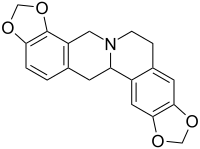
Tetrahydrocoptisine
Tetrahydrocoptisine (also known as stylopine) is an alkaloid isolated from Corydalis impatiens.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Stylopine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H17NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 323.348 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Li, W.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, T.; Liu, X.; Xing, W.; Niu, X. (2013). "Anti-inflammatory effect of tetrahydrocoptisine from Corydalis impatiens is a function of possible inhibition of TNF-α, IL-6 and NO production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated peritoneal macrophages through inhibiting NF-κB activation and MAPK pathway". European Journal of Pharmacology. 715 (1–3): 62–71. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.06.017. PMID 23810685.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.