Simonellite
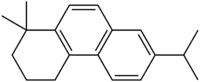
Simonellite (1,1-dimethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-7-isopropyl phenanthrene) is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with a chemical formula C19H24. It is similar to retene.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1-Dimethyl-6-(propan-2-yl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrophenanthrene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H24 | |
| Molar mass | 252.38 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Simonellite occurs naturally as an organic mineral derived from diterpenes present in conifer resins.[1] It is named after its discoverer, Vittorio Simonelli (1860–1929), an Italian geologist. It forms colorless to white orthorhombic crystals.[2] It occurs in Fognano, Tuscany, Italy.
Simonellite, together with cadalene, retene and ip-iHMN, is a biomarker of higher plants, which makes it useful for paleobotanic analysis of rock sediments.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.