Simpson's rule
In numerical integration, Simpson's rules are several approximations for definite integrals, named after Thomas Simpson (1710–1761).
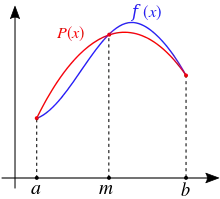
The most basic of these rules, called Simpson's 1/3 rule, or just Simpson's rule, reads
In German and some other languages, it is named after Johannes Kepler, who derived it in 1615 after seeing it used for wine barrels (barrel rule, Keplersche Fassregel). The approximate equality in the rule becomes exact if f is a polynomial up to and including 3rd degree.
If the 1/3 rule is applied to n equal subdivisions of the integration range [a, b], one obtains the composite Simpson's 1/3 rule. Points inside the integration range are given alternating weights 4/3 and 2/3.
Simpson's 3/8 rule, also called Simpson's second rule, requires one more function evaluation inside the integration range and gives lower error bounds, but does not improve on order of the error.
If the 3/8 rule is applied to n equal subdivisions of the integration range [a, b], one obtains the composite Simpson's 3/8 rule.
Simpson's 1/3 and 3/8 rules are two special cases of closed Newton–Cotes formulas.
In naval architecture and ship stability estimation, there also exists Simpson's third rule, which has no special importance in general numerical analysis, see Simpson's rules (ship stability).
Simpson's 1/3 rule
Simpson's 1/3 rule, also simply called Simpson's rule, is a method for numerical integration proposed by Thomas Simpson. It is based upon a quadratic interpolation. Simpson's 1/3 rule is as follows:
where is the step size.
The error in approximating an integral by Simpson's rule for is
where (the Greek letter xi) is some number between and .[1][2]
The error is asymptotically proportional to . However, the above derivations suggest an error proportional to . Simpson's rule gains an extra order because the points at which the integrand is evaluated are distributed symmetrically in the interval .
Since the error term is proportional to the fourth derivative of at , this shows that Simpson's rule provides exact results for any polynomial of degree three or less, since the fourth derivative of such a polynomial is zero at all points. Another way to see this result is to note that any interpolating cubic polynomial can be expressed as the sum of the unique interpolating quadratic polynomial plus an arbitrarily scaled cubic polynomial that vanishes at all three points in the interval, and the integral of this second term vanishes because it is odd within the interval.
If the second derivative exists and is convex in the interval , then
Quadratic interpolation
One derivation replaces the integrand by the quadratic polynomial (i.e. parabola) that takes the same values as at the end points and and the midpoint . One can use Lagrange polynomial interpolation to find an expression for this polynomial,
Using integration by substitution, one can show that[3][2]
Introducing the step size , this is also commonly written as
Because of the factor, Simpson's rule is also referred to as "Simpson's 1/3 rule" (see below for generalization).
Averaging the midpoint and the trapezoidal rules
Another derivation constructs Simpson's rule from two simpler approximations: the midpoint rule
and the trapezoidal rule
The errors in these approximations are
and
respectively, where denotes a term asymptotically proportional to . The two terms are not equal; see Big O notation for more details. It follows from the above formulas for the errors of the midpoint and trapezoidal rule that the leading error term vanishes if we take the weighted average This weighted average is exactly Simpson's rule.
Using another approximation (for example, the trapezoidal rule with twice as many points), it is possible to take a suitable weighted average and eliminate another error term. This is Romberg's method.
Undetermined coefficients
The third derivation starts from the ansatz
The coefficients α, β and γ can be fixed by requiring that this approximation be exact for all quadratic polynomials. This yields Simpson's rule. (This derivation is essentially a less rigorous version of the quadratic interpolation derivation, where one saves significant calculation effort by guessing the correct functional form.)
Composite Simpson's 1/3 rule
If the interval of integration is in some sense "small", then Simpson's rule with subintervals will provide an adequate approximation to the exact integral. By "small" we mean that the function being integrated is relatively smooth over the interval . For such a function, a smooth quadratic interpolant like the one used in Simpson's rule will give good results.
However, it is often the case that the function we are trying to integrate is not smooth over the interval. Typically, this means that either the function is highly oscillatory or lacks derivatives at certain points. In these cases, Simpson's rule may give very poor results. One common way of handling this problem is by breaking up the interval into small subintervals. Simpson's rule is then applied to each subinterval, with the results being summed to produce an approximation for the integral over the entire interval. This sort of approach is termed the composite Simpson's 1/3 rule, or just composite Simpson's rule.
Suppose that the interval is split up into subintervals, with an even number. Then, the composite Simpson's rule is given by
Dividing the interval into subintervals of length and introducing the points for (in particular, and ), we have
This composite rule with corresponds with the regular Simpson's rule of the preceding section.
The error committed by the composite Simpson's rule is
where is some number between and , and is the "step length".[4][5] The error is bounded (in absolute value) by
This formulation splits the interval in subintervals of equal length. In practice, it is often advantageous to use subintervals of different lengths and concentrate the efforts on the places where the integrand is less well-behaved. This leads to the adaptive Simpson's method.
Simpson's 3/8 rule
Simpson's 3/8 rule, also called Simpson's second rule, is another method for numerical integration proposed by Thomas Simpson. It is based upon a cubic interpolation rather than a quadratic interpolation. Simpson's 3/8 rule is as follows:
where is the step size.
The error of this method is
where is some number between and . Thus, the 3/8 rule is about twice as accurate as the standard method, but it uses one more function value. A composite 3/8 rule also exists, similarly as above.[6]
A further generalization of this concept for interpolation with arbitrary-degree polynomials are the Newton–Cotes formulas.
Composite Simpson's 3/8 rule
Dividing the interval into subintervals of length and introducing the points for (in particular, and ), we have
While the remainder for the rule is shown as[6] we can only use this if is a multiple of three. The 1/3 rule can be used for the remaining subintervals without changing the order of the error term (conversely, the 3/8 rule can be used with a composite 1/3 rule for odd-numbered subintervals).
Alternative extended Simpson's rule
This is another formulation of a composite Simpson's rule: instead of applying Simpson's rule to disjoint segments of the integral to be approximated, Simpson's rule is applied to overlapping segments, yielding[7]
The formula above is obtained by combining the composite Simpson's 1/3 rule with the one consisting of using Simpson's 3/8 rule in the extreme subintervals and Simpson's 1/3 rule in the remaining subintervals. The result is then obtained by taking the mean of the two formulas.
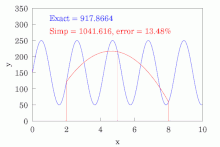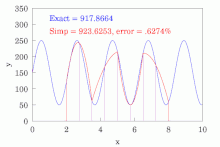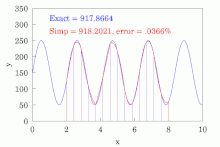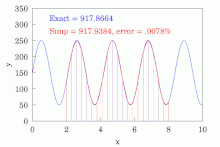
Simpson's rules in the case of narrow peaks
In the task of estimation of full area of narrow peak-like functions, Simpson's rules are much less efficient than trapezoidal rule. Namely, composite Simpson's 1/3 rule requires 1.8 times more points to achieve the same accuracy as trapezoidal rule.[8] Composite Simpson's 3/8 rule is even less accurate. Integration by Simpson's 1/3 rule can be represented as a weighted average with 2/3 of the value coming from integration by the trapezoidal rule with step h and 1/3 of the value coming from integration by the rectangle rule with step 2h. The accuracy is governed by the second (2h step) term. Averaging of Simpson's 1/3 rule composite sums with properly shifted frames produces the following rules:
where two points outside of the integrated region are exploited, and
where only points within integration region are used. Application of the second rule to the region of 3 points generates 1/3 Simpon's rule, 4 points - 3/8 rule.
These rules are very much similar to the alternative extended Simpson's rule. The coefficients within the major part of the region being integrated are one with non-unit coefficients only at the edges. These two rules can be associated with Euler–MacLaurin formula with the first derivative term and named First order Euler–MacLaurin integration rules.[8] The two rules presented above differ only in the way how the first derivative at the region end is calculated. The first derivative term in the Euler–MacLaurin integration rules accounts for integral of the second derivative, which equals the difference of the first derivatives at the edges of the integration region. It is possible to generate higher order Euler–Maclaurin rules by adding a difference of 3rd, 5th, and so on derivatives with coefficients, as defined by Euler–MacLaurin formula.
Composite Simpson's rule for irregularly spaced data
For some applications, the integration interval needs to be divided into uneven intervals – perhaps due to uneven sampling of data, or missing or corrupted data points. Suppose we divide the interval into even number of subintervals of widths . Then the composite Simpson's rule is given by[9]
where
are the function values at the th sampling point on the interval .
In case of odd number of subintervals, the above formula are used up to the second to last interval, and the last interval is handled separately by adding the following to the result:[10]
where
| Example implementation in Python |
from collections.abc import Sequence
def simpson_nonuniform(x: Sequence[float], f: Sequence[float]) -> float:
"""
Simpson rule for irregularly spaced data.
:param x: Sampling points for the function values
:param f: Function values at the sampling points
:return: approximation for the integral
See ``scipy.integrate.simpson`` and the underlying ``_basic_simpson``
for a more performant implementation utilizing numpy's broadcast.
"""
N = len(x) - 1
h = [x[i + 1] - x[i] for i in range(0, N)]
assert N > 0
result = 0.0
for i in range(1, N, 2):
h0, h1 = h[i - 1], h[i]
hph, hdh, hmh = h1 + h0, h1 / h0, h1 * h0
result += (hph / 6) * (
(2 - hdh) * f[i - 1] + (hph**2 / hmh) * f[i] + (2 - 1 / hdh) * f[i + 1]
)
if N % 2 == 1:
h0, h1 = h[N - 2], h[N - 1]
result += f[N] * (2 * h1 ** 2 + 3 * h0 * h1) / (6 * (h0 + h1))
result += f[N - 1] * (h1 ** 2 + 3 * h1 * h0) / (6 * h0)
result -= f[N - 2] * h1 ** 3 / (6 * h0 * (h0 + h1))
return result
|
| Example implementation in R |
SimpsonInt <- function(fx, dx) {
n <- length(dx)
h <- diff(dx)
stopifnot(exprs = {
length(fx) == n
all(h >= 0)
})
res <- 0
for (i in seq(1L, n - 2L, 2L)) {
hph <- h[i] + h[i + 1L]
hdh <- h[i + 1L] / h[i]
res <- res + hph / 6 *
((2 - hdh) * fx[i] +
hph ^ 2 / (h[i] * h[i + 1L]) * fx[i + 1L] +
(2 - 1 / hdh) * fx[i + 2L])
}
if (n %% 2 == 0) {
hph <- h[n - 1L] + h[n - 2L]
threehth <- 3 * h[n - 1L] * h[n - 2L]
sixh2 <- 6 * h[n - 2L]
h1sq <- h[n - 1L] ^ 2
res <- res +
(2 * h1sq + threehth) / (6 * hph) * fx[n] +
(h1sq + threehth) / sixh2 * fx[n - 1L] -
(h1sq * h[n - 1L]) / (sixh2 * hph) * fx[n - 2L]
}
res
}
|
See also
Notes
- Atkinson 1989, equation (5.1.15).
- Süli & Mayers 2003, §7.2.
- Atkinson 1989, p. 256.
- Atkinson 1989, pp. 257–258.
- Süli & Mayers 2003, §7.5.
- Matthews 2004.
- Weisstein, Equation 35.
- Kalambet, Kozmin & Samokhin 2018.
- Shklov 1960.
- Cartwright 2017, Equation 8. The equation in Cartwright is calculating the first interval whereas the equations in the Wikipedia article are adjusting for the last integral. If the proper algebraic substitutions are made, the equation results in the values shown.
References
- Atkinson, Kendall E. (1989). An Introduction to Numerical Analysis (2nd ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-50023-2.
- Burden, Richard L.; Faires, J. Douglas (2000). Numerical Analysis (7th ed.). Brooks/Cole. ISBN 0-534-38216-9.
- Cartwright, Kenneth V. (September 2017). "Simpson's Rule Cumulative Integration with MS Excel and Irregularly-spaced Data" (PDF). Journal of Mathematical Sciences and Mathematics Education. 12 (2): 1–9. Retrieved 18 December 2022.
- Kalambet, Yuri; Kozmin, Yuri; Samokhin, Andrey (2018). "Comparison of integration rules in the case of very narrow chromatographic peaks". Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems. 179: 22–30. doi:10.1016/j.chemolab.2018.06.001. ISSN 0169-7439.
- Matthews, John H. (2004). "Simpson's 3/8 Rule for Numerical Integration". Numerical Analysis - Numerical Methods Project. California State University, Fullerton. Archived from the original on 4 December 2008. Retrieved 11 November 2008.
- Shklov, N. (December 1960). "Simpson's Rule for Unequally Spaced Ordinates". The American Mathematical Monthly. 67 (10): 1022–1023. doi:10.2307/2309244. JSTOR 2309244.
- Süli, Endre; Mayers, David (2003). An Introduction to Numerical Analysis. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-00794-1.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Newton-Cotes Formulas". MathWorld. Retrieved 14 December 2022.
External links
- "Simpson formula", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001 [1994]
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Simpson's Rule". MathWorld.
- Simpson's 1/3rd rule of integration — Notes, PPT, Mathcad, Matlab, Mathematica, Maple at Numerical Methods for STEM undergraduate
- A detailed description of a computer implementation is described by Dorai Sitaram in Teach Yourself Scheme in Fixnum Days, Appendix C
This article incorporates material from Code for Simpson's rule on PlanetMath, which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.