Sierra de Ayllón
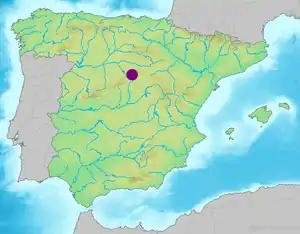
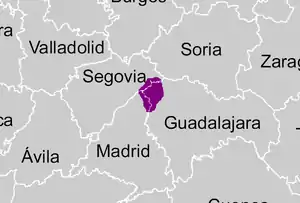
The Sierra de Ayllón (Ayllón mountain chain) or Macizo de Ayllón (Ayllón massif) is a mountain chain of the Iberian Peninsula, belonging to the Sistema Central, of which it constitutes one of its easternmost spurs. It is located between the Spanish provinces of Guadalajara, Segovia and Madrid. The mountain chain consists of a natural area protected within the Natura 2000 network as a Site of Community Importance and Special Protection Area for Birds, located in the northwest of the province of Guadalajara in the autonomous community of Castilla-La Mancha. The natural area of Ayllón occupies the Paleozoic massif of the Sierra de Ayllón, in the province of Guadalajara, including the main core whose highest peak is the Pico del Lobo (2269 m), and the Sierras de la Concha (1865 m), Pico Ocejón (2048 m) and Alto Rey (1852 m).
| Sierra de Ayllón | |
|---|---|
 Main ridge of the Sierra de Ayllón from the Tejera Negra beech forest. | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 2272m MSL |
| Coordinates | 41°10′0.12″N 3°25′59.99″W |
| Dimensions | |
| Length | 46 km N–S |
| Width | 37 km W-E |
| Area | 1200 km² approximately |
| Geography | |
 Sierra de Ayllón Location in Spain | |
| Country | Spain |
| Division | Province of Guadalajara, Community of Madrid, Province of Segovia |
| Main rivers | Berbellido, Duratón, Jarama, Jaramillo and Sorbe |
| Peaks | Lobo, Cebollera Vieja, Ocejón, Buitrera and Santuy |
| Passes | El Cardoso, La Hiruela, La Quesera and Somosierra |
| Parent range | Sistema Central |
The Sierra de Ayllón is the eastern end of the Sistema Central, where the bioclimatic level is dominant. Supramediterranean, with notable representations of the oromediterranean level and occasional areas of the cryo-Mediterranean. The massif was raised during the alpine orogeny, having a very broken relief, with steep slopes and a complicated and dense hydrographic system. It borders to the west with the Sierra de Somosierra and the Sierra del Rincón, to the east with the Sierra de Pela and Alto Rey mountain, to the north with the Meseta Norte and to the south with the Campiña de Guadalajara.
From its mountains rise the Jarama and Sorbe rivers, as well as other minor rivers such as the Jaramilla river, Berbellido river, Sonsaz river or del Ermito river. In its valleys grow the southernmost beech forests in Europe —Tejera Negra, La Pedrosa and Montejo beech forests—, without missing in its flora the holm oak, oak and Scotch pine. Among its fauna are wolves, vultures and small mammals. The part of the mountain chain in the province of Guadalajara is located within the Sierra Norte de Guadalajara Natural Park[1] and the Sonsaz Hunting Reserve extends over a large part of its territory.[2]
Geology and lithology
The outcropping materials are mainly slate and quartzites of the Ordovician and Silurian periods, with outcrops in some areas (El Cardoso, Hiendelaencina, etc.) of Precambrians gneiss. The natural area of Ayllón extends towards the south following the valleys of the main rivers (Lozoya, Jarama, Sorbe, Bornova, Cristóbal), in whose canyons habitats and communities of great ecological value are located. There are also periglacial reliefs (quartzite cliffs) and remains of glacial activity in the vicinity of Pico del Lobo.[3]
Geological evolution
| Location Map |
|---|
 |
 |
The geological evolution of the mountain chain is marked by two major foldings: on the one hand, the Hercynian orogeny, towards the Silurian period, when mountain ranges are formed throughout western Europe by huge magmatic masses that give rise mainly to granitic rocks, gneisses and slate, and the erosion of seawater that by then occupied a large part of the Iberian Peninsula; on the other hand, the alpine orogeny from the Cenozoic Era that raised again the mountain ranges of the Sistema Central and when the current hydrographic system was established, forming the valleys and the silhouettes of the mountains. The last glaciation partly affected the Macizo de Ayllón forming some glacial cirques such as those found at the source of the Berbellido river, next to the Pico del Lobo, and at the Peña Cebollera Vieja.
Lithological zones
The Sierra de Ayllón is divided into three main lithological zones depending on the type of rock that predominates in each one:
Granitic zones
From west to east, from Puerto de Somosierra to El Cervunal, and from north to south, from Riaza to Puerto del Cardoso, following the right bank of the Ermito river, granite abounds among the rocks that form the mountains of this area of the Sierra de Ayllón.
Gneissic zones
The gneiss is, however, the least widespread of the three predominant rocks in the Sierra de Ayllón. It forms mainly in the area of El Cardoso de la Sierra to the south until the Jarama river acts as a natural boundary between the Sierra de Ayllón and the Campiña.
Slate zones
The slate is the most common rock seen in the Macizo de Ayllón, as well as being the one typically used in the constructions of the villages in the area. Likewise, the slate areas can be classified according to the type of slate that gives shape:
- The clayey slate extends in several mountain ridges: from El Cardoso de la Sierra towards Pico del Lobo, and from there towards Puerto de la Quesera.
- The dark slate is typical of the northern slope of the massif corresponding to the provinces of Segovia and Soria, from Pico de la Buitrera to Grado del Pico. Many of these areas are mixed with sandstones and agglomerates from the Triassic and Neogene periods. It also covers a wider area from the Sonsaz River to the south.
Orography and relief
There are three relief units that form the Macizo de Ayllón: the peneplain, areas of undulating surface located at the ends of the massif, mainly to the north and south; the valleys, short in the north and very long and narrow in the south, leaving little room for meadows, and the mountain range itself. The mountain chain is distributed in a main ridge, which runs from west to east to the north of the mountain chain, and three secondary ridges, which leave the main one from north to south.

- The main ridge runs along the north of the mountain chain from west to east, from Peña Cebollera, through Cervunal, Pico del Lobo, Puerto de la Quesera, Peña de la Quesera, Peña de la Silla, Parrejón and Pico de la Buitrera, until, losing a lot of altitude, it joins the Sierra de Pela between Grado del Pico and Villacadima.
- The Cebollera ridge is the most westerly, nestling between the Madarquillos and the Jarama rivers. It starts in the Cebollera Vieja towards the Cabeza del Tempraneigo and divides in two descending towards the south through Cuchar Quemado, Alto de la Fuente de Cabezuelas, Cebollera Nueva, Cerro de la Porrilla and Alto de la Dehesa de Horcajuelo up to Peña la Sisa and Pico de la Dehesilla, in the area of Horcajo, Horcajuelo and Montejo, on one side, and Collado de las Nieves, Cerro de Recuenco, Sierra de Escalba, Puerto del Cardoso, Pico de las Bañaderas, Puerto de la Hiruela and Alto del Porrejón, on the other hand.
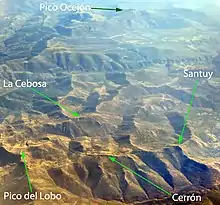 Aerial view of part of the Sierra de Ayllón
Aerial view of part of the Sierra de Ayllón - The central mountain ridges are divided by the Jarama river to the north between it and the Jaramilla river and to the south between the Jarama and the Lozoya river. They are mountains, in general, of lower altitude. They are composed by several hills:
- One runs from the Cevurnal towards Majada de los Carneros, Cabeza Pinillo, Cerrón and Santuy to the banks of the Berbellido river.
- Another, from Las Peñuelas down through La Cebosa and Pico del Águila, Morra del Segoviano, Cabeza Grande, Cerrajo and Cerro de Corralejo to the mouth of the Jaramilla river in the Jarama.
- To the south are the lower elevations, distributed anarchically, such as Cerro San Cristóbal, Pico de la Tornera, Pico de la Centenera, Cabezas and Palancar.
- The eastern ridge is the most important of the secondary ridges. Although only Pico de Ocejón exceeds 2000m of altitude, most of its mountains rise around 1700m and 1900m. There are several hills that also form this ridge:
- The main hill is the one that forms the Sierra del Ocejón. From Pico del Granero, Tiñosa, Corralón and Atalaya it extends between the rivers Jaramilla and Sonsaz to the south by Cabezo de San Pedro, Regajo de las Yeguas, Cerrito Collado, Campachuelo, Campo and Pico de Ocejón.
- The Loma de Pinarejo from Atalaya to the southeast through the Cabeza Arca and Pinarejo to the banks of the Sorbe. Other smaller hills, such as Las Llanadas and Bubillejo, arise from this area.
- The Loma de la Torrecilla is the center of the Tejera Negra beech forest, forming the right bank of the Lillas river. From Cervunalillo through Alto de la Escaleruela and Alto del Hornillo to where the Sorbe takes its name.
The "two-thousands" of the Sierra de Ayllón
In the heart of the Sierra de Ayllón rise the last peaks of more than 2000 meters of the Sistema Central.[4]
| Mountain | Subsidiary of | Height | Ridge | Province | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pico del Lobo | — | 2272 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°11′3″N 3°27′54″W |
| Alto de las Mesas | Pico del Lobo | 2257 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°11′10″N 3°27′53″W |
| Buitrera de los Lobos, S peak | Pico del Lobo | 2221 m | Main | Guadalajara | 41°10′41″N 3°27′50″W |
| Buitrera de los Lobos, S-SE peak | Pico del Lobo | 2215 m | Main | Guadalajara | 41°10′51″N 3°27′48″W |
| Las Pañuelas, central peak | — | 2211 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°11′31″N 3°27′47″W |
| Las Pañuelas, W peak | Las Pañuelas, main peak | 2204 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°11′19″N 3°27′59″W |
| Cerrón | — | 2197 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°9′17″N 3°28′22″W |
| Las Pañuelas, E peak | Las Pañuelas, main peak | 2194 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°11′30″N 3°27′39″W |
| El Cervunal | Pico del Lobo | 2194 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°10′52″N 3°28′48″W |
| Peña Cebollera Vieja or Tres Provincias | — | 2129 m | Main | Guadalajara, Segovia and Madrid | 41°9′58″N 3°32′18″W |
| Peña de los Abantos | Cebollera Vieja | 2124 m | Cebollera | Guadalajara and Madrid | 41°9′53″N 3°32′18″W |
| Cerro de la Majada de los Carneros | — | 2078 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°10′13″N 3°28′42″W |
| Cabeza del Tempraniego or La Pedriza | — | 2071 m | Cebollera | Guadalajara and Madrid | 41°9′23″N 3°32′10″W |
| Peñon de Matarredonda | Cerrón | 2065 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°9′13″N 3°27′55″W |
| Loma de Cabeza Pinillo | — | 2061 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°9′41″N 3°27′46″W |
| El Rocín | La Cebosa | 2051 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°9′41″N 3°26′18″W |
| Pico Ocejón | — | 2049 m | Eastern | Guadalajara | 41°6′20″N 3°15′15″W |
| La Cebosa | — | 2048 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°9′35″N 3°26′17″W |
| Coto de Montejo, El Corco or Cuchar Quemado | — | 2047 m | Cebollera | Madrid | 41°8′23″N 3°32′48″W |
| Cerro del Picaño | — | 2046 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°8′30″N 3°27′26″W |
| Pico de la Buitriera | — | 2038 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°15′13″N 3°23′55″W |
| Cerro del Picaño, W peak | Cerro del Picaño, central peak | 2033 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°8′30″N 3°27′55″W |
| Loma de Cabeza Pinillo, E peak | Loma del Picaño, central peak | 2032 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°9′42″N 3°27′36″W |
| Cerro de Mesa Peñota | Pico de la Buitrera | 2026 m | Central | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°15′31.6″N 3°24′4.72″W |
| Alto del Cervunalillo | — | 2018 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°14′44″N 3°23′53″W |
| Alto del Parrejón | — | 2017 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°14′20″N 3°24′12″W |
| Cerro Ortigosa | Cerro del Picaño y Cerrón | 2011 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°9′38″N 3°28′7″W |
| Cerro del Picaño, SE peak | Cerro Picaño, central peak | 2008 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°8′13″N 3°27′10″W |
| Cerro del Aventurero | Las Pañuelas, central peak | 2003 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°12′11″N 3°27′10″W |
Other outstanding peaks
| Mountain | Height | Ridge | Province | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peña de la Tiñosa or Pico del Granero | 1971 m | Main | Guadalajara | 41°13′1″N 3°23′39″W |
| Peña de la Silla | 1937 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°12′53″N 3°24′2″W |
| Satuy or Cerro de la Calahorra | 1927 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°7′24″N 3°28′2″W |
| Campo | 1919 m | Eastern | Guadalajara | 41°8′45″N 3°16′43″W |
| Campachuelo | 1899 m | Eastern | Guadalajara | 41°8′17″N 3°16′43″W |
| Atalaya | 1884 m | Eastern | Guadalajara | 41°11′53″N 3°24′50″W |
| Pico de la Tornera | 1865 m | Central | Guadalajara and Madrid | 41°1′11″N 3°24′43″W |
| Cebollera Nueva | 1834 m | Cebollera | Madrid | 41°6′53″N 3°33′54″W |
| Peña de la Cabra | 1831 m | Central | Madrid | 41°0′43″N 3°28′49″W |
| Pico de la Centenera | 1809 m | Central | Guadalajara and Madrid | 41°0′1″N 3°23′44″W |
| Valdebecerril | 1766 m | Main | Guadalajara and Segovia | 41°15′25″N 3°20′44″W |
| Majada de la Sierra | 1695 m | Main | Guadalajara | 41°15′5″N 3°17′14″W |
| Loma del Pinarejo | 1694 m | Eastern | Guadalajara | 41°10′21″N 3°15′34″W |
| Pico del Águila | 1650 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°9′38″N 3°22′50″W |
| Cabeza de Cabida | 1597 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°7′10″N 3°22′35″W |
| Cerro San Cristóbal | 1588 m | Central | Guadalajara | 41°3′21″N 3°22′23″W |
| Alto de las Cabras | 1543 m | Eastern | Guadalajara | 41°11′42″N 3°14′46″W |
| Cabeza de Ranas | 1492 m | Eastern | Guadalajara | 41°6′15″N 3°20′9″W |
| Cabezas | 1437 m | Central | Guadalajara | 40°59′32″N 3°20′2″W |
Climate
The mountain climate of the Sierra de Ayllón is marked by two fundamental factors: on the one hand, the latitude, marking the Mediterranean character with hot summers and low rainfall; on the other hand, the orientation of the massif causes the interception of the low-pressure areas of Atlantic origin bringing with it a greater rainfall on the northern slopes than in the south. This second factor, together with the fact that the northern slopes receive less sunlight and, therefore, maintain a lower temperature, leads to a greater accumulation of snow in winter on the northern slopes than on the southern slopes.

The heaviest rainfall occurs in winter, usually in the form of snow, coinciding with the summer, a long dry season. The average annual rainfall is between 800 and 1000 mm.
The coldest months correspond to the central months of winter, December and January, and when periods in which cold waves of Central Europe that cause heavy snowfall to relatively low altitudes are approaching. The average minimum temperature reached in winter is around 2 °C or 3 °C in the valleys; the average maximum temperature is reached in the months of July and August around 15 °C. The thermal amplitude in autumn and spring periods can be very wide, with pleasant days and extremely cold nights in some cases, becoming more severe in the valley bottoms. The number of days with frost varies between 50 and 150 depending on the southern or northern slope.[5]
Hydrography
From the Sierra of Ayllón waters flow into two large basins: the Douro Basin, to the north, and the Tagus Basin, to the south.
Douro Basin
It is the last foothills of the mountain chain which pours water to the northern slope. The rivers and streams pour their waters directly from the mountain to the valley, so they are generally short and not very abundant. Two rivers stand out above the rest, the Duratón river and the Riaza river, both of which flow into the Douro river after a long journey. They are exceptions. The rest of the fluvial currents pour their waters into these two main rivers.
Duratón River
Although it does not begin to take shape until it joins the rivers Caslilla and de la Hoz at Sepúlveda, the Duratón river, which rises on the southern slopes on the Madrid side of the Cebollera Vieja, receives water on its right bank from small streams that originate in the Sierra de Ayllón. From the northern slope of the Cebollera Vieja, it receives water from two streams that usually dry up in summer in most of its sections, the Cerezuelo river and the Serrano river, both of which rise on the slopes of the Pico del Lobo.
Riaza River
The Riaza river rises near Puerto de la Quesera and receives water from the Sierra de Ayllón, mainly on its right bank. Its tributaries are longer, although equally of little flow. The Aguisejo river, which rises near Villacadima and in turn receives water from other smaller streams including the Arroyo de Vadillo, which after rising in the Pedrosa beech forest under the Mesa Peñota, flows into the left bank of the Aguisejo river, and the Cobos river, which has its source in the Majada de la Sierra, one of the last northern foothills of the Macizo de Ayllón.
Thus, the Duratón river and the Aguisejo river border the Macizo de Ayllón from west to east in the north.
Tagus Basin
The southern slope of the Sierra de Ayllón, which flows into the Tagus Basin, originates in the northern foothills of the massif. It is much more complicated than the northern slope and the rivers and streams, much longer, run tortuously squeezed between mountains, giving rise to ravines and gorges, until they flow into the two main rivers in the area: the Jarama and the Sorbe.
Jarama River
It rises at the foot of the Cebollera Vieja and receives its major tributaries on its left bank, extending its basin from the Loma de la Cebollera to the Sierra del Ocejón. Many of them, including the Jarama itself, erode the rock to create deep ravines, making some of them suitable for the construction of dams such as the El Vado reservoir or the planned but not begun Matallana reservoir. The main tributaries of the Jarama through the Sierra de Ayllón are the Ermito river, which has its source under the Cervunal; the Berbellido river, which rises in Pico del Lobo and passes through Bocígano; the Jaramilla river, which after rising under Puerto de la Quesera leaves a deep and beautiful gorge to its mouth; the Arroyo de Vallosera, which rises in Pico de la Tornera and after cutting through a gorge in the area of La Vereda flows into the El Vado reservoir, next to the ruins of El Vado, and Arroyo del Soto, union of several minor streams that flow down from Ocejón and leave between it and Cabeza de Ranas a valley where Majaelrayo, Robleluengo, Campillo, El Espinar and Roblelacasa are located.
Sorbe River

The Sorbe River is the natural boundary between the Sierra de Ayllón, on its right bank, and the Sierra de Alto Rey, on its left bank. It is the result of the union of two minor rivers in the area known as Junta de los ríos, between ravines on the slopes of Alto de las Cabras and Peña del Osar, on the Alto Rey side, and Peña de Pinarejo, on the Ayllón side. From the Sierra de Pela, to the north, with springs between Ribalópez and El Portillo, Arroyo de la Dehesa or Sorbe de Galve river, which leaves a wide valley where Cantalojas and Galve de Sorbe settle. From the Tejera Negra beech forest, to the west, flows the Lillas river, which rises under Pico de la Buitrera and which in turn receives water from another tributary with year-round flow, the Zarza river or Arroyo de la Hoz, which also crosses Tejera Negra after rising under Alto del Parrejón. After joining the two rivers, the Sorbe, a river with a considerable flow in rainy and thawing periods, flows through deep cliffs to the Beleña reservoir, leaving the Pozo de los Ramos dam between the mountains. The Sorbe flows between Alarilla and Humanes, under the Muela de Alarilla, in the Henares river.
Together with the Lillas and the Arroyo de la Dehesa, the Sorbe receives water from the Sierra de Ayllón from three other tributaries with permanent flow, which also follow winding paths and leave deep cuts in their courses. Further north, the Sonsaz river, which gives its name to the extensive hunting reserve that encompasses a large part of the valleys and mountains of the Sierra de Ayllón. It rises under the Atalaya and follows a winding path between mountains until it flows into the Sorbe river between Peña del Pinarejo and the Loma de las Piquerinas. To the north of the Ocejón rises the Arroyo de la Chorrera, which passes through Valverde and leaves the Chorreras de Despeñalagua on its way before flowing into the river. And under the southern slope of the Ocejón the Seco river or Barranco del Covachón, which passes through Palancares.
Fauna
Hunting has been incessant in the Sierra de Ayllón since ancient times, which has caused the disappearance of several species in the area such as the bear, which was probably present until the 18th century, or the wolf, which was present until the 1960s, and which seems to be present again in the massif in the 2000s.[6] Today the National Hunting Reserve of Sonsaz, which extends its 68,106ha over a large part of the mountain chain, and the beech forests de Tejera Negra and Montejo are the perfect refuge for the wild fauna of the area. Depending on the location in the massif, different animal species can be found:
- In the riverbank areas amphibians and insects abound everywhere and with them small birds such as the white-throated dipper, the nightingale and the kingfisher. If the river flow is constant, otters can be observed.
- Among holm oaks and junipers the rabbit stands out, prey for several bird of prey. Other birds such as hoopoes, woodpigeons, partridges and magpies can also be found in these areas.
- In the mid-mountains between oaks and pines there are abundant birds such as the fringilla, the great tit, the blue tit, the firecrest, the great spotted woodpecker and the jay. Also for mammals such as roe deers, wild boars and foxes, which are also adapted to other areas of the mountain chain. The mid-mountains are also favourable for nocturnal animals such as wildcats, badgers and beech martens and birds such as earless owls, scops owls and eagle owls.
- In the higher areas there are red-billed choughs, ravens, wheatears, accentors and rock thrushes, as well as griffon vultures and golden eagles[7] in the rockier areas.
Among the insects it is worth mentioning the great diversity that exists in the Macizo de Ayllón. Numerous species of lepidoptera, coleoptera, hymenoptera and diptera can be observed throughout the mountain chain, some of them autochthonous and exclusive to the area.
The humid forests of the mountain chain also provide habitat for nemoral species such as the woodcock (Scolopax rusticola), a scarce nester, wintering and regular migrant, the barbastelle bat (Barbastella barbastellus), the also nesting tree pipit (Anthus trivialis), the song thrush (Turdus philomelos)and the red-backed shrike (Lanius collurio), with breeding areas further north.
The hydrographic system in the mountain chain has a high degree of conservation until the arrival of the rivers to the line of regulating reservoirs located south of the natural area, (Pontón de la Oliva, Vado reservoir, Beleña reservoir, Alcorlo reservoir). The absence of polluting industries and the reduced human population (<2 people per /km²) guarantee the absence of water pollution. Thus, the rivers of this area represent an unbeatable habitat for the European otter, with abundant populations. Native fish such as the iberian nase (Chondrostoma polylepis), the bermejuela (Rutilus arcasii) and the colmilleja (Cobitis paludica and Cobitis pyrenaicus). Birds such as the kingfisher (Alcedo atthis) and mammals such as the desman (Galemys pyrenaicus), which maintains here isolated populations of the main core distribution of the species in the Sistema Central, very vulnerable to external disturbances and probably threatened by the proliferation of the American mink.
The frequent cliffs and crags form a habitat of exceptional importance for a wide range of rupicolous birds. The natural area of Ayllón exceeds the numerical criteria established in the EU Birds Directive for the golden eagle, (Aquila chrysaetos), griffon vulture (Gyps fulvus), peregrine falcon (Falco peregrinus) and eagle-owl (Bubo bubo), being also abundant the red-billed chough (Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax). Other species of great interest such as Bonelli's eagle (Hieraaetus fasciatus), Egyptian vulture (Neophron percnopterus) the common rock trush and the blue rock thrush (Monticola saxatilis and Monticola solitarius) use the Sierra de Ayllón as a breeding area.
The importance of the natural area of Ayllón for some rare or endemic invertebrate species, such is the case of Lucanus cervus, Parnassius apollo sp. escalerae, Plebicula nivescens, Ocnogyna tatreillei, Hyphoraia dejeani, Euphydryas aurinia or Nymphalis antiopa, should be highlighted.
Vegetation
.jpg.webp)
The Sierra of Ayllón is included in the Carpetano-Ibérico-Leonesa[8][9] chorological province, in the Guadarrámic sector, forming the Ayllonan subsector with its own chorological identity, the most mature arboreal vegetation corresponds in most of the supramediterranean territory to Pyrenean oak groves, reserving the holm oak groves to the basal areas, sloping sills and the steep slopes of the fluvial gorges. The Pyrenean oak grove has been intensively exploited as a source of firewood by man until a few decades ago, so many of its masses have the appearance of small or medium-sized groves in recovery, although extensive mature Pyrenean oak groves are preserved (El Cardoso). If the conditions are more humid, humid Pyrenean oak groves or beech forests appear, of relict presence in Ayllón (Tejera Negra), with interesting enclaves of yews, holly, rowan or climatic birch trees. Under oromediterranean or more continental conditions, climax pine forests of Scotchs pine (Coeno-Pinetum sylvestris) appear, as occurs on the northern slopes of the Sierra de Alto Rey and Condemios.
The most widespread vegetation in this mountain chain is scrub, due to the effects of human occupation (grazing and firewood cutting). Depending on the ecological conditions, the landscape is dominated by heaths in the more humid and elevated areas and by rockrose in the drier and basal areas. There are many types of vegetation that can be found in the Sierra de Ayllón, although the forests are not very extensive due to the incessant hand of man who for centuries has been obtaining firewood and charcoal and has been opening pastures for livestock, mostly transhumant.
Different vegetation can be found established in three bioclimatic levels: one mesomediterranean below 1000m and dominated by holm oak; another supramediterranean between 1000m and 2000m where oaks and, depending on the area, beeches predominate, and another oromediterranean above 2000m mainly covered by cytisus, Cornish heath, rockrose, steppes and junipers. The peaks of the Sierra de Ayllón are located in the bioclimatic levels gold[10] and cryo-Mediterranean,[11] with communities characteristic of these high altitudes, very rich in endemic species.[12] Thus, there are psicroxerophilous grasslands at the highest altitudes (Hieracio myriadeni-Festucetum indigestae), cytisus (Senecioni carpetani-Cytisetum oromediterranei), chionophilous cervunales (Campanula herminii-Festucetum ibericae), hygrophilous oromediterranean cervunales (Luzulo carpetanae-Pedicularietum sylvaticae, Campanulo herminii-Festucetum rivularis), rupicolous communities (Saxifragetum willkommianae) and oromediterranean glericolous (Digitali carpetanae-Senecionetum carpetani, Rumicetum suffruticosi, Criptogrammo crispae-Dryopteridetum oreadis).
The northern slopes, enjoying more rainfall, show a greater extension of oak and beech forests, while the southern slopes are mostly covered with holm oak forests. At the same time, during the second half of the 20th century, numerous reforestations have been carried out, more or less successful in the landscape, with Scotch pines and bog pines. Therefore, oak, beech, birch, pine and, to a lesser extent, holm oak and arar, are the most frequently found trees in the massif. The basic lithologys outcrop in certain enclaves to the south of the mountain chain, along a Mesozoic outcrop that borders the mountain chain. In the area where the Jarama river crosses this outcrop there is a well-developed limestone sickle, with isolated basophilic rufic communities, accompanied by a magnificent Portuguese oaks forest with maples (Cephalanthero rubrae-Quercetum faginae), which in the wetter area transforms into avellanae (Geo urbani-Coryletum avellanae). The fluvial gallery vegetation is well represented in its supramediterranean siliceous variants. Of special interest are the alder groves (Galio broteriani-Alnetum glutinoseae), of great extension and an excellent degree of conservation in the rivers Jarama, Sorbe and Bornoba, this type of habitat is in increasing expansion, due to the abandonment of traditional activities.
Oak

In the domain of humid beech and Pyrenean oak forests there are heaths (Erico arboreae-Arctostaphylletum crassifoliae, Halimio ocymoidis-Ericetum aragonensis, Junipero nanae-Vaccinietum myrtilli), of great importance because they are very scarce in the rest of the Sistema Central. These heaths are a refuge for numerous plant species of Atlantic habit (Genistella tridentata, Genista pilosa, Avenula sulcata, etc.). They are also accompanied by Portuguese brooms (Genisto floridae-Cytisetum scoparii, Genisto floridae-Adenocarpetum hispanici, Genisto cineracestis-Cytisetum oromediterranei), communities of Carpathian-Iberian-Leonian optima, which are here at the extreme end of their distribution area.
In spite of the great exploitation that the oak forests have suffered in the Sierra de Ayllón for their timber value, the extension of pastures and charcoal production, the oak is still the most widespread tree in the massif. Two types of oaks are found in the area:
- The marcescence Pyrenean oak, that which keeps its leaf dry on the branches during the winter, and which extends, above all, along the entire northern slope of the mountain chain and the area marked by the Berbellido and Jarama rivers.
- The deciduous sessile oak, scarce in the area, although some specimens can be seen in the Montejo beech forest.
The Pyrenean oak groves of the Sierra de Ayllón, (Festuco heterophyllae-Quercetum pyrenaicae and Luzulo forsteri-Quercetum pyrenaicae), are the most extensive and representative of Castilla-La Mancha, presenting as characteristic cortege Arenaria montana, Luzula forsteri, Viola riviniana, Poa nemoralia, Primula veris, Viola sylvatica, Holcus molli, Conopodium bourgaei, etc.. The abandonment of charcoal production and the great reduction in the use of firewood outlines an optimistic future for the natural recovery of the Pyrenean oak grove in this mountain chain.
Beechwoods

The rest of the Sierra de Ayllón is included in the supramediterranean bioclimatic level,[13] an area where the most extensive of the three relict beech forests of the Sistema Central (Tejera Negra beech forest) is located, which today is a natural park. Within it, the beech forests (Galio rotundifolii-Fagetum), in remarkable regeneration after the declaration of protected area and the suppression of the exploitation of beech, and the birches (Melico-Betuletum celtibericae), also relict, which occupy the bottoms of the ravines and watercourses with high edaphic humidity. These forests, together with the humid Pyrenean oak groves (Festuco heterophyllae-Quercetum pyrenaicae), constitute important refuges of Eurosiberian plant species absent in other areas of the Meseta.
Although the beech[14] is not the most widespread tree in the Macizo de Ayllón, the beech forests in the area do represent the unique fact of being among the southernmost in Europe, which has led to their protection. The beech forests of the area are grouped in three sketches:
- The Montejo beech forest, with 250ha, is located on the right bank of the Jarama, in the province of Madrid, and some specimens of beech trees surrounded by oaks are preserved, yews, ash, holly, sorbus, birch and European crab apple trees.
- The Pedrosa beech forest, the smallest of the three with 87ha, is in the surroundings of Puerto de la Quesera on the province of Segovia side and is formed by middle-aged beech trees.
- The Tejera Negra beech forest extends its 1391ha under the hill formed between Pico de la Buitrera and the Parrejón, at the headwaters of the rivers Lillas and Zarza river, in the province of Guadalajara. It is formed by young beech trees because the forest was largely cut down in the 1960s, being difficult to find any centenary specimen. In any case, it has recovered quite well and is gaining extension and ground to the repopulation of Scotch pine.
Birch
The birch has a certainly small presence in the Sierra de Ayllón. Because of its resistance to cold and because it can grow in poor soils it can be found in the high areas of some rivers. The birch tree of Somosierra is a good example.[15]
Pine
The extension of pine in the area corresponds mainly to reforestation policies in the second half of the 20th century due to its rapid growth, the high value of its wood and its great geological amplitude. There are three types of pine trees that repopulate the mountain chain: Scotch pine mainly, and then bog pine and Austrian pine. The autumn humidity also favors the proliferation of a large number of fungi in the pine forests, with the milk-caps standing out above all others.
Holm oak and juniper
The holm oak groves occupy the sunny areas of the valleys, highlighting the examples of Tamajón, Valverde and Umbralejo. Also noteworthy is the isolated presence of a juniper in Tamajón, which occupies both Cretaceous dolomites and silurian slates, a very singular fact given the ecology of Juniperus thurifera. On the dolomites of Tamajón there is a very well developed limestone pavement, with forms reminiscent of the Ciudad Encantada and accompanied by calcareous rupicolous communities (Chaenorhino-Sarcocapnetum) and terophytic communities (Saxifrago tridactylitae-Hornungietum petrae). The juniper, despite being a Mediterranean tree, adapts to continental climatic conditions. In the surroundings of Tamajón and Galve de Sorbe there are also good examples of juniper groves.
Shrubland and pastures
The degradation of the forests, the abandoned crops and the forest fires that occurred over time favored the extension of scrubes and pastures, good for livestock feeding. Depending on the altitude and exposure of the slope can be found cytisus, juniper, Cornish heath, codesos, hiniestas or rockroses.
Population
It reaches a total extension of 94.686,40 ha distributed in 819,14 ha in Albendiego, 447,76 ha in Arbancón, 1.316,06 ha in Bustares, 9.063,91 ha in Campillo de Ranas, 11.707,33 ha in Cantalojas, 18.468,44 ha in El Cardoso de la Sierra, 1.060,58 ha in Cogolludo, 467,59 ha in Condemios de Abajo, 3.516,27 ha in Galve de Sorbe, 1.899,43 ha in Gascueña de Bornova, 453,93 ha in Hiendelaencina, 3.046,31 ha in La Huerce, 5.505,19 ha in Majaelrayo, 154,82 ha in Miedes de Atienza, 88,10 ha in La Miñosa, 374,68 ha in Las Navas de Jadraque, 1.865,70 ha in El Ordial, 2.709,10 ha in Prádena de Atienza, 44,28 ha in Puebla de Valles, 736,89 ha in Retiendas, 8.763,26 ha in Tamajón, 38,41 ha in La Toba, 3.198,04 ha in Tortuero, 206,02 ha in Ujados, 2.060,02 ai n Valdepeñas de la Sierra, 1.916,45 ha in Valdesotos, 4.531,46 ha in Valverde de los Arroyos, 870,99 ha in Villares de Jadraque, 510,29 ha in Zarzuela de Jadraque and 1.516,87 ha in Semillas.
Population history
As indicated above, the mountains of the Sierra de Ayllón have been populated since ancient times. Arevaci to the east, Vaccaei to the north and Carpetani to the south, followed by Celts and Celtiberians populated the valleys of the mountain chain attracted by the hunting and livestock possibilities as well as by the isolation provided by its mountains allowing them a better survival before the neighboring peoples.[16]
From the 3rd or 2nd century B.C. the Romans remained in the area. The crisis of the Empire in the 3rd century provokes that the population of the area is concentrated in the big latifundia villas located in the areas of Riaza, Atienza and Cogolludo in regime of autarchy. However, the settlers of the Macizo de Ayllón, due to the isolation of the area, practically continued with their unchanged life. The settlement of the Visigoths in the 6th century in the Iberian Peninsula, who continued with the feudal structures of the Later Roman Empire, would not affect the way of life or the population settlement in the Sierra de Ayllón, remaining so until the arrival of the Muslims to the Iberian Peninsula in the 8th century.
During the first centuries of Muslim rule, the pastoral and livestock practices of the area were maintained until the 11th century, when the Christian conquest arrived in the Sistema Central, making the Sierra de Ayllón a frontier between the Christian kingdom of Castile to the north and the Muslim Taifa of Toledo to the south. This fact leads to an increasing instability in the whole Sistema Central which causes the depopulation of the area and the emigration of the population to the Meseta Norte and Meseta Sur of the mountains of Ayllón.
With the conquest in 1085 by Alfonso VI of what from then on would be called Extremadura Castellana and the consequent transfer of the fighting frontier to the banks of the Tagus river, the valleys of the Macizo de Ayllón would be repopulated from then until the end of the 13th century with Castilians, Leonese and Galicians, with people who were once again cattle breeders. Many of the old tainas were reconverted into small villages with a permanent population that maintained the ways of life of before the depopulation. Monastic repopulation was granted by Alfonso VIII in 1164 and was carried out by the Knights Templar of the houses of Albendiego and Bonaval, who founded small monasteries such as Royal Site of Santuy.
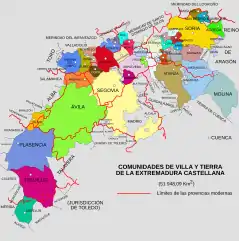
The creation in 1214 of a convent and a factory in Ayllón by Francis of Assisi would give jurisdiction to the town and grant it as Común de Tierra what today is known as Tierras de Ayllón, hence the name given to the entire mountain chain that concerns us because a large part of it belongs to the Comunidad de Villa y Tierra de Ayllón. Thus, with the creation of the Comunidades de Villa y Tierra the different towns that flourished again in the Sierra de Ayllón were divided into several of these: El Cardoso de la Sierra, Colmenar de la Sierra, El Vado, the area of the Cebollera Vieja and Cebollera Nueva, Somosierra, Santo Tomé del Puerto, Cerezos de Abajo and Cerezos de Arriba came under the jurisdiction of the Común de Villa y Tierra de Sepúlveda, which passed during the 14th century in good part to the Mendoza family, within the Marquisate of Montesclaros since the 15th century, from which fact still remains a House between El Cardoso and Colmenar; the area between the Sierra del Ocejón and the rivers Jaramilla and Berbedillo reaching south to Almiruete were included within the Común de Villa y Tierra de Ayllón, in the hands of the Marquis of Villena; Riofrío and Hontanares under the jurisdiction of the Comunidad de Cilla y Tierra de Fresno de Cantespino; from the Sierra del Ocejón and the Sorbe river eastward, including the term of Valverde de los Arroyos, is under the jurisdiction of the Común de Villa y Tierra de Atienza, and later, towards the 14th century, would be included in the newly created County of Galve, in the hands of the Zúñiga and, later, of the Mendoza and the dukes of Alba; the south of the massif in the districts of Valdepeñas, Tortuero and Valdesotos came under the jurisdiction of the Común de Villa y Tierra de Uceda, controlled since 1249 by Sancho of Castile, archbishop of Toledo and son of king Ferdinand III; Tamajón would remain as a land of Royal manor forming its own jurisdiction.
Under this seignorial organization would remain the political organization of the area, with its perceptible variables that occur over time, until the abolition of the lordships in the 19th century in favor of the provincialist vision that began to impose itself. Meanwhile, life in the mountains of Ayllón followed the same course as in ancient times. The peace of these lands was only punctuated by the war against the French Napoleonic Empire between 1808 and 1810, when the Macizo de Ayllón was the scene of battles for the control of the mountain passes.
During the Confiscation Law promoted by Juan Álvarez Mendizábal in 1836, the communal properties, which were many in the area, were put up for sale, and thus began the first economic and demographic decline of the Sierra of Ayllón in the Late modern period. It is in this period when villages such as Pedehuste, La Mata de Robledo, El Bustar, Pinarejo or Catar de Pie Mediano were depopulated, of which only a few vestiges or isolated tainas remain in the middle of the mountain.
The National Plan of Economic Stabilization of 1959 and its consequent industrial development makes that during the decade of the 60s the region loses almost half of its population by the emigration of this one to the great metropolitan areas in growth, mainly those of Madrid, Barcelona and Bilbao. In the 1970s, a second wave of emigration, mainly to Madrid, Guadalajara and Segovia, left many of the villages uninhabited. In these new waves of depopulation, the construction of the reservoirs of El Vado and Matallana (the latter was never built) caused the two villages that give it its name to disappear from the map, while the difficult living conditions, the lack of economic prosperity due to the isolation of the area and the forced expropriations due to reforestation, are the reasons why others such as Umbralejo, La Vereda or La Vihuela also lost their population. As for the rest of the towns in the area, the loss of inhabitants is continuous, although it is true that in some areas there is a stabilization of the population due mainly to rural tourism in some of its municipalities, which gives a certain air, although scarce, of economic prosperity in the Sierra de Ayllón.
Populations
Due to the living conditions in a high mountain climate, the population in the area has always been scarce, although nowadays, and for decades, it also suffers from the problem of depopulation. So much so that the approximate population density of 0.8 people per km² in the area is one of the lowest in Europe, with almost 900 km² in the heart of the mountain chain divided between less than 800 inhabitants.
The Sierra of Ayllón extends through the following municipalities encompassing its various Villages, including the abandoned ones:[17]
Villages in the heart of the mountain chain
- Almiruete, in the municipal district of Tamajón
- Becerril, in the municipal district of Riaza
- Campillo de Ranas
- Campillejo
- El Espinar
- Matallana
- Roblelacasa
- Robleluengo
- La Vereda
- El Cardoso de la Sierra
 Church of Colmenar de la Sierra
Church of Colmenar de la Sierra- Bocígano
- El Bustar (abandoned)
- Pinarejo (abandoned)
- Cabida
- Colmenar de la Sierra
- Corralejo
- La Hiruela Vieja or La Hiruelilla (abandoned)
- Peñalba de la Sierra
- Santuy (abandoned)
- La Vihuela (abandoned)
- Bocígano
- La Hiruela
- Majaelrayo
- El Muyo, in the municipal district of Riaza
- Palancares, in the municipal district of Tamajón
- La Pinilla, in the municipal district of Cerezo de Arriba
- Puebla de la Sierra
- Retiendas
- Riofrío de Riaza
- El Vado (abandoned), in the municipal district of Tamajón.
- Valverde de los Arroyos
- Majadas Viejas (abandoned)
- La Mata de Robledo (abandoned)
- Pedehuste or Peyuste (abandoned)
- Zarzuela de Galve
Villages on the northern slope, adjacent to the Meseta Norte
- Cerezo de Abajo
- Cerezo de Arriba
- Grado del Pico
- Riaza
 Main Square of Riaza
Main Square of Riaza- Hontanares (abandoned)
- Madriguera
- Martín Muñoz de Ayllón
- El Negredo
- Serracín
- Villacorta
- Santibáñez de Ayllón
- Santo Tomé del Puerto
- Rosuero
- Villarejo
Villages on the western slope, adjacent to the SSierra de Somosierra
- Horcajo de la Sierra
 Horcajuelo de la Sierra
Horcajuelo de la Sierra- Aoslos
- Horcajuelo de la Sierra
- Madarcos
- Montejo de la Sierra
- Prádena del Rincón
- Robregordo
- Somosierra
Villages on the southern slope, adjacent to the Campiña de Guadalajara
- Tamajón
 Hermitage of the Enebrales, at the entrance to the Sierra de Ayllón from the south, next to the Ciudad Encantada de Tamajón.
Hermitage of the Enebrales, at the entrance to the Sierra de Ayllón from the south, next to the Ciudad Encantada de Tamajón. - Tortuero
- Valdepeñas de la Sierra
- Alpedrete de la Sierra
- Valdesotos
Villages on the eastern slope, adjacent to Sierra de Pela and Sierra de Alto Rey
- Cantalojas
- Villacadima (abandoned)
- Galve de Sorbe
- La Huerce
- Umbralejo (abandoned)
- Valdepinillos
In the villages located in the heart of the Sierra de Ayllón, as well as on the eastern and southern slopes, the so-called "black architecture" is developed, a type of construction based on black slate, abundant throughout the Sierra de Ayllón, which gives a blackish tone to the villages in the area. On the northern slope is more common the "red architecture", so called due to the reddish tone of its constructions based on mixing clay and slate.
Economy
Although scarce, there is population in this area since ancient times, always dedicated to hunting. In fact, the origin of many villages such as El Cardoso de la Sierra, El Bustar or Catar de Pie Mediano (now gone) is in the settlement of the so-called gentes de armas, that is, hunters, in different places that allowed them to hunt the prey in batida.[18]
Livestock goat, bovine and vaccine has been another important economic sector in the area. This phenomenon gave rise to the appearance of a type of construction typical of the area, the taina, often grouped in teinadas, giving rise, on some occasions, to the origin of towns such as Roblelacasa, Majaelrayo or Valverde de los Arroyos.
Today there are two main economic engines in the area. On the one hand, the retirements, due to the high average age of its inhabitants. On the other hand, there is tourism, especially in the villages surrounding Pico Ocejón and in the Riaza area. Numerous rural lodgings, hikers and mountaineers routes through mountains and forests, and La Pinilla ski resort are its main tourist attractions. However, this is not generalized, and in areas where tourism is scarce, either because of their isolation or poor communication, as is the case of El Cardoso de la Sierra, depopulation is even more pronounced than in the more touristy areas.
Communications

The Sierra de Ayllón is one of the worst communicated areas of central Spain, even within itself. Traditionally the paths and footpaths between the mountains have been the main means of communication between the villages of the massif and between them and the surrounding valleys. Today, the abrupt orography results in narrow roads and forest tracks, with no other possible means of transport.
Depending on the area of the mountain chain you want to reach, there are four ways to get to the heart of the Macizo de Ayllón:
- From the south from Guadalajara, the most common and busiest route, taking the CM-101 to Humanes, where it continues along the CM-1004 to Tamajón. After Tamajón, the road turns into a "Y" towards Majaelrayo, on the left (GU-186), and towards Valverde de los Arroyos, on the right (GU-211). These two roads have recently undergone renovations due to their heavy traffic, especially on weekends, and the deplorable state they were in.[19]
- From the west from the A-1, between Buitrago del Lozoya and Somosierra, through Puerto del Cardoso → take the detour to Horcajo de la Sierra following the M-141 to Montejo de la Sierra where you can take the M-139 towards Puerto del Cardoso to El Cardoso de la Sierra by the GU-187, or by the M-137 to La Hiruela and, from there, the GU-137 to the different villages of the municipality of El Cardoso.
- From the north from Riaza on the SG-112 through Riofrío de Riaza to Puerto de la Quesera. From there a road leads to Majaelrayo after more than 30 km of road between forests, valleys and mountains.
- From the east, the CM-1006, which links Jadraque and Cogolludo with Galve de Sorbe and the CM-110 (road from Sigüenza to Ayllón through Atienza), has a detour through Umbralejo to Valverde de los Arroyos on the GU-211, which cannot be used by buses and trucks due to the closeness of its curves and the narrowness of the bridges over the Sorbe river and the Arroyo de los Vallejos.
On the other hand, the communications between the different zones of the mountain chain are based on small and narrow roads:
- The western and eastern zones, separated by the Jaramilla river, are joined by a narrow, winding road that is impassable in times of snow and heavy rains, making the two areas completely cut off from each other, being only accessible to the municipal district of El Cardoso de la Sierra only by the Community of Madrid despite being part of the province of Guadalajara.
- The northern and southern areas are joined by a long road, which joins Majaelrayo and Riaza through Puerto de la Quesera, which can be impassable in times of heavy snowfall. Along its 41 km, only Riofrío de Riaza, very close to Riaza, can be found as a town; and there's also a forest track, about 22 km long, which joins Majaelrayo and Cantalojas through the Tejera Negra beech forest without passing through any other town.
Notes
- Declaración del Parque Natural de la Sierra Norte de Guadalajara (10 March 2011). "Law 5" (in Spanish).
- Additional information: Hernández de Miguel, José María (1996). "Variabilidad y biología de los Iberodorcadion Breuning, 1947, de la Sierra de Guadarrama (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae, Lamiinae)" (in Spanish). Tesis Doctoral – Universidad Complutense de Madrid. Archived from the original on 6 October 2003.
- EcoRed. "El medio físico y glaciarismo de la sierra de Ayllón" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 7 November 2002.
- Pliego Vega (1998)
- Díaz Martínez & López Ballesteros (2003)
- Redacción La Crónica. "El lobo ronda por Ayllón" (in Spanish). La Crónica de Guadalajara.
- Pico del Lobo. "El águila real en la sierra de Ayllón" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 19 February 2003.
- "Carpetano-ibérico-leonesa Province" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 14 March 2009. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- "Vegetation series of the Carpetano-Iberian-Leonese Province" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 15 September 2007. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- "Series vegetales oromediterráneas" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 15 September 2007. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- "Series vegetales crioromediterráneas" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 15 September 2007. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- "Endemismos vegetales de la Provincia Carpetano-ibérico-leonesa" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 15 September 2007. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- "Supramediterranean vegetation series" (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 15 September 2007. Retrieved 6 May 2009.
- Information about the beech tree, its climatic importance and its extension in the Iberian Peninsula in Jardín actual – "Hayedos en otoño", by Agustín Carretero (in Spanish).
- "El abedular de Somosierra: Uno de los bosques más singulares y recónditos de la sierra de Guadarrama". Madrid Diario (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 11 November 2007.
- Interesting historical notes in Castellote Herrero and Alba Pardo (2000), Díaz Martínez and López Ballesteros (2003), Ferrer Vidal (1991), Miguel López (1982) and Nieto Taberné and Alegre Carvajal (1998).
- There are still remains of the abandoned areas mentioned here, even though some of them have not been inhabited for centuries. There are many others of which only toponymic references remain and which do not appear in this list.
- Alfonso XI, Rey de Castilla y de León (1991). "XI and XII". El libro de la montería (facs.) (in Spanish). Vol. III. Valladolid: Editorial Lex Nova.
- Diputación de Guadalajara. "Terminado el ensanchamiento de la carretera Tamajón-Valverde" (in Spanish).
Bibliography
- Ares Mateos, Alfredo (2005). Evolución de suelos ácidos y podsolizados meridionales europeos: macizo de Ayllón, España (in Spanish). Madrid: Universidad Complutense de Madrid, servicio de publicaciones. ISBN 84-669-2005-6.
- Catellote Herrero, Eulalia; Alba Pardo, Marina (2000). Arquitectura negra de la provincia de Guadalajara (in Spanish). Toledo: JCCM, servicio de publicaciones. ISBN 84-7788-215-0.
- Díaz Martínez, Miguel Ángel; López Ballesteros, José Alberto (2003). La sierra de Ayllón (in Spanish). Madrid: Ediciones El Senderista. ISBN 84-95368-22-6.
- Ferrer Vidal, Jorge (1991). Viaje por la sierra de Ayllón (in Spanish). Valladolid: Ámbito Ediciones. ISBN 84-86770-52-1.
- Hernández Bermejo, J. Esteban (1984). Ecología de los hayedos meridionales ibéricos: el macizo de Ayllón (in Spanish). Madrid: Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación, centro de publicaciones. ISBN 84-7479-282-7.
- Hita, Carlos de (1995). La sierra de Guadarrama y el macizo de Ayllón (in Spanish). Madrid: Anaya-Touring. ISBN 84-8165-343-8.
- Luceño Garcés, Modesto; Vargas Goméz, Pablo (1991). Guia botánica del Sistema Central Español (in Spanish). Editorial Pirámide. ISBN 84-368-0558-5.
- Mecha López, Pedro (2005). Modelización territorial aplicada a la gestión forestal en la vertiente sur de la Sierra de Ayllón (in Spanish). Madrid: Digibis Publicaciones Digitales. ISBN 84-934621-1-X.
- Miguel López, Miguel Ángel (1982). Guía del Macizo de Ayllón (in Spanish). Madrid: Editorial Tierra de Fuego. ISBN 84-300-8353-7.
- Nieto Taberné, Tomás; Alegre Carvajal, Esther (1998). Guía de la Arquitectura Negra de Guadalajara (in Spanish). Guadalajara: Aache ediciones. ISBN 84-95179-00-8.
- Pliego Vega, Domingo (1998). Los dosmiles de la sierra de Ayllón (in Spanish). Madrid: Desnivel ediciones. ISBN 84-89969-03-5.
- Rincón Hércules, Manuel (1991). Andar por el macizo de Ayllón (in Spanish). Madrid: Acción Divulgativa. ISBN 84-7955-008-2.
External links
- Hiking routes through the mountain chain of Ayllón and other mountain chains of the Sistema Central (in Spanish) – Hiking and trekking
- Hiking routes through the mountain chain of Ayllón and other mountain chains of the Sistema Central (in Spanish) – Sistema Central
- Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 (in Spanish) – Conservation of natural habitats and wildlife.
- Complete Directive 92/43/EEC (in Spanish)


