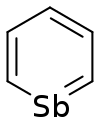
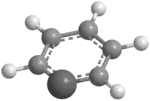
Stibinin
Stibinin, also known as stibabenzene,[1] is an organic chemical compound. Stibinin has the chemical formula C5H5Sb. The molecule, stibinin, is a derivative of benzene, with one of the carbon atoms in the 6-membered ring replaced by an antimony (Sb) atom. Stibinin is a molecule that is considered to be an organoantimony compound due to it containing carbon, hydrogen, and antimony atoms.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Stibinine | |||
| Other names
Antimonin; Stibabenzene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C5H5Sb | |||
| Molar mass | 186.855 g·mol−1 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Laboratory synthesis
The synthesis of stibinin can be accomplished in a three step process. The final product can be isolated, even though the molecule is highly labile. The first step of this synthesis involves the treatment of penta-1,4-diyne with dibutylstannane as shown in the figure below.[2]
- C5H4 + Bu2SnH2 → C13H24Sn

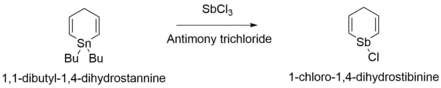
The second step of the synthesis involves reacting the product of the first step, 1,1-dibutyl-1,4-dihydrostannine, with antimony trichloride, to yield 1-chloro-1-stibacyclohexa-2,5-diene.[1]
- C13H24Sn + SbCl3 → C5H6SbCl
The final step of the synthesis of stibinin involves treating 1-chloro-1-stibacyclohexa-2,5-diene with a base, such as DBN, to yield the final product of stibinin.
- C5H6SbCl + DBN → C5H6Sb
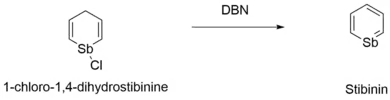
Similar compounds
It is noted that other benzene derivatives with one carbon replaced with a group 15 element can be synthesized via a similar synthetic pathway to that which stibinin is synthesized. The reaction of 1,1-dibutyl-1,4-dihydrostannine with arsenic trichloride, phosphorus tribromide, or bismuth trichloride can yield arsabenzene, phosphabenzene, or 1-chloro-1-bismacyclohexa-2,5-diene respectively. Treatment of 1-chloro-1-bismacyclohexa-2,5-diene with a base, such as DBN, can yield the product bismabenzene.[3]

See also
- 6-membered aromatic rings with one carbon replaced by another group: borabenzene, silabenzene, germabenzene, stannabenzene, pyridine, phosphorine, arsabenzene, stibabenzene, bismabenzene, pyrylium, thiopyrylium, selenopyrylium, telluropyrylium

References
- Ashe, Arthur J. (December 1971). "Stibabenzene". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 93 (24): 6690–6691. doi:10.1021/ja00753a069. ISSN 0002-7863.
- Ashe, Arthur J.; Fang, Xiangdong; Fang, Xinggao; Kampf, Jeff W. (December 2001). "Synthesis of 1,2-Dihydro-1,2-azaborines and Their Conversion to Tricarbonyl Chromium and Molybdenum Complexes". Organometallics. 20 (25): 5413–5418. doi:10.1021/om0106635. ISSN 0276-7333.
- Ashe, Arthur J. (February 2016). "The Route to Phosphabenzene and Beyond" (PDF). European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry. 2016 (5): 572–574. doi:10.1002/ejic.201600007. hdl:2027.42/117476. ISSN 1434-1948.