Scottish east coast fishery
The Scottish east coast fishery has been in existence for more than a thousand years, spanning the Viking Age right up to the present day.
A brief history
The fishery has always been for both whitefish and herring. The Norsemen came to Scotland from the 9th to 11th centuries and settled in the Northern Isles, Western Isles and on the mainland. They had fish as a large part of their diet, and excavations of Viking sites in Orkney and Shetland have found middens (kitchen waste areas) containing large quantities of fish bones. These bones were mainly of cod, saithe and ling but herring, haddock and whiting bones were also found. They used the line fishing method with hooks and bait.

The Dutch had a near monopoly of the herring fishing from the 15th to the 17th centuries. The boats, called busses, were very large. They lay overnight with the drift nets set to catch the herring and were hauled by hand in the morning. The herring were salted and placed in barrels. These barrels were then transferred to small boats called jagers, which were tenders to the busses. These boats took the fish to the markets.
The 18th century saw some Scottish fishermen emulate this Dutch method of fishing. In 1718, the government introduced the bounty system to promote large scale fishing. This meant that the government paid a bounty to the boat owner based on the tonnage of the vessel and would also pay a bounty to anyone for simply building a fishing boat. This continued until 1820 and did much to encourage the growth of the fishery. The fishery was valuable and the fleets often came under attack from French and Spanish privateers. Because of this, armed ships were employed to accompany and defend the fishing boats. Despite this, the Dutch style of fishing didn't produce the results the government wanted. The bulk of the Scottish fishery was still using the line and bait method in inshore waters. However, in 1785 the government instituted barrel bounties, which meant that the bounties were payable based on the amount of cured herring produced. This encouraged the herring curers to enter into contracts with the fishermen whereby they would be guaranteed a price for their catch.
The 19th century saw the greatest growth in sea fishing on the Scottish east coast. In the early years of that century the boats were very small, made of wood and were either one or two masted. They were not expensive to build and small repairs were carried out by the fishermen themselves. These early boats needed to be light so they could be dragged up the beaches.
The fishermen did not venture far from the shore, as these boats were undecked and unstable under stormy conditions. In 1848, a violent storm hit the country and 124 boats were sunk, and 100 fishermen lost their lives. The government appointed Captain John Washington to enquire into the disaster and to make recommendations (the Washington Report). He pointed out that the boats were too small and being without decks prone to water inundation. However, not all of the fishermen were happy about larger decked boats. They felt that heavier boats would be harder to row and decks would make it easier for men to be washed overboard. Also beaching the boats would be impossible. But a good many fishermen took a contrary view and felt that the decked boats was a good idea. They realised that the boats could fish further from the shore and would be better in storm conditions. Larger boats could hold more fish and so profits would be greater. The first decked boat was built in Eyemouth in 1856 and this soon became the norm for the Scottish fishing fleet. These sail boats were of three main types: Skaffies, Fifies and Zulus. Common to all three types were the lug sails, which may have given rise to their name - luggers. The need for the larger boats spurred on the building of harbours all along the east coast, in the 1850s and 1860s. This heralded an enormous change in the size of the herring fishery. Initially, the market for the pickled herring was Ireland and the West Indies where it was fed to slaves. The market received a setback in the 1830s following the ending of slavery on British-owned plantations and, from 1845 to 1851 when the Great Irish Famine forced a mass emigration from Ireland. However, improvements in curing techniques produced a superior product and soon meant that new markets opened up in Russia and the Baltic countries.
The fishermen, with the support of the curers, invested in larger boats and additional nets. The fleet grew quickly but was still could only fish for herring during the two months when the fish were off the Scottish east coast. By 1880, there were around 7,000 Scottish boats involved in herring fishing so the fishing season needed to be extended. This led to a migration of a sizeable number of boats and curers to the west coast in May and June. By 1880, the numbers of boats fishing the west coast numbered more than 1,000. In the 1860s, Scottish boats were also to be found in East Anglian waters for the Autumn fishing. Initially, Scottish curers were not present in any great numbers in this fishery but by the end of the 19th century large numbers were represented in Great Yarmouth and Lowestoft. By this time, the Scottish fleet actually outnumbered the local one. The curers soon turned their attention to Shetland for the early summer fishing causing the local Shetland fishermen to adopt the drift net and larger boats. By the early 20th century, more than 1,800 boats fished the Shetland waters.
In 1884 the herring industry faced a crisis. The curers wanted an end to the contract system because they could not balance quantity and costs with market conditions and so wanted a move to an auction process. Fishermen wanted the status quo but reluctantly agreed and from 1887 the herring were auctioned.
The peak of the herring fishery industry and also its main decline came between 1900 and the First World War. Steam-powered fishing boats appeared towards the end of the 19th century and it was steam drifters that would take the volume of the catch to new heights. The powered winches allowed longer nets to be deployed and their speed enabled the boats to get to market quickly and to return to sea. In those early years of the 20th century, the Scottish catch reached 2 million barrels annually.
Before the First World War, Germany and Russia were the main market for British herring. After the war, however, Germany was racked by inflation and was impoverished. Russia underwent the 1917 Revolution and civil war. Other European countries started to compete strongly with the British fleets and for twenty years the industry went into a steep decline. The beginnings of the seine net fishing began in Scotland in 1921 but the use of the large inefficient steam boats greatly hindered this new whitefish fishery. After the Second World War, the Scottish east coast fleet, with government assistance, was totally regenerated becoming mainly a whitefish industry. This in turn declined in the 1970s and 1980s due to overfishing and the subsequent imposition of quotas by the European Union. The herring industry continued to shrink. From the 1960s, trawling and purse-netting were the main methods of pelagic fishing, which not only includes herring but also mackerel. Although a quota is placed on the total herring catch and with no limit on mackerel, this sector is now the healthiest in the Scottish fleet.
Fishing boat development
The Scandinavian influence

The Norsemen were skilled seamen and boat builders and their boat designs depended on their needs. Trading vessels were wide, to allow large cargo storage, while raiding boats were long and narrow and very fast. They all used the clinker fashion of planking, i.e. the planks overlapped one another. The boats used for fishing were scaled-down versions of their cargo boats. The Scandinavian influence affected boat building long after the Viking period came to an end. Yoles from the Orkney Island of Stroma were built in the same way as the Norse boats. Early Scottish boat builders copied the Scandinavian designs with their clinker planking and characteristic sharp stems and sterns.
The Skaffie
From the beginning of the 19th century a class of boat called the Skaffie appeared. These were favoured mainly in the Moray Firth region. The early skaffie boats were small with rounded stems and raked sterns. They were two-masted with a tall dipping lugsail and a mizzen sail. Their short keel gave them good manoeuvrability in good weather, but they tended to be unstable in bad weather. They were usually crewed by around six people. Above all, though, they were light enough to be hauled up on to the beaches. The boats were un-decked and provided no shelter for the crew. Because of the vulnerability of the boats, they stayed only a few miles out to sea in full view of the land. These boats were gradually built bigger and could be around 42 feet (13 m) long, and partially decked. This came about because the harbours that were constructed from the mid to late19th century meant that the boats no longer needed to be beached. Skaffies were not built in any great numbers after 1900.
The Fifie

The "Fifie" then became the predominant fishing boat on the Scottish east coast. They were used from the 1850s until well into the 20th century. Fifies had a vertical stem and stern with a broad beam, which made them very stable. Their long keel was a disadvantage, especially manoeuvring in confined spaces. These boats were two masted with a main dipping lugsail and a mizzen sail. The masts were set quite far forward and aft to release a good working space. Fifies built from 1860 onwards were all decked, and from the 1870s onwards the bigger boats were built with carvel planking, i.e. the planks were laid edge-to-edge instead of the overlapping clinker style of previous boats. Some boats were now being built up to about 70 feet (21 m) in length and were very fast.
The Zulu

In 1879, Lossiemouth fisherman, William "Dad" Campbell came up with a radical design for his new boat. It had the vertical stem of the Fifie and the steeply raked stern of the Skaffie, and he called this boat Nonesuch, registration number INS 2118. She was relatively small, 52 feet (16 m) overall with a 39-foot keel length (12 m). The Nonesuch had her registration closed on 12 January 1901 after having been broken up. The Zulu War raging in South Africa at the time gave the name to this new class of boat.
The Zulu boats were built to the carvel method of planking. The shape of the Zulus gave the boats a long deck but a shorter keel, which greatly improved their manoeuvrability. Zulus were two-masted boats and carried three sails - a dipping lug fore, a standing lug mizzen and a jib. The sails were very heavy and difficult to haul, and the masts had to be very long and strong. Masts could be 60 feet (18 m) tall on boats of 80 feet (24 m) in length. Their design produced very fast boats that became invaluable to herring fishing fleets. They got to the fishing grounds quickly and returned swiftly with the catch. Because of these qualities, the Zulus rapidly became very popular along the entire east coast. As the 20th century approached, steam capstans were introduced, and this made the hauling of the sails and nets much easier for the crews. One of the best of those was the capstans patented and built by MacDonald Brothers of Portsoy, in 1908.
The steam boat
The earliest steam powered fishing boats first appeared in the 1890s and used the trawl system of fishing as well as lines and drift nets. These were large boats, usually 80–90 feet (24–27 m) in length with a beam of around 20 feet (6.1 m). They weighed 40-50 tons and travelled at 9–11 knots (17–20 km/h; 10–13 mph). The first steam boats were made of wood, but steel hulls were soon introduced and were divided into watertight compartments. They were well designed for the crew with a large building that contained the wheelhouse and the deckhouse. The boats built in the 20th century only had a mizzen sail, which was used to help steady the boat when its nets were out. The main function of the mast was now as a crane for lifting the catch ashore. They also had a steam capstan on the foredeck near the mast for hauling nets. The boats had narrow, high funnels so that the steam and thick coal smoke was released high above the deck and away from the fishermen. These funnels were nicknamed woodbines because they looked like the popular brand of cigarette. These boats had a crew of twelve made up of a skipper, driver, fireman (to look after the boiler) and nine deck hands. The earliest purpose built fishing vessels were designed and made by David Allan (Born 1840 Orkney)In Leith in March 1875, he converted a drifter to steam power.In 1877 it is said that he built the first screw propelled steam trawler in the world. This vessel was Pioneer LH854.She was of wooden construction with two masts and carried a gaff rigged main and mizen using booms, and a single foresail. Pioneer is mentioned in the Shetland Times of 4 May 1877. In 1878 he completed three steam-powered trawlers: Forward for Methven of Leith and Onward for Sharp and Murray of Cellardyke. In an interview with the Scotsman Mr. Allan stated that his motivation for auxiliary power was to increase the safety of fishermen. However local fishermen saw power trawling as a threat, remember that local boats of this period were 45 feet (14 m) or so, Mr. Allan's largest were 105 feet (32 m). Some landowners questioned the sustainability of fish stocks to power trawlers. The Lammas Drive of 1878 states" It was reported that D. Allan of Granton had built two steam drifters the Forward and the Onward. The latter was unable to get a Celardyke crew so she fished from Aberdeen." During this time Mr. Allan was also skippering the boats to ensure that they were successful in their catches. In total he built ten boats at Leith between 1877 and 1881. Twenty-one boats were completed at Granton, his last vessel being Degrave in 1886. Because of the prejudices mentioned, most of these were sold to foreign owners, France, Belgium, Spain and the West Indies amongst them. A full, complete account of his ventures can be found on Grantontrawlers.com. David Allan was buried on Christmas Day in South Shields in 1911. On page 14 of the Daily Mirror of 27 December 1911 there is a photograph and a line drawing of Onward. It reads "The death was announced in South Shields of Mr David Allan, the founder of the steam fishing industry. In 1877 he designed and built the steam Drifter Onward especially for fishing purposes. He afterwards commanded and worked the vessel himself."
Steam fishing boats had many advantages. They were usually about 20 ft longer (6.1 m) than the sailing vessels so they could carry more nets and catch more fish. This was important, as the market was growing quickly at the beginning of the 20th century. They could travel faster and further and with greater freedom from weather, wind and tide. Because less time was spent travelling to and from the fishing grounds, more time could be spent fishing. The steam boats also gained the highest prices for their fish, as they could return quickly to harbour with their fresh catch. The main disadvantage of the steam boats, though, was their high operating costs. Their engines were mechanically inefficient and took up much space, while fuel and fitting out costs were very high. Before the First World War, building costs were between £3,000 and £4,000, at least three times the cost of the sail boats. To cover these high costs, they needed to fish for longer seasons. The higher expenses meant that more steam drifters were company-owned or jointly owned. As the herring fishing industry declined, steam boats became too expensive.
The seine netter
.jpg.webp)
Petrol and paraffin engines began to be used in 1906. At first, they were mainly fitted to smaller boats of between 18 and 30 feet (5.5 and 9.1 m) in length, and they provided auxiliary power to assist the sails. However, as diesel engines became more powerful, the sails were replaced altogether, and the engines were fitted in larger and larger boats. Motor engines were relatively cheap, making them affordable to individual Fishermen. Early engines cost less than £100, and fuel costs were low. These boats also needed less maintenance than steam vessels. The two most popular engine brands were the Gardiner and Kelvin engines. The compact engines meant they could be fitted to existing sailing drifters such as Fifies and Zulus. The traditional Fifie style was better suited to the installation of a motor, which led to the custom building of a number of modified Fifie design boats with motors.
In 1920, though, the government changed the rules by removing the guaranteed price for the herring and prices dropped dramatically. In 1921, some Lossiemouth skippers noticed that the Danish seine net boats were landing huge quantities of plaice and other white fish at the English east coast ports. Their interest resulted in a few buying some seine nets and winches and trying this form of fishing. As they perfected seine net fishing, more of the Lossiemouth fleet converted to seine net. But boat design for this type of fishing was still proving to be an obstacle. That, and the cost of the majority steam boats prompted a new style of fishing boat. John Campbell, nephew of William Campbell who designed the first Zulu boat built a wooden boat that resembled, to some extent, the "Fifie" but had a broad beam. His boat, the Marigold, did very well and over a relatively short period the entire Lossiemouth fleet (the first in Scotland) converted to the seine net. Other east coast ports followed on very quickly.
The trawler
Today, trawl fishing is the main industrial method of catching white fish. These trawlers can catch and store massive amounts of fish. They possess highly sensitive electronic equipment and remove the chance element from fishing. They operate by trawling the nets along the sea bed where the kind of fish they want to catch are located.
Bottom trawling – single boat
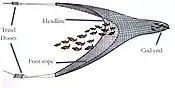
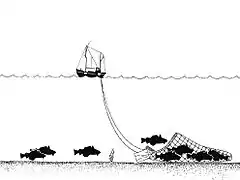
This the commonest of the towed fishing gear; it is also known as "otter trawling". Trawl nets are shaped like a funnel with the sides extended ahead to guide the fish into the net. Otter boards (sometimes called "doors") spread the towing wires and keep the net open horizontally. The mouth of the net is held open vertically by the use of floats attached to the headline, while weight distributed along the ground rope allows the net to make good contact with the sea floor. The otter boards would scrape along the seabed making noises that attract fish. The fish would congregate between the boards keeping up with them until they tired and the net would then overtake them. This method is used mainly to catch the demersal species such as cod, haddock, whiting and flatfish. The boats themselves can be less than 10 metres in length for inshore fishing to 60 metres or more for deep sea fishing.
With the decline in the volumes of roundfish, the growth in fishing for high-priced species such as monkfish and flatfish is being seen. In this case, scraper trawls are used. The nets are shaped differently with a lower headline, longer wings allowing a greater area to be swept.
Bottom trawling – two boats
In pair trawling, each boat has a wire fastened to the net. Because of this, otterboards are not required to hold the mouth of the net open, as the boats maintain at their maximum a distance apart of around 0.25 nautical miles (0.46 km). The boats, because they share the load, can be smaller and less powerful yet can tow relatively large gear. These boats can be anything from 15 to 30 metres in length and have a typical combined power of 1,000 horsepower (750 kW). Again, this form of fishing is mainly for demersal species.
Seine netting
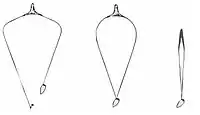
Scottish seining, sometimes called fly dragging, has the net attached to two long ropes usually made of leaded polypropylene and around 3 km in length. The net is deployed in a triangular fashion with the first rope attached to a marker buoy, the dhan, to which the boat returns to complete the set. Both ropes are then winched in as the boat steams ahead slowly. Winch speed is gradually increased as the net gets closer to keep the net moving forward and also to herd the fish into the net. Like the trawl, floats and weighted footrope keep the mouth of the net open and in contact with the seabed. This method of fishing takes place on grounds on the continental shelf and not in deep sea. Seine netting is for all forms of whitefish.
Twin beam trawling
The beam trawl is one where a beam, up to 12 metres in length, is attached to a skid at each end. The beam is situated on top of the skids effectively keeping the top of the net open and the fish are channelled between the skids. Two beam trawls are deployed alongside each other from outrigger booms on each side of the boat. This method is primarily for taking flatfish but these vessels can be used also for scallop dredging.
Twin rig trawl
This method is to use two trawls side by side. Three wires attach to this combination. Instead of having individual wires connected to each of the nets sides, a common wire attaches to the two inner sides and the outer sides of each net are wired individually. Again otter boards allow the net mouths to spread apart horizontally while floats and ground ropes provide the vertical forces. This gear is usually used for catching target fish such as monkfish, flatfish and nephrops.
Line fishing
Line fishing used no nets. Line fishing boats harnessed a single line, up to a kilometre long, that was trailed behind the vessel. At intervals along that line drop lines were suspended at the end of which was tied a large hook onto which bait was hung. Halibut, cod, haddock, lemon sole, ling and skate were the predominant prey. The line would be released and reeled in using winches. The largest line fishing boat in the Scottish fleet was the Radiation which sailed out of Aberdeen and which predominantly fished Icelandic and Faroe Isles' waters.
Fishing for pelagic species (fish occurring in mid and upper water)
Pelagic gears are designed to catch species such as herring, mackerel, scad, blue whiting and sprats. However pelagic fishing from boats from the Scottish east coast ports normally catch herring and an amount of blue whiting from the northern North Sea.
Methods
- Single boat pelagic trawl – similar to the demersal trawl but the gear is generally lighter, as it does not have to cope with dragging across the seabed.
- Pelagic pair trawling – operate in a similar method to the demersal pair trawl and again with lighter gear.
Ancillary industries
- Boat Builders
- Fish Curers
- Coopers
- Net Makers
- Rope Makers
- Sale Makers
- Fish Salesmen (auctioneers) and Ship Chandlers
- Fish Processors
- Whaling in Scotland
References
- Herring Fishing in Scotland: Coull, Dr J.R.


