Sextant
A sextant is a doubly reflecting navigation instrument that measures the angular distance between two visible objects. The primary use of a sextant is to measure the angle between an astronomical object and the horizon for the purposes of celestial navigation.

The estimation of this angle, the altitude, is known as sighting or shooting the object, or taking a sight. The angle, and the time when it was measured, can be used to calculate a position line on a nautical or aeronautical chart—for example, sighting the Sun at noon or Polaris at night (in the Northern Hemisphere) to estimate latitude (with sight reduction). Sighting the height of a landmark can give a measure of distance off and, held horizontally, a sextant can measure angles between objects for a position on a chart.[1] A sextant can also be used to measure the lunar distance between the moon and another celestial object (such as a star or planet) in order to determine Greenwich Mean Time and hence longitude.
The principle of the instrument was first implemented around 1731 by John Hadley (1682–1744) and Thomas Godfrey (1704–1749), but it was also found later in the unpublished writings of Isaac Newton (1643–1727).
In 1922, it was modified for aeronautical navigation by Portuguese navigator and naval officer Gago Coutinho.
Navigational sextants
.jpg.webp)
Like the Davis quadrant, the sextant allows celestial objects to be measured relative to the horizon, rather than relative to the instrument. This allows excellent precision. Also, unlike the backstaff, the sextant allows direct observations of stars. This permits the use of the sextant at night when a backstaff is difficult to use. For solar observations, filters allow direct observation of the Sun.
Since the measurement is relative to the horizon, the measuring pointer is a beam of light that reaches to the horizon. The measurement is thus limited by the angular accuracy of the instrument and not the sine error of the length of an alidade, as it is in a mariner's astrolabe or similar older instrument.
A sextant does not require a completely steady aim, because it measures a relative angle. For example, when a sextant is used on a moving ship, the image of both horizon and celestial object will move around in the field of view. However, the relative position of the two images will remain steady, and as long as the user can determine when the celestial object touches the horizon, the accuracy of the measurement will remain high compared to the magnitude of the movement.
The sextant is not dependent upon electricity (unlike many forms of modern navigation) or for that matter anything reliant on human-controlled signals (such as GPS satellites). For these reasons it is considered to be an eminently practical back-up navigation tool for ships.
Design
The frame of a sextant is in the shape of a sector which is approximately 1⁄6 of a circle (60°),[2] hence its name (sextāns, sextantis is the Latin word for "one sixth"). Both smaller and larger instruments are (or were) in use: the octant, quintant (or pentant) and the (doubly reflecting) quadrant[3] span sectors of approximately 1⁄8 of a circle (45°), 1⁄5 of a circle (72°) and 1⁄4 of a circle (90°), respectively. All of these instruments may be termed "sextants".
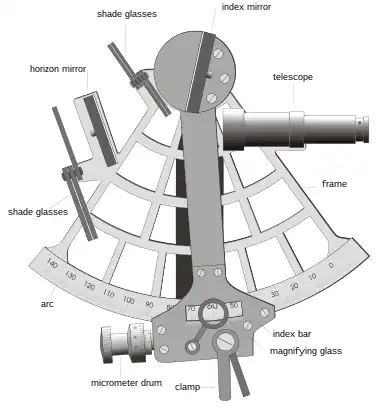

Attached to the frame are the "horizon mirror", an index arm which moves the index mirror, a sighting telescope, Sun shades, a graduated scale and a micrometer drum gauge for accurate measurements. The scale must be graduated so that the marked degree divisions register twice the angle through which the index arm turns. The scales of the octant, sextant, quintant and quadrant are graduated from below zero to 90°, 120°, 140° and 180° respectively. For example, the sextant illustrated has a scale graduated from −10° to 142°, which is basically a quintant: the frame is a sector of a circle subtending an angle of 76° at the pivot of the index arm.
The necessity for the doubled scale reading follows from consideration of the relations of the fixed ray (between the mirrors), the object ray (from the sighted object) and the direction of the normal perpendicular to the index mirror. When the index arm moves by an angle, say 20°, the angle between the fixed ray and the normal also increases by 20°. But the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection so the angle between the object ray and the normal must also increase by 20°. The angle between the fixed ray and the object ray must therefore increase by 40°. This is the case shown in the graphic.
There are two types of horizon mirrors on the market today. Both types give good results.
Traditional sextants have a half-horizon mirror, which divides the field of view in two. On one side, there is a view of the horizon; on the other side, a view of the celestial object. The advantage of this type is that both the horizon and celestial object are bright and as clear as possible. This is superior at night and in haze, when the horizon and/or a star being sighted can be difficult to see. However, one has to sweep the celestial object to ensure that the lowest limb of the celestial object touches the horizon.
Whole-horizon sextants use a half-silvered horizon mirror to provide a full view of the horizon. This makes it easy to see when the bottom limb of a celestial object touches the horizon. Since most sights are of the Sun or Moon, and haze is rare without overcast, the low-light advantages of the half-horizon mirror are rarely important in practice.
In both types, larger mirrors give a larger field of view, and thus make it easier to find a celestial object. Modern sextants often have 5 cm or larger mirrors, while 19th-century sextants rarely had a mirror larger than 2.5 cm (one inch). In large part, this is because precision flat mirrors have grown less expensive to manufacture and to silver.
An artificial horizon is useful when the horizon is invisible, as occurs in fog, on moonless nights, in a calm, when sighting through a window or on land surrounded by trees or buildings. There are two common designs of artificial horizon. An artificial horizon can consist simply of a pool of water shielded from the wind, allowing the user to measure the distance between the body and its reflection, and divide by two. Another design allows the mounting of a fluid-filled tube with bubble directly to the sextant.
Most sextants also have filters for use when viewing the Sun and reducing the effects of haze. The filters usually consist of a series of progressively darker glasses that can be used singly or in combination to reduce haze and the Sun's brightness. However, sextants with adjustable polarizing filters have also been manufactured, where the degree of darkness is adjusted by twisting the frame of the filter.
Most sextants mount a 1 or 3-power monocular for viewing. Many users prefer a simple sighting tube, which has a wider, brighter field of view and is easier to use at night. Some navigators mount a light-amplifying monocular to help see the horizon on moonless nights. Others prefer to use a lit artificial horizon.
Professional sextants use a click-stop degree measure and a worm adjustment that reads to a minute, 1/60 of a degree. Most sextants also include a vernier on the worm dial that reads to 0.1 minute. Since 1 minute of error is about a nautical mile, the best possible accuracy of celestial navigation is about 0.1 nautical miles (190 m). At sea, results within several nautical miles, well within visual range, are acceptable. A highly skilled and experienced navigator can determine position to an accuracy of about 0.25-nautical-mile (460 m).[4]
A change in temperature can warp the arc, creating inaccuracies. Many navigators purchase weatherproof cases so that their sextant can be placed outside the cabin to come to equilibrium with outside temperatures. The standard frame designs (see illustration) are supposed to equalise differential angular error from temperature changes. The handle is separated from the arc and frame so that body heat does not warp the frame. Sextants for tropical use are often painted white to reflect sunlight and remain relatively cool. High-precision sextants have an invar (a special low-expansion steel) frame and arc. Some scientific sextants have been constructed of quartz or ceramics with even lower expansions. Many commercial sextants use low-expansion brass or aluminium. Brass is lower-expansion than aluminium, but aluminium sextants are lighter and less tiring to use. Some say they are more accurate because one's hand trembles less. Solid brass frame sextants are less susceptible to wobbling in high winds or when the vessel is working in heavy seas, but as noted are substantially heavier. Sextants with aluminum frames and brass arcs have also been manufactured. Essentially, a sextant is intensely personal to each navigator, and they will choose whichever model has the features which suit them best.
Aircraft sextants are now out of production, but had special features. Most had artificial horizons to permit taking a sight through a flush overhead window. Some also had mechanical averagers to make hundreds of measurements per sight for compensation of random accelerations in the artificial horizon's fluid. Older aircraft sextants had two visual paths, one standard and the other designed for use in open-cockpit aircraft that let one view from directly over the sextant in one's lap. More modern aircraft sextants were periscopic with only a small projection above the fuselage. With these, the navigator pre-computed their sight and then noted the difference in observed versus predicted height of the body to determine their position.
Taking a sight
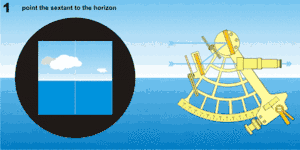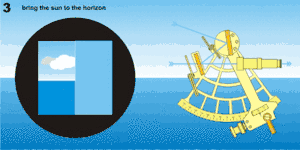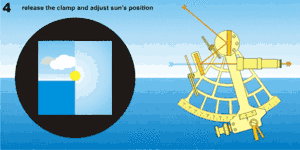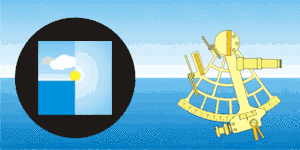
A sight (or measure) of the angle between the Sun, a star, or a planet, and the horizon is done with the 'star telescope' fitted to the sextant using a visible horizon. On a vessel at sea even on misty days a sight may be done from a low height above the water to give a more definite, better horizon. Navigators hold the sextant by its handle in the right hand, avoiding touching the arc with the fingers.[5]
For a Sun sight, a filter is used to overcome the glare such as "shades" covering both index mirror and the horizon mirror designed to prevent eye damage. By setting the index bar to zero, the Sun can be viewed through the telescope. Releasing the index bar (either by releasing a clamping screw, or on modern instruments, using the quick-release button), the image of the Sun can be brought down to about the level of the horizon. It is necessary to flip back the horizon mirror shade to be able to see the horizon, and then the fine adjustment screw on the end of the index bar is turned until the bottom curve (the lower limb) of the Sun just touches the horizon. "Swinging" the sextant about the axis of the telescope ensures that the reading is being taken with the instrument held vertically. The angle of the sight is then read from the scale on the arc, making use of the micrometer or vernier scale provided. The exact time of the sight must also be noted simultaneously, and the height of the eye above sea-level recorded.[5]
An alternative method is to estimate the current altitude (angle) of the Sun from navigation tables, then set the index bar to that angle on the arc, apply suitable shades only to the index mirror, and point the instrument directly at the horizon, sweeping it from side to side until a flash of the Sun's rays are seen in the telescope. Fine adjustments are then made as above. This method is less likely to be successful for sighting stars and planets.[5]
Star and planet sights are normally taken during nautical twilight at dawn or dusk, while both the heavenly bodies and the sea horizon are visible. There is no need to use shades or to distinguish the lower limb as the body appears as a mere point in the telescope. The Moon can be sighted, but it appears to move very fast, appears to have different sizes at different times, and sometimes only the lower or upper limb can be distinguished due to its phase.[5]
After a sight is taken, it is reduced to a position by looking at several mathematical procedures. The simplest sight reduction is to draw the equal-altitude circle of the sighted celestial object on a globe. The intersection of that circle with a dead-reckoning track, or another sighting, gives a more precise location.
Sextants can be used very accurately to measure other visible angles, for example between one heavenly body and another and between landmarks ashore. Used horizontally, a sextant can measure the apparent angle between two landmarks such as a lighthouse and a church spire, which can then be used to find the distance off or out to sea (provided the distance between the two landmarks is known). Used vertically, a measurement of the angle between the lantern of a lighthouse of known height and the sea level at its base can also be used for distance off.[5]
Adjustment
Due to the sensitivity of the instrument it is easy to knock the mirrors out of adjustment. For this reason a sextant should be checked frequently for errors and adjusted accordingly.
There are four errors that can be adjusted by the navigator, and they should be removed in the following order.
- Perpendicularity error
- This is when the index mirror is not perpendicular to the frame of the sextant. To test for this, place the index arm at about 60° on the arc and hold the sextant horizontally with the arc away from you at arm's length and look into the index mirror. The arc of the sextant should appear to continue unbroken into the mirror. If there is an error, then the two views will appear to be broken. Adjust the mirror until the reflection and direct view of the arc appear to be continuous.
- Side error
- This occurs when the horizon glass/mirror is not perpendicular to the plane of the instrument. To test for this, first zero the index arm then observe a star through the sextant. Then rotate the tangent screw back and forth so that the reflected image passes alternately above and below the direct view. If in changing from one position to another, the reflected image passes directly over the unreflected image, no side error exists. If it passes to one side, side error exists. The user can hold the sextant on its side and observe the horizon to check the sextant during the day. If there are two horizons there is side error; adjust the horizon glass/mirror until the stars merge into one image or the horizons are merged into one. Side error is generally inconsequential for observations and can be ignored or reduced to a level that is merely inconvenient.
- Collimation error
- This is when the telescope or monocular is not parallel to the plane of the sextant. To check for this you need to observe two stars 90° or more apart. Bring the two stars into coincidence either to the left or the right of the field of view. Move the sextant slightly so that the stars move to the other side of the field of view. If they separate there is collimation error. As modern sextants rarely use adjustable telescopes, they do not need to be corrected for collimation error.
- Index error
- This occurs when the index and horizon mirrors are not parallel to each other when the index arm is set to zero. To test for index error, zero the index arm and observe the horizon. If the reflected and direct image of the horizon are in line there is no index error. If one is above the other adjust the index mirror until the two horizons merge. This can be done at night with a star or with the Moon.
See also
Notes
- Seddon, J. Carl (June 1968). "Line of Position from a Horizontal Angle". Journal of Navigation. 21 (3): 367–369. doi:10.1017/S0373463300024838. ISSN 1469-7785.
- A.), McPhee, John (John; NSW., Museums and Galleries (2008). Great Collections : treasures from Art Gallery of NSW, Australian Museum, Botanic Gardens Trust, Historic Houses Trust of NSW, Museum of Contemporary Art, Powerhouse Museum, State Library of NSW, State Records NSW. Museums & Galleries NSW. p. 56. ISBN 9780646496030. OCLC 302147838.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - This article treats the doubly reflecting quadrant, not its predecessor described at quadrant.
- Dutton's Navigation and Piloting, 12th edition. G.D. Dunlap and H.H. Shufeldt, eds. Naval Institute Press 1972, ISBN 0-87021-163-3
- Dixon, Conrad (1968). "5. Using the sextant". Basic Astro Navigation. Adlard Coles. ISBN 0-229-11740-6.
References
- Bowditch, Nathaniel (2002). The American Practical Navigator. Bethesda, MD: National Imagery and Mapping Agency. ISBN 0-939837-54-4. Archived from the original on 2007-06-24.
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 24 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 765–767.
- Cutler, Thomas J. (December 2003). Dutton's Nautical Navigation (15th ed.). Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-55750-248-3.
- Department of the Air Force (March 2001). Air Navigation (PDF). Department of the Air Force. Retrieved 2014-12-28.
- Great Britain Ministry of Defence (Navy) (1995). Admiralty Manual of Seamanship. The Stationery Office. ISBN 0-11-772696-6.
- Maloney, Elbert S. (December 2003). Chapman Piloting and Seamanship (64th ed.). New York: Hearst Communications. ISBN 1-58816-089-0.
- Martin, William Robert (1911). . In Chisholm, Hugh (ed.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 19 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 284–298.
External links
- Her Majesty's Nautical Almanac Office Archived 2011-02-21 at the Wayback Machine
- The History of HM Nautical Almanac Office Archived 2016-06-24 at the Wayback Machine
- Chapter 17 from the online edition of Nathaniel Bowditch's American Practical Navigator
- Understand difference in Antique & Replica Sextant Archived 2017-08-17 at the Wayback Machine
- CD-Sextant - Build your own sextant Simple do-it-yourself project.
- Lunars web site. online calculation
- Complete celnav theory book, including Lunars