". PLOS ONE. 8 (5): e63354. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...863354S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063354. PMC 3653934. PMID 23691032.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.