Invasion of Georgia (1742)
In the 1742 Invasion of Georgia, Spanish forces based in Florida attempted to seize and occupy disputed territory held by the British colony of Georgia. The campaign was part of a larger conflict which became known as the War of Jenkins' Ear. Local British forces under the command of the Governor James Oglethorpe rallied and defeated the Spaniards at the Battle of Bloody Marsh and the Battle of Gully Hole Creek, forcing them to withdraw. Britain's ownership of Georgia was formally recognized by Spain in the subsequent Treaty of Madrid.
| Invasion of Georgia (1742) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of War of Jenkins' Ear | |||||||
 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
|
Land: 900 soldiers, militia & Indians[1][2] sea: 5 vessels[3] |
Land: 1,950 soldiers, marines & militia sea: 36 vessels[1][2][4] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| Light | Over two hundred killed, more captured or wounded | ||||||
Background
The colony of Georgia had been an issue of contention between Britain and Spain since its foundation in 1733. Spain claimed the territory for its own colony of Florida and disputed what was regarded as an illegal occupation by the British settlers. The Convention of Pardo in 1739 had attempted to settle the dispute, but Spain still refused to abandon its claim. When the War of Jenkins' Ear broke out that same year, Spain began drawing up plans for an invasion.
The British governor of Georgia, James Oglethorpe, organized a small force and launched a British invasion of Florida in 1740, hoping to preempt a Spanish invasion of Georgia. The British besieged St. Augustine but were forced to withdraw. The stage was then set for the Spanish commander Manuel de Montiano to launch his long-awaited attack on Georgia. Because of the pressing demands on British resources in other theatres, no further reinforcements or aid could be dispatched to defend the colony from attack.
Invasion

Landing
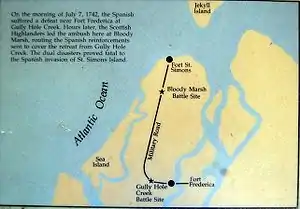
Spanish governor Don Manuel de Montiano commanded the invasion force, which by some estimates totalled between 4,500 and 5,000 men. Of that number, roughly 1,900 to 2,000 were ground assault troops. Oglethorpe's forces, consisting of regulars, militia, and native Indians numbered fewer than 1,000. The garrison at Fort St. Simons resisted the invasion with cannonade, but was not able to prevent the landing. On the 5 July 1742 Montiano landed nearly 1,900 men from 36 ships near Gascoigne Bluff, close to the Frederica River. Faced with a superior force, Oglethorpe decided to withdraw from Fort St. Simons before the Spanish could mount an assault. He ordered the small garrison to spike the guns, and to slight the fort (doing what damage they could), to deny the Spanish full use of the military asset. The Spanish took over the fort the following day, establishing it as their base on the island. Montiano began gathering intelligence about the strength of British opposition.
Battle of Gully Hole Creek

After landing troops and supplies, and consolidating their position at Fort St. Simons, the Spanish began to cautiously reconnoiter beyond their perimeter. They found the road between Fort St. Simons and Fort Frederica, but first assumed the narrow track was just a farm road. On July 18, the Spanish undertook a reconnaissance in force along the road with approximately 115 men under the command of Captain Sebastian Sanchez. One and a half miles from Fort Frederica, Sanchez' column made contact with Oglethorpe's soldiers, under command of Noble Jones. The ensuing skirmish became known as the Battle of Gully Hole Creek. The Spanish were routed, with nearly a third of their soldiers either killed or captured. Oglethorpe's forces advanced up Military Road in the direction of Fort St. Simons, in pursuit of the retreating Spanish. Spanish prisoners revealed that a larger Spanish force was advancing in the opposite direction, along the road from Fort St. Simons to Frederica. Oglethorpe left to gather reinforcements.
Battle of Bloody Marsh

The British advance party, in pursuit of the defeated Spanish reconnaissance force, engaged in a subsequent skirmish, then fell back in face of advancing Spanish reinforcements. When the British reached a bend in the road, Lieutenants Southerland and Macoy ordered the column to stop. There, the regiments and allied Indians took cover in the dense forest. They watched as the Spanish broke ranks, stacked arms and, taking out their kettles, prepared to cook dinner. The British forces attacked the Spanish off-guard, killing roughly two hundred Spaniards.[5][6][7][8][9][10][11] The Battle of Bloody Marsh blunted the Spanish advance, and ultimately proved decisive. Oglethorpe was credited with the victory.
Withdrawal
Montiano regrouped his forces and stood poised for a further advance. Oglethorpe continued to press the Spanish, trying to dislodge them from the island. A few days later, approaching a Spanish settlement on the south side, he learned of a Frenchman who had deserted the British and gone to the Spanish. Worried that the deserter might report the true number of the small British force, Oglethorpe spread out his drummers, to make them sound as if they were accompanying a larger force. He wrote to the deserter, addressing him as if a spy for the British, saying that the man just needed to continue his stories until Britain could send more men. The prisoner who was carrying the letter took it to the Spanish officers, as Oglethorpe had hoped. The timely arrival of British ships reinforced the misconception among the Spanish that British reinforcements were arriving. The Spanish left St. Simons on 25 July, ending their last invasion of colonial Georgia.
Aftermath

In the months after the invasion, Oglethorpe considered launching further counter-attacks against Florida, but circumstances were not favourable. The focus of the war had shifted from the Americas to Europe and arms, supplies and troops were not readily available. The region descended into an uneasy peace, occasionally punctuated by minor skirmishes. The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle ended the war in 1748 and recognised the status of Georgia as a British colony, formally ratified by Spain in the subsequent Treaty of Madrid. Its position was further secured in 1763 when Florida became a British possession as part of the Treaty of Paris ending the Seven Years' War.
The War of Jenkins' Ear is commemorated annually on the last Saturday in May at Wormsloe Plantation in Savannah, Georgia.[12]
Notes
- Conlin p. 53
- Murrin P.63
- Marley p. 262
- Marley p. 261
- History of Georgia By Robert Preston Brooks page 77
- Robert Preston Brooks (1913). History of Georgia. Atkinson, Mentzer. p. 77.
- Florida's Past: People and Events That Shaped the State, Volume 1 By Gene M. Burnett page 181
- The American Colonial Wars: a concise history, 1607–1775 Nathaniel Claiborne Hale, General Society of Colonial Wars (U.S.) Hale House, 1967 page 54
- Society of Colonial Wars, 1892–1967: seventy-fifth anniversary (General Society of Colonial Wars, 1967) page 231
- Thomas Spalding of Sapelo, Ellis Merton Coulter, (Louisiana State University Press, 1940) page 278
- A History of Florida By Caroline Mays Brevard, Henry Eastman Bennett page 75
- "Wormsloe Historic Site | Georgia State Parks". Gastateparks.org. Archived from the original on 2010-11-27. Retrieved 2012-12-18.
References
- Conlin, Joseph R. (2008), The American Past: A Survey of American History, Belmont, USA: Cengage Learning, ISBN 978-0-495-56610-6
- Marley, David (1998), Wars of the Americas: a chronology of armed conflict in the New World, 1492 to the present, Santa Barbara, USA: ABC-CLIO, ISBN 978-0-87436-837-6
- Murrin, John M.; Johnson, Paul E.; McPherson, James M.; Gerstle, Gary (2007), Liberty, Equality, Power: A History of the American People, Compact, Boston, USA: Cengage Learning, ISBN 978-0-495-41101-7