Atlantic Reserve Fleet, Norfolk
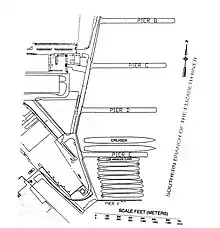
Atlantic Reserve Fleet, Norfolk was a part of the United States Navy reserve fleets, also called a mothball fleet, and was used to store the many surplus ships after World War II. The Atlantic Reserve Fleet was just south of the Norfolk Naval Shipyard, called the South Gate Annex in Portsmouth, Virginia, 2 mi (3.2 km) south of Norfolk, Virginia. The reserve fleet was stored in the freshwater of the Elizabeth River, Southern Branch near the Jordan Bridge. The freshwater was good for long-term storage for ships. Some ships in the fleet were reactivated for the Korean War and Vietnam War.[1][2][3][4]
| Atlantic Reserve Fleet, Norfolk South Gate Annex South Gate Annex Naval Inactive Ship Maintenance Facility | |
|---|---|
| Part of Norfolk Naval Shipyard | |
| Portsmouth, Virginia, United States | |
 Atlantic Reserve Fleet, Norfolk, South Gate Annex | |
| Coordinates | 36.802400°N 76.294702°W |
| Type | Reserve Fleet |
| Site information | |
| Owner | |
| Operator | |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1946 |
Norfolk.jpg.webp)
_laid_up_at_the_Norfolk_Naval_Shipyard_on_1_November_1983_(6442362).jpg.webp)
The Norfolk Naval Shipyard's Hampton Roads Facilities at Portsmouth includes: the South Gate Annex, Scott Center Annex, St. Helena Annex and St. Julien's Creek Annex. [5][6][7][8]
Reserve ship examples
- The USS Massachusetts (BB-59) was stored for 18 years at the Atlantic Reserve Fleet. Massachusetts was placed in the Atlantic Reserve Fleet in 1947. On June 8, 1965, she departed, and the Navy transferred ownership of the battleship to the State of Massachusetts. She became a museum ship in Battleship Cove, Fall River, Massachusetts.[9][10][11]
- USS Casa Grande (LSD-13), a Casa Grande-class dock landing ship was stored at Atlantic Reserve Fleet from 1946 to 1950. In 1950, she was recommissioned and put back in service.[12][13]
- USS Briareus (AR-12), a cargo ship, was stored at the Atlantic Reserve Fleet from 1946 to 1951. In 1951, she was recommissioned and put back in service.[14]
- USS Albemarle (AV-5), a Curtiss-class seaplane tender was placed in the fleet in 1960, in 1965 she was converted to the USNS Corpus Christi Bay (T-ARVH-1), a floating aeronautical maintenance facility for helicopters.[15]
- USS Deuel (APA-160), a Haskell-class attack transport, was placed in the fleet May 1946, and recommissioned in October 1950.[16]
South Gate Annex Naval Inactive Ship Maintenance Facility
South Gate Annex Naval Inactive Ship Maintenance Facility (NISMF) is at the former Atlantic Reserve Fleet site. The South Gate Annex Naval Inactive Ship Maintenance Facility is used as temporary storage of inactivated nuclear-powered ships, with the fuel removed.[17][18]
See also
- James River Reserve Fleet
- Portsmouth Naval Shipyard Museum
- Naval Medical Center Portsmouth
- Drydock Number One, Norfolk Naval Shipyard
References
- South Gate Annex
- youtube.com, The Mothball Fleet
- youtube.com The USN Mothball Fleet - Storing up for a rainy day
- pilotonline.com Archive: Decaying fleet could break apart, unleash disastrous spill, By Scott Harper, Sep 16, 2009
- globalsecurity.org St. Helena Annex
- Hisotical Marker St. Helena Annex
- "St. Julien's Creek Annex (US Navy)". Mid-Atlantic Superfund. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. August 2009. Archived from the original on 27 September 2009. Retrieved 2010-01-08.
- milbases.com Norfolk Naval Shipyard
- "Exhibits". battleshipcove.org. Retrieved 3 May 2019.
- heraldnews.com, Dedicated group worked tirelessly to get the battleship to Fall River, Staff Writer, The Herald News, 2015
- UN Navy USS Massachusetts (BB-59)
- |Casa Grande, Naval Historical Center, accessed 29 March 2008
- USS Casa Grande (LSD-13), NavSource Online, accessed 29 March 2008
- navsource USS Briareus (AR-12)
- navsource USS Albemarle (AV-5)
- https://www.navsource.org/archives/10/03/03160.htm navsource USS Deuel (APA-160)]
- NISMF Portsmouth, Virginia
- globalsecurity.org Norfolk Naval Shipyard