Secondary surveillance radar
Secondary surveillance radar (SSR)[1] is a radar system used in air traffic control (ATC), that unlike primary radar systems that measure the bearing and distance of targets using the detected reflections of radio signals, relies on targets equipped with a radar transponder, that reply to each interrogation signal by transmitting encoded data such as an identity code, the aircraft's altitude and further information depending on its chosen mode. SSR is based on the military identification friend or foe (IFF) technology originally developed during World War II; therefore, the two systems are still compatible. Monopulse secondary surveillance radar (MSSR), Mode S, TCAS and ADS-B are similar modern methods of secondary surveillance.


Overview
Primary radar
The rapid wartime development of radar had obvious applications for air traffic control (ATC) as a means of providing continuous surveillance of air traffic disposition. Precise knowledge of the positions of aircraft would permit a reduction in the normal procedural separation standards, which in turn promised considerable increases in the efficiency of the airways system. This type of radar (called a primary radar) can detect and report the position of anything that reflects its transmitted radio signals including, depending on its design, aircraft, birds, weather and land features. For air traffic control purposes this is both an advantage and a disadvantage. Its targets do not have to co-operate, they only have to be within its coverage and be able to reflect radio waves, but it only indicates the position of the targets, it does not identify them. When primary radar was the only type of radar available, the correlation of individual radar returns with specific aircraft typically was achieved by the controller observing a directed turn by the aircraft. Primary radar is still used by ATC as a backup/complementary system to secondary radar, although its coverage and information is more limited.[2][3][4]
Secondary radar

The need to be able to identify aircraft more easily and reliably led to another wartime radar development, the Identification Friend or Foe (IFF) system, which had been created as a means of positively identifying friendly aircraft from unknowns. This system, which became known in civil use as secondary surveillance radar (SSR), or in the US as the air traffic control radar beacon system (ATCRBS), relies on a piece of equipment aboard the aircraft known as a "transponder." The transponder is a radio receiver and transmitter pair which receives on 1030 MHz and transmits on 1090 MHz. The target aircraft transponder replies to signals from an interrogator (usually, but not necessarily, a ground station co-located with a primary radar) by transmitting a coded reply signal containing the requested information.[5]

Both the civilian SSR and the military IFF have become much more complex than their war-time ancestors, but remain compatible with each other, not least to allow military aircraft to operate in civil airspace. SSR can provide much more detailed information, for example, the aircraft altitude, as well as enabling the direct exchange of data between aircraft for collision avoidance. Most SSR systems rely on Mode C transponders, which report the aircraft pressure altitude. The pressure altitude is independent of the pilot's altimeter setting,[6] thus preventing false altitude transmissions if altimeter is adjusted incorrectly. Air traffic control systems recalculate reported pressure altitudes to true altitudes based on their own pressure references, if necessary.
Given its primary military role of reliably identifying friends, IFF has more secure (encrypted) messages to prevent "spoofing" by the enemy, and is used on many types of military platforms including air, sea and land vehicles.
Standards and specifications
The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It publishes annexes to the Convention and Annex 10 addresses Standards and Recommended Practices for Aeronautical Telecommunications. The objective is to ensure that aircraft crossing international boundaries are compatible with the Air Traffic Control systems in all countries that may be visited. Volume III, Part 1 is concerned with digital data communication systems including the data link functions of Mode S while volume IV defines its operation and signals in space.[7]
The American Radio Technical Commission for Aeronautics (RTCA) and the European Organization for Civil Aviation Equipment (Eurocae) produce Minimum Operational Performance Standards for both ground and airborne equipment in accordance with the standards specified in ICAO Annex 10. Both organisations frequently work together and produce common documents.
ARINC (Aeronautical Radio, Incorporated) is an airline run organisation concerned with the form, fit and function of equipment carried in aircraft. Its main purpose is to ensure competition between manufacturers by specifying the size, power requirements, interfaces and performance of equipment to be located in the equipment bay of the aircraft.
Operation
The purpose of SSR is to improve the ability to detect and identify aircraft while automatically providing the Flight Level (pressure altitude) of an aircraft. An SSR ground station transmits interrogation pulses on 1030 MHz (continuously in Modes A, C and selectively, in Mode S) as its antenna rotates, or is electronically scanned, in space. An aircraft transponder within line-of-sight range 'listens' for the SSR interrogation signal and transmits a reply on 1090 MHz that provides aircraft information. The reply sent depends on the interrogation mode. The aircraft is displayed as a tagged icon on the controller's radar screen at the measured bearing and range. An aircraft without an operating transponder still may be observed by primary radar, but would be displayed to the controller without the benefit of SSR derived data. It is typically a requirement to have a working transponder in order to fly in controlled air space and many aircraft have a back-up transponder to ensure that condition is met.[8]
Interrogation modes
There are several modes of interrogation, each indicated by the difference in spacing between two transmitter pulses, known as P1 and P3.[7] Each mode produces a different response from the aircraft. A third pulse, P2, is for side lobe suppression and is described later. Not included are additional military (or IFF) modes, which are described in Identification Friend or Foe.
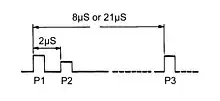
| Mode | P1–P3 pulse spacing | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| A | 8 µs | Identity |
| B | 17 µs | Identity |
| C | 21 µs | Altitude |
| D | 25 µs | Undefined |
| S | 3.5 µs | Multipurpose |

A mode-A interrogation elicits a 12-pulse reply, indicating an identity number associated with that aircraft. The 12 data pulses are bracketed by two framing pulses, F1 and F2. The X pulse is not used. A mode-C interrogation produces an 11-pulse response (pulse D1 is not used), indicating aircraft altitude as indicated by its altimeter in 100-foot increments. Mode B gave a similar response to mode A and was at one time used in Australia. Mode D has never been used operationally.
The new mode, Mode S, has different interrogation characteristics. It comprises pulses P1 and P2 from the antenna main beam to ensure that Mode-A and Mode-C transponders do not reply, followed by a long phase-modulated pulse.[7]
The ground antenna is highly directional but cannot be designed without sidelobes. Aircraft could also detect interrogations coming from these sidelobes and reply appropriately. However these replies can not be differentiated from the intended replies from the main beam and can give rise to a false aircraft indication at an erroneous bearing. To overcome this problem the ground antenna is provided with a second, mainly omni-directional, beam with a gain which exceeds that of the sidelobes but not that of the main beam. A third pulse, P2, is transmitted from this second beam 2 µs after P1. An aircraft detecting P2 stronger than P1 (therefore in the sidelobe and at the incorrect main lobe bearing), does not reply.[7]
Deficiencies
A number of problems are described in an ICAO publication of 1983 entitled Secondary Surveillance Radar Mode S Advisory Circular.[9]
Mode A
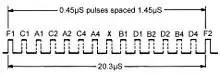
Although 4,096 different identity codes available in a mode A reply may seem enough, once particular codes have been reserved for emergency and other purposes, the number is significantly reduced. Ideally an aircraft would keep the same code from take-off until landing even when crossing international boundaries, as it is used at the air traffic control centre to display the aircraft's callsign using a process known as code/callsign conversion. Clearly the same mode A code should not be given to two aircraft at the same time as the controller on the ground could be given the wrong callsign with which to communicate with the aircraft.[7]
Mode C
The mode C reply provides height increments of 100 feet, which was initially adequate for monitoring aircraft separated by at least 1000 feet. However, as airspace became increasingly congested, it became important to monitor whether aircraft were not moving out of their assigned flight level. A slight change of a few feet could cross a threshold and be indicated as the next increment up and a change of 100 feet. Smaller increments were desirable.
FRUIT
Since all aircraft reply on the same frequency of 1090 MHz, a ground station will also receive aircraft replies originating from responses to other ground stations. These unwanted replies are known as FRUIT (False Replies Unsynchronized with Interrogator Transmissions or alternatively False Replies Unsynchronized In Time). Several successive FRUIT replies could combine and appear to indicate an aircraft which does not exist. As air transport expands and more aircraft occupy the airspace, the amount of FRUIT generated will also increase.[9]
Garble
FRUIT replies can overlap with wanted replies at a ground receiver, thus causing errors in extracting the included data. A solution is to increase the interrogation rate so as to receive more replies, in the hope that some would be clear of interference. The process is self-defeating as increasing the reply rate only increases the interference to other users and vice versa.[9]
Synchronous garble
If two aircraft paths cross within about two miles slant range from the ground interrogator, their replies will overlap and the interference caused will make their detection difficult. Typically the controller will lose the longer range aircraft, just when the controller may be most interested in monitoring them closely.[9]
Capture
While an aircraft is replying to one ground interrogation it is unable to respond to another interrogation, reducing detection efficiency. For a Mode A or C interrogation the transponder reply may take up to 120 µs before it can reply to a further interrogation.[9]
Antenna
.jpg.webp)
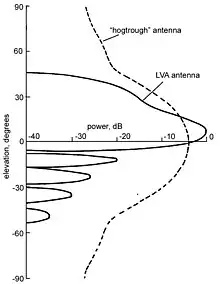
The ground antenna has a typical horizontal 3 dB beamwidth of 2.5° which limits the accuracy in determining the bearing of the aircraft. Accuracy can be improved by making many interrogations as the antenna beam scans an aircraft and a better estimate can be obtained by noting where the replies started and where they stopped, and taking the centre of the replies as the direction of the aircraft. This is known as a sliding window process.[1]
The early system used an antenna known as a hogtrough. This has a large horizontal dimension to produce a narrow horizontal beam and a small vertical dimension to provide coverage from near the horizon to nearly overhead. There were two problems with this antenna. First, nearly half the energy is directed at the ground where it is reflected back up, and interferes with, the upward energy causing deep nulls at certain elevation angles and loss of contact with aircraft. Second, if the surrounding ground is sloping, then the reflected energy is partly offset horizontally, distorting the beam shape and the indicated bearing of the aircraft. This was particularly important in a monopulse system with its much improved bearing measurement accuracy.[10]
Developments to address the deficiencies
The deficiencies in modes A and C were recognised quite early in the use of SSR and in 1967 Ullyatt published a paper[11] and in 1969 an expanded paper,[12] which proposed improvements to SSR to address the problems. The essence of the proposals was new interrogation and reply formats. Aircraft identity and altitude were to be included in the one reply so collation of the two data items would not be needed. To protect against errors a simple parity system was proposed – see Secondary Surveillance Radar – Today and Tomorrow.[13] Monopulse would be used to determine the bearing of the aircraft thereby reducing to one the number of interrogations/replies per aircraft on each scan of the antenna. Further each interrogation would be preceded by main beam pulses P1 and P2 separated by 2 µs so that transponders operating on modes A and C would take it as coming from the antenna sidelobe and not reply and not cause unnecessary FRUIT.[12]
The FAA was considering similar problems but assumed that a new pair of frequencies would be required. Ullyatt showed that the existing 1030 MHz and 1090 MHz frequencies could be retained and the existing ground interrogators and airbornes transponders, with suitable modifications, could be used. The result was a Memorandum of Understanding between the US and the UK to develop a common system. In the US the programme was called DABS (Discrete Address Beacon System), and in the UK Adsel (Address selective).[14]
Monopulse, which means single pulse, had been used in military track-and-follow systems whereby the antenna was steered to follow a particular target by keeping the target in the centre of the beam. Ullyatt proposed the use of a continuously rotating beam with bearing measurement made wherever the pulse may arrive in the beam.[15]
The FAA engaged MIT Lincoln Laboratory to further develop the system and it produced a series of ATC Reports defining all aspects of the new joint development.[16] Added to Ullyatt's concept was the use of a more powerful 24-bit parity system using a cyclic redundancy code, which not only ensured the accuracy of the received data without the need for repetition but also allowed errors caused by an overlapping FRUIT reply to be corrected. A proposed aircraft identity code comprised 24 bits with 16 million permutations. This allowed each aircraft to be assigned its own unique address. Blocks of addresses are allocated to different countries[17] and further allocated to particular airlines so that the address could readily identify them also. The Lincoln Laboratory report ATC 42 entitled Mode S Beacon System: Functional Description gave details on the proposed new system.[18]
The two countries reported the results of their development in a joint paper, ADSEL/DABS – A Selective Address Secondary Surveillance Radar.[14] This was followed at a conference at ICAO Headquarters in Montreal, at which a low-power interrogation test by Lincoln Laboratory successfully communicated with an upgraded commercial SSR transponder of UK manufacture.
The only thing needed was an international name. Much had been made of the proposed new features but the existing ground SSR interrogators would still be used, albeit with modification, and the existing aircraft transponders, again with modification. The best way of showing that this was an evolution not a revolution was to still call it SSR but with a new mode letter. Mode S was the obvious choice, with the S standing for select. In 1983 ICAO issued an advisory circular describing the new system.[9]
Improved antenna
The problem with the existing standard "hogtrough" antenna was caused by the energy radiated toward the ground, which was reflected up and interfered with the upwards directed energy. The answer was to shape the vertical beam. This necessitated a vertical dipole array suitably fed to produce the desired shape. A five-foot vertical dimension was found to be optimum and it has become the international standard.[10]
Monopulse secondary surveillance radar
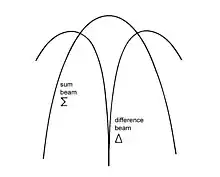
The Mode S system was intended to operate with just a single reply from an aircraft, a system known as monopulse. The accompanying diagram shows a conventional main or "sum" beam of an SSR antenna to which has been added a "difference" beam. To produce the sum beam the signal is distributed horizontally across the antenna aperture. This feed system is divided into two equal halves and the two parts summed again to produce the original sum beam. However the two halves are also subtracted to produce a difference output. A signal arriving exactly normal, or boresight, to the antenna will produce a maximum output in the sum beam but a zero signal in the difference beam. Away from boresight the signal in the sum beam will be less but there will be a non-zero signal in the difference beam. The angle of arrival of the signal can be determined by measuring the ratio of the signals between the sum and difference beams. The ambiguity about boresight can be resolved as there is a 180° phase change in the difference signal either side of boresight. Bearing measurements can be made on a single pulse, hence monopulse, but accuracy can be improved by averaging measurements made on several or all of the pulses received in a reply from an aircraft. A monopulse receiver[15] was developed early in the UK Adsel programme and this design is still used widely. Mode S reply pulses are deliberately designed to be similar to mode A and C replies so the same receiver can be used to provide improved bearing measurement for the SSR mode A and C system with the advantage that the interrogation rate can be substantially reduced thereby reducing the interference caused to other users of the system.[19]
Lincoln Laboratory exploited the availability of a separate bearing measurement on each reply pulse to overcome some of the problems of garble whereby two replies overlap making associating the pulses with the two replies. Since each pulse is separately labelled with direction this information can be used to unscramble two overlapping mode A or C replies. The process is presented in ATC-65 "The ATCRBS Mode of DABS".[20] The approach can be taken further by also measuring the strength of each reply pulse and using that as a discriminate as well.[1] The following table compares the performance of conventional SSR, monopulse SSR (MSSR) and Mode S.[19]
| Standard SSR | Monopulse SSR | Mode S | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Replies per scan | 20–30 | 4–8 | 1 |
| Range accuracy | 230 m rms | 13 m rms | 7 m rms |
| Bearing accuracy | 0.08° rms | 0.04° rms | 0.04° rms |
| Height resolution | 100 ft (30 m) | 100 ft | 25 ft (7.6 m) |
| Garble resistance | Poor | Good | Best |
| Data capacity (uplink) | 0 | 0 | 56 – 1,280 bits |
| Data capacity (downlink) | 23 bits | 23 bits | 56 – 1,280 bits |
| Identity permutations | 4,096 | 4,096 | 16 million |
The MSSR replaced most of the existing SSRs by the 1990s and its accuracy provided for a reduction of separation minima in en-route ATC from 10 nautical miles (19 km; 12 mi) to 5 nautical miles (9.3 km; 5.8 mi)[21]
MSSR resolved many of the system problems of SSR, as changes to the ground system only, were required. The existing transponders installed in aircraft were unaffected. It undoubtedly resulted in the delay of Mode S.[16]
Mode S
A more detailed description of Mode S is given in the Eurocontrol publication Principles of Mode S and Interrogator Codes[8] and the ICAO circular 174-AN/110 Secondary Surveillance Radar Mode S Advisory Circular.[9] The 16 million permutations of the 24-bit aircraft address codes have been allocated in blocks to individual states and the assignment is given in ICAO Annex 10, Volume III, Chapter 9.[17]
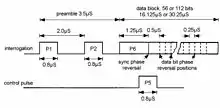
A mode S interrogation comprises two 0.8 µs wide pulses,[18] which are interpreted by a mode A & C transponder as coming from an antenna sidelobe and therefore a reply is not required. The following long P6 pulse is phase modulated with the first phase reversal, after 1.25 µs, synchronising the transponder's phase detector. Subsequent phase reversals indicate a data bit of 1, with no phase reversal indicating a bit of value 0. This form of modulation provides some resistance to corruption by a chance overlapping pulse from another ground interrogator. The interrogation may be short with P6 = 16.125 µs, mainly used to obtain a position update, or long, P6 = 30.25 µs, if an additional 56 data bits are included. The final 24 bits contain both the parity and address of the aircraft. On receiving an interrogation, an aircraft will decode the data and calculate the parity. If the remainder is not the address of the aircraft then either the interrogation was not intended for it or it was corrupted. In either case it will not reply. If the ground station was expecting a reply and did not receive one then it will re-interrogate.[9]
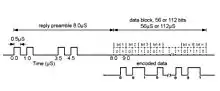
The aircraft reply[18] consists of a preamble of four pulses spaced so that they cannot be erroneously formed from overlapping mode A or C replies. The remaining pulses contain data using pulse position amplitude modulation. Each 1 µs interval is divided into two parts. If a 0.5 µs pulse occupies the first half and there is no pulse in the second half then a binary 1 is indicated. If it is the other way round then it represents a binary 0. In effect the data is transmitted twice, the second time in inverted form. This format is very resistant to error due to a garbling reply from another aircraft. To cause a hard error one pulse has to be cancelled and a second pulse inserted in the other half of the bit period. Much more likely is that both halves are confused and the decoded bit is flagged as "low confidence".[20]
The reply also has parity and address in the final 24 bits. The ground station tracks the aircraft and uses the predicted position to indicate the range and bearing of the aircraft so it can interrogate again and get an update of its position. If it is expecting a reply and if it receives one then it checks the remainder from the parity check against the address of the expected aircraft. If it is not the same then either it is the wrong aircraft and a re-interrogation is necessary, or the reply has been corrupted by interference by being garbled by another reply. The parity system has the power to correct errors as long as they do not exceed 24 µs, which embraces the duration of a mode A or C reply, the most expected source of interference in the early days of Mode S. The pulses in the reply have individual monopulse angle measurements available, and in some implementations also signal strength measurements, which can indicate bits that are inconsistent with the majority of the other bits, thereby indicating possible corruption. A test is made by inverting the state of some or all of these bits (a 0 changed to a 1 or vice versa) and if the parity check now succeeds the changes are made permanent and the reply accepted. If it fails then a re-interrogation is required.[9]
Mode S operates on the principle that interrogations are directed to a specific aircraft using that aircraft's unique address. This results in a single reply with aircraft range determined by the time taken to receive the reply and monopulse providing an accurate bearing measurement. In order to interrogate an aircraft its address must be known. To meet this requirement the ground interrogator also broadcasts All-Call interrogations, which are in two forms.[9]
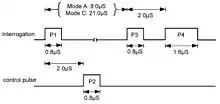
In one form, the Mode A/C/S All-Call looks like a conventional Mode A or C interrogation at first and a transponder will start the reply process on receipt of pulse P3. However a Mode S transponder will abort this procedure upon the detection of pulse P4, and instead respond with a short Mode S reply containing its 24 bit address. This form of All-Call interrogation is now not much used as it will continue to obtain replies from aircraft already known and give rise to unnecessary interference. The alternative form of All-Call uses short Mode S interrogation with a 16.125 µs data block. This can include an indication of the interrogator transmitting the All-Call with the request that if the aircraft has already replied to this interrogator then do not reply again as aircraft is already known and a reply unnecessary.[9]
The Mode S interrogation can take three forms:
| Name | Form | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Surveillance | Short | Position update |
| Comm-A | Long | Contains 56 data bits |
| Comm-C | Long | Up to 16 long interrogations strung together to transmit up to 1280 bits |
The first five bits, known as the uplink field (UF) in the data block indicate the type of interrogation. The final 24 bits in each case is combined aircraft address and parity. Not all permutations have yet been allocated but those that have are shown:[9]
| Uplink field (UF) | Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Binary | Decimal | |
| 00000 | 0 | Short air-air surveillance (TCAS) |
| 00100 | 4 | Surveillance, altitude request |
| 00101 | 5 | Surveillance, Mode A identity request |
| 01011 | 11 | Mode S only All-Call |
| 10000 | 16 | Long air-air surveillance (TCAS) |
| 10100 | 20 | Comm-A including altitude request |
| 10101 | 21 | Comm-A including Mode A identity request |
| 11000 | 24 | Comm-C (extended length message) |
Similarly the Mode S reply can take three forms:[9]
| Name | Form | Use |
|---|---|---|
| Surveillance | Short | Position update |
| Comm-B | Long | Contains 56 data bits |
| Comm-D | Long | Up to 16 long interrogations strung together to transmit up to 1280 bits |
The first five bits, known as the downlink field (DF) in the data block indicate the type of reply. The final 24 bits in each case is combined aircraft address and parity. Eleven permutations have been allocated.[9]
| Downlink field (DF) | Application | |
|---|---|---|
| Binary | Decimal | |
| 00000 | 0 | Short air-air surveillance (TCAS) |
| 00100 | 4 | Surveillance, altitude reply |
| 00101 | 5 | Surveillance, Mode A identity reply |
| 01011 | 11 | All-Call reply containing aircraft address |
| 10000 | 16 | Long air-air surveillance (TCAS) |
| 10001 | 17 | Extended squitter |
| 10010 | 18 | TIS-B |
| 10011 | 19 | Military extended squitter |
| 10100 | 20 | Comm-B reply including altitude |
| 10101 | 21 | Comm-B reply including Mode A identity |
| 10110 | 22 | Military use |
| 11000 | 24 | Up to 16 long replies strung together to transmit up to 1280 bits |
A transponder equipped to transmit Comm-B replies is fitted with 256 data registers each of 56 bits. The contents of these registers are filled and maintained from on-board data sources. If the ground system requires this data then it requests it by a Surveillance or Comm-A interrogation.[9]
ICAO Annex 10 Volume III, Chapter 5 lists the contents of all those currently allocated. A reduced number are required for current operational use.[22][23] Other registers are intended for use with TCAS and ADS-B. The Comm-B Data Selector (BDS) numbers are in hexadecimal notation.
| Register | Data |
|---|---|
| BDS 6,0 | Magnetic heading |
| BDS 6,0 | Indicated airspeed |
| BDS 6,0 | Mach number |
| BDS 6,0 | Vertical rate |
| BDS 5,0 | Roll angle |
| BDS 5,0 | Track angle rate |
| BDS 5,0 | True track angle |
| BDS 5,0 | Ground speed |
| BDS 4,0 | Selected vertical intent |
Extended squitter
Starting in 2009, the ICAO defined an "extended squitter" mode of operation;[24] it supplements the requirements contained in ICAO Annex 10, Volumes III and IV. The first edition specified earlier versions of extended squitter messages:
- Version 0
- Extends Mode S to deal with basic ADS-B exchanges, to add traffic information broadcast (TIS-B) format information, as well as uplink and downlink broadcast protocol information.
- Version 1
- Better describes surveillance accuracy and integrity information (navigation accuracy category, navigation integrity category, surveillance integrity level), and additional parameters for TIS-B and ADS-B rebroadcast (ADS-R).
- Version 2
- The second edition introduced yet a new version of extended squitter formats and protocols to:[25]
- enhance integrity and accuracy reporting
- add a number of additional parameters to support identified operational needs for the use of ADS-B not covered by Version 1 (including capabilities to support airport surface applications)
- modify several parameters, and remove a number of parameters, which are no longer required to support ADS-B applications
See also
- Air traffic control radar beacon system, all encompassing description
- Automatic dependent surveillance-broadcast, free flight enhancement
- Traffic collision avoidance system
- Transponder landing system
- Gillham code
References
- Secondary Surveillance Radar, Stevens M.C. Artech House, ISBN 0-89006-292-7
- "Air Traffic Services Surveillance Systems, Including An Explanation of Primary and Secondary Radar". www.airwaysmuseum.com. Retrieved 2009-06-20.
- "AIR TRAFFIC CONTROL RADAR". Argos Press. Archived from the original on 2009-09-18. Retrieved 2009-06-20.
- "Secondary Surveillance Radar in ATC Systems: A description of the advantages and implications to the controller of the introduction of SSR facilities". Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology. Retrieved 2009-06-20.
- Illman, Paul E. (1998). The pilot's radio communications handbook (Fifth Edition, Paperback). McGraw-Hill. p. 111. ISBN 0-07-031832-8.
- Instrument Flying Handbook. U.S. Department of Transportation, FAA. 2008. pp. 3–7.
- ICAO Annex 10, Volume IV
- Principles of Mode S Operation and Interrogator Codes
- ICAO Circular 174-AN/110 Secondary Surveillance Radar Mode S Advisory Circular
- Stevens, M.C. "Multipath and interference effects in secondary surveillance radar systems", Proc. Inst.Electr. Eng., Part F, 128(1), 43–53, 1981
- Ullyatt, C. Secondary radar in the era of auto-tracking, IEE Comf. Pub., 28, 140, 1967
- Ullyatt, C. Sensors for the ATC environment with special reference to SSR, Electron. Civil Aviat., 3, C1–C3, 1969
- Stevens, M. C., Secondary Surveillance Radar – Today and Tomorrow, SERT Avionics Symposium, Swansea, July 1974.
- Bowes R.C., Drouilhet P.R., Weiss H.G. and Stevens M.C., ADSEL/DABS – A Selective Address Secondary Surveillance Radar,AGARD Conference Proceedings No. 188. 20th Symposium of the Guidance and Control Panel held in Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, 20–23 May 1975
- Stevens, M.C. Precision secondary radar, Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng., 118(12), 1729–1735, 1971
- The Story of Mode S: An Air Traffic Control Data Link Technology: Mode S Today, Chang E., Hu R., Lai D., Li R., Scott Q., Tyan T., December 2000
- "ICAO Annex 10 Volume III: Chapter 9. Aircraft Addressing System" (PDF). ICAO Annex 10. ICAO. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-11-22. Retrieved 2017-06-02.
- Orlando V.A.; Drouilhet P.R. (August 1986). "ATC-42 Mode S Beacon System: Functional Description (Rev D)" (PDF). Lincoln Laboratory. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 2, 2012. Retrieved March 29, 2014.
- Stevens, M.C. Surveillance in the Mode S Era, CAA/IEE Symposium on ATC, London. March 1990
- Gertz J. L. (January 1977). "ATC-65 The ATCRBS Mode of DABS" (PDF). Lincoln Laboratory (MIT). Archived from the original (PDF) on March 5, 2016. Retrieved March 29, 2014.
- FAA (2004). Aviation System Capital Investment Plan. DIANE Publishing Company. ISBN 978-0-7881-3348-0.
- Manual on Mode S Specific Services, Panel Working Group B Surveillance and Conflict Resolution Systems, September 2001
- Carriage of SSR Mode S Transponders for IFR Flights Operating as General Traffic, www.caa.co.uk/docs/810/
- ICAO (2008). ICAO Doc 9871, Technical Provisions for Mode S and Extended Squitter (1 ed.). International Civil Aviation Organization. ISBN 978-92-9231-117-9.
- ICAO (2012). ICAO Doc 9871, Technical Provisions for Mode S and Extended Squitter (2 ed.). International Civil Aviation Organization. ISBN 978-92-9249-042-3.
Further reading
- Industry specifications
- Annex 10 - Volume IV - Surveillance Radar and Collision Avoidance Systems Archived 2014-05-06 at the Wayback Machine; 4th Edition; ICAO; 280 pages; 2007.
- DO-181E Minimum Operational Performance Standards for ATCRBS / Mode S Airborne Equipment; Rev E; RTCA; 2011.