Wind River Basin
The Wind River Basin or Shoshone Basin is a semi-arid intermontane foreland basin in central Wyoming, United States. It is bounded by Laramide uplifts on all sides. On the west is the Wind River Range and on the North are the Absaroka Range and the Owl Creek Mountains. The Casper Arch separates the Wind River from the Powder River Basin to the east and the Sweetwater Uplift (Granite Range) lies to the south.[1][2] The basin contains a sequence of 10,000–12,000 feet (3,000–3,700 meters) of predominantly marine sediments deposited during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic Eras.[1][2] During the Laramide over 18,000 feet (5,500 meters) of Eocene lacustrine and fluvial sediments were deposited within the basin. Following the Eocene an additional 3,000 feet (910 meters) of sediments were deposited before, and as the basin was uplifted in the late Tertiary.[3][4]
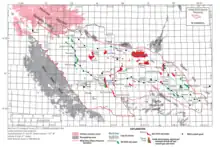
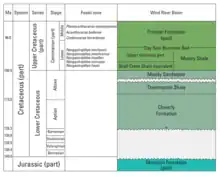
The geological formations within the basin are significant producers of petroleum and natural gas.[1] The basin contains over 60 oil and gas fields mostly as structural traps within seventeen different formations. The primary reservoirs include the Pennsylvanian Tensleep Sandstone, the Permian Phosphoria Formation and the Cretaceous Muddy Creek and Frontier sandstones.[3]
The first oil strike within the basin was from the Dallas dome in the western part of the basin. This discovery in 1884 was the first commercial production in Wyoming.[3]
The Wind River Basin is home to the cities of Riverton and Lander as well as the towns of Shoshoni, Pavilion, and Hudson, the Census Designated Place of Crowheart, and the unincorporated communities of Kinnear, Morton, and Midvale Much of the Wind River Basin is within the boundaries of the Wind River Indian Reservation. The basin is drained primarily by the Wind River and its tributaries.
See also
References
- James E. Fox; Gordon L. Dolton. "Wind River Basin Province (035)" (PDF). United States Geological Survey.
- H. H. R. Sharkey (1956). "Structural Control of Oil Fields in Wind River Basin, Wyoming". AAPG Bulletin. 40 (4): 792. doi:10.1306/5CEAE445-16BB-11D7-8645000102C1865D.
- Geologic Atlas of the Rocky Mountain Region. Rocky Mountain Association of Geologists. 1972. pp. 273–274.
- Thomas M. Finn; Mark J. Pawlewicz (2013). "Maps Showing Thermal Maturity of Upper Cretaceous Marine Shales in the Wind River Basin, Wyoming". Reston, Va.: United States Geological Survey.