Sodium sulfosuccinate esters
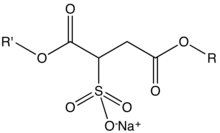
Sodium sulfosuccinate esters are organic compounds with the formula NaO3SCH(CO2R')CH2CO2R where R and R' can be H or alkyl groups. They comprise a large class of surfactants and emulsifiers used in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and cleaning agents. They are colorless salts. These materials can be further classified into monoesters (R' = H, R = alkyl) and diesters (R and R' = alkyl).[1]
Synthesis
They are produced by treatment of maleic anhydride with alcohols. The resulting mono or diesters are then treated with sodium sulfite, which, concomitant with protonation, adds to the C=C bond.
Application
A high volume example is sodium bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate. This is perhaps best known as the laxative docusate, however its main use is as a surfactant for which it finds common use in personal-care and household-care products, often under the name Aerosol-OTs.[1] It is unusual in that it is able to form microemulsions without the use of co-surfactants, and it has a rich variety of aqueous-phase behavior including multiple liquid crystalline phases.[2]
References
- Deepika; Tyagi, V. K (2006). "Sulfosuccinates as Mild surfactants". Journal of Oleo Science. 55 (9): 429–439. doi:10.5650/jos.55.429.
- Nave, Sandrine; Eastoe, Julian; Penfold, Jeff (November 2000). "What Is So Special about Aerosol-OT? 1. Aqueous Systems". Langmuir. 16 (23): 8733–8740. doi:10.1021/la000341q.