Slag (welding)
Welding slag is a form of slag, or vitreous material produced as a byproduct of some arc welding processes, most specifically shielded metal arc welding (also known as stick welding), submerged arc welding, and flux-cored arc welding. Slag is formed when flux, the solid shielding material used in the welding process, melts in or on top of the weld zone (also known as Dross). Slag is the solidified remaining flux after the weld area cools.[1]

Flux
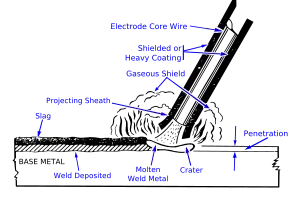
Welding flux is a combination of carbonate and silicate materials used in welding processes to shield the weld from atmospheric gases. When the heat of the weld zone reaches the flux, the flux melts and outgasses. The gases produced push the atmospheric gas back, preventing oxidation (and reactions with nitrogen).
The melted flux covers the molten metal in the weld zone. Flux materials are chosen so that the density of the melted flux / slag is lower than that of the metal being welded, so that the flux floats to the very top of the weld puddle and leaves pure or nearly pure metal to solidify below.
Flux materials may also contribute to metal behavior in the molten metal, with physical or chemical alterations to the molten metal.
The flux cover also helps thermally insulate the weld and reduce the cooling rate.
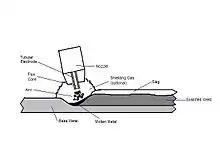
Inclusions
It is possible for areas of slag to become embedded within the solidified metal, if it did not float to the top of the molten metal for some reason. These are called inclusions and are a form of welding defect. Inclusions may be visible on the surface after cleaning, or may be completely contained within the metal, in that case they can only be detected on X-rays of the weld, requiring grinding or drilling to remove (followed by re-welding that section).
Processes

Four welding processes use flux in slag-producing manners:
- Shielded metal arc welding, also known as SMAW
- Flux-core arc welding, also known as FCAW or FC
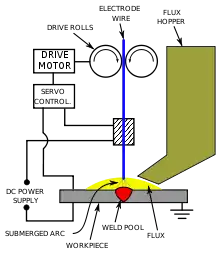
- Submerged arc welding
- Electroslag welding
Removal of slag
Slag does not contribute to strength or protection of metals after the welding process; it is waste material. Removal of the slag is necessary for four reasons:
- ability to inspect the quality of the weld area;
- aesthetics, or visual appearance;
- if a second layer or pass of welding is to be made on top of the first;
- to clean and clear the surface for coatings such as paint or oil.
Removal is usually done using manual or power tools. Manual tools may include a welding or chipping hammer, which has a pointed tip on one end to break up large chunks of slag efficiently, or wire brushes. Power tools include angle grinders with grinder disks or wire brush wheels.
See also
References
- Modern Welding Technology (6th Edition), Howard B. Cary& Scott Helzer, 2004, ISBN 978-0131130296