Sideroxylon tenax
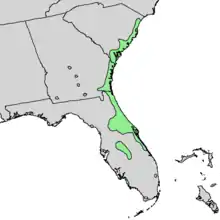
Sideroxylon tenax, called the tough bully,[3] is a plant species native to Florida, Georgia, South Carolina and the southernmost part of North Carolina. It grows on dry, sandy soil in pine forests, pine-oak woodlands, and hummocks at elevations less than 100 m.[4][5]
| Tough bully | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
| Illustration of Sideroxylon tenax with the synonym Bumelia tenax | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Sapotaceae |
| Genus: | Sideroxylon |
| Species: | S. tenax |
| Binomial name | |
| Sideroxylon tenax L. 1767 | |
 | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
Synonymy
| |
Sideroxylon tenax is a shrub or tree up to 8 m (almost 27 feet) tall. Stems are armed with thorns. Leaves are up to 7 cm (2.8 inches) long, upper side green and sometimes shiny, underside covered with a layer of brown hairs. Flowers are white, up to 5 mm (0.2 inches) across, borne in groups of up to 40 flowers. Berries are very dark purple, almost black, spherical to egg-shaped, about 10 mm (0.4 inches) across.[4][6][7][8][9][10][11]
References
- "NatureServe Explorer 2.0 - Sideroxylon tenax, Tough Bumelia". explorer.natureserve.org. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- The Plant List, Sideroxylon tenax
- USDA, NRCS (n.d.). "Sideroxylon tenax". The PLANTS Database (plants.usda.gov). Greensboro, North Carolina: National Plant Data Team. Retrieved 14 November 2015.
- Flora of North America Sideroxylon tenax
- Goldblatt, P. 1991. In M. Johnson, Cytology. Pp. 15--22 in T. D. Pennington, The Genera of Sapotaceae. Kew, Royal Botanic Gardens.
- BONAP (Biota of North America Project) 2014 county distribution map, Sideroxylon tenax
- Rafinesque, Constantine Samuel. 1840. Autikon Botanikon (2): 73.
- Rafinesque, Constantine Samuel. 1838. Sylva Telluriana 35.
- Pennington, T. D. 1990. Sapotaceae. Flora Neotropica 52: 1–771.
- Wunderlin, R. P. 1998. Guide to the Vascular Plants of Florida i–x, 1–806. University Press of Florida, Gainesville.
- Plant Information Center, photos of specimens from University of North Carolina Herbarium, Sideroxylon tenax
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
