Structure of the Norwegian Army
The Structure of the Norwegian Army has seen considerable change over the years. In 2009 the Army introduced the new command and control organization. As of June 2021 the army is organized as follows:[1]
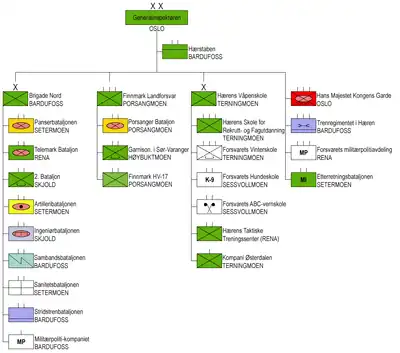

Chief of Staff
The Chief of the Army and the Army Staff are based in Bardufoss, Northern Norway.
- Chief of the Army
- Army Staff (Hærstaben)
Brigade Nord
Brigade Nord (English: Brigade North) is the largest unit in the Norwegian Army. The Brigade has several battalions across Norway, including Telemark Battalion at Camp Rena, eastern Norway.
|
|
Brigade Command, in Bardufoss[1] | ||||
|
|
Armoured Battalion (Panserbataljonen), in Setermoen[1] with Leopard 2A4NO main battle tanks and CV90 infantry fighting vehicles | ||||
|
|
Telemark Battalion (Telemark Bataljon), in Rena[1] with Leopard 2A4NO main battle tanks and CV90 infantry fighting vehicles | ||||
|
|
2nd Battalion (2. Bataljon), mechanized infantry in Skjold[1] with Bandvagn 206 vehicles, are converting to a Armoured Battalion identical to Telemark Battalion | ||||
|
|
Artillery Battalion (Artilleribataljonen), in Setermoen[1] with K9 Thunder,and Slamraam self-propelled howitzers and Army missile battery | ||||
|
|
Combat Engineer Battalion (Ingeniørbataljonen), in Skjold[1] | ||||
|
|
Signals Battalion (Sambandsbataljonen), in Bardufoss[1] | ||||
|
|
Medical Battalion (Sanitetsbataljonen), in Setermoen[1] | ||||
|
|
Combat Service Support Battalion (Stridstrenbataljonen), in Bardufoss[1] | ||||
|
|
Military Police Company (Militærpoliti-kompaniet), in Bardufoss[1] |
Finnmark Land Command
Further north, the Finnmark Land Command[4] is in charge of safeguarding Norway's northernmost land territories and the land border to Russia. It is a joint command, including an army staff and army and Home Guard units.
- Finnmark Land Command (Finnmark Landforsvar), in Porsangmoen[5][6]
- Porsanger Battalion (Porsanger Bataljon), cavalry battalion in Porsangmoen with a K9 Thunder battery [6][7]
- Garrison of Sør-Varanger (Garnisonen i Sør-Varanger), infantry battalion in Høybuktmoen[1][6] guarding the Norway–Russia border
- 17th Home Guard District Finnmark (Finnmark Heimevernsdistrikt 17), in Porsangermoen[6]
Norwegian Army Land Warfare Centre
- Norwegian Army Land Warfare Centre (Hærens våpenskole), in Terningmoen and Rena[1][4]
- Norwegian Army Land Warfare Centre departments:
- Maneuver School (Manøverskolen)
- Artillery School (Artilleriskolen)
- Engineer School (Ingeniørskolen)
- Logistics School (Logistikkskolen)
- Signals School (Sambandsskolen)
- Medical School (Sanitetsskolen)
- Army Recruit and Vocational Training School (Hærens skole for rekrutt- og fagutdanning), in Terningmoen and Rena
- Team Leader School (Lagførerskolen)
- NATO Centre of Excellence - Cold Weather Operations (Forsvarets Vinterskole), in Terningmoen,[1] manages as the Norwegian School of Winter Warfare[8]
- Armed Forces dog training establishment(Forsvarets hundeskole), in Sessvollmoen
- Armed Forces CBRN-defense School (Forsvarets ABC-vernskole), in Sessvollmoen
- Army Tactical Training Center (Hærens Taktiske Treningssenter), in Rena
- (Security) Company Østerdalen (Kompani Østerdalen), in Terningmoen
- Norwegian Army Land Warfare Centre departments:
Other units
- His Majesty The King's Guard (Hans Majestet Kongens Garde), in Huseby[1][4]
- Intelligence Battalion (Etterretningsbataljonen), in Setermoen[1] Military Intelligence & Electronic Warfare unit
- Army Logistic Regiment (Trenregimentet i Hæren), in Bardufoss[1] - maintenance, catering, etc.
- Armed Forces Military Police Department (Forsvarets militærpolitiavdeling), in Rena
Special forces
The Army's special forces unit Forsvarets Spesialkommando (FSK) is no longer part of the army. With the establishment of the Norwegian Special Operations Command in 2014, Norway's two special forces units (FSK and Marinejegerkommandoen) were united under the one command in the Norwegian Armed Forces, with the Air Force's 339 Special Operations Aviation Squadron at Rygge Air Station joining later as the SOC's air force component.[9][10][11]
References
- "The Army". Forsvaret. Retrieved 20 June 2021.
- "Contract to deliver Mobile Ground Based Air Defence to the Norwegian Army worth 583 MNOK".
- "404" (PDF).
{{cite web}}: Cite uses generic title (help) - https://www.forsvaret.no/soldater-og-ansatte/regelverk/English-NORAF.pdf/_/attachment/inline/30db7135-ff83-475c-a151-22894164b8f8:e6756e51768d437889c9fc0af3ded409177cafba/English-NOV2020.pdf
- "Viktig satsing i nord". ddd. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Nye Finnmark landforsvar: Slik blir styrkingen i nord". ddd. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Dette er Finnmarks nye bataljon". Norwegian Armed Forces. Retrieved 30 June 2020.
- "Centre of Excellence – Cold Weather Operations". Norwegian Armed Forces. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- "The Norwegian Special Forces".
- "Forsvarets spesialstyrker". 9 August 2021.
- "339 special operations aviation squadron (SOAS)".
