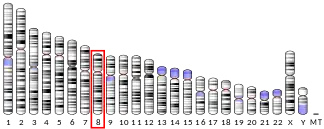
Syndecan-2
Syndecan-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDC2 gene.[5]
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a transmembrane (type I) heparan sulfate proteoglycan and is a member of the syndecan proteoglycan family. The syndecans mediate cell binding, cell signaling, and cytoskeletal organization and syndecan receptors are required for internalization of the HIV-1 tat protein. The syndecan-2 protein functions as an integral membrane protein and participates in cell proliferation, cell migration and cell-matrix interactions via its receptor for extracellular matrix proteins. Altered syndecan-2 expression has been detected in several different tumor types.[6]
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000169439 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000022261 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- David G, Bai XM, Van der Schueren B, Marynen P, Cassiman JJ, Van den Berghe H (June 1994). "Spatial and temporal changes in the expression of fibroglycan (syndecan-2) during mouse embryonic development". Development. 119 (3): 841–54. doi:10.1242/dev.119.3.841. PMID 8187643.
- "Entrez Gene: SDC2 syndecan 2".
- Maximov A, Tang TS, Bezprozvanny I (February 2003). "Association of the type 1 inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate receptor with 4.1N protein in neurons". Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 22 (2): 271–83. doi:10.1016/s1044-7431(02)00027-1. PMID 12676536. S2CID 2317354.
- Cohen AR, Woods DF, Marfatia SM, Walther Z, Chishti AH, Anderson JM, Wood DF (July 1998). "Human CASK/LIN-2 binds syndecan-2 and protein 4.1 and localizes to the basolateral membrane of epithelial cells". J. Cell Biol. 142 (1): 129–38. doi:10.1083/jcb.142.1.129. PMC 2133028. PMID 9660868.
- Utani A, Nomizu M, Matsuura H, Kato K, Kobayashi T, Takeda U, Aota S, Nielsen PK, Shinkai H (August 2001). "A unique sequence of the laminin alpha 3 G domain binds to heparin and promotes cell adhesion through syndecan-2 and -4". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (31): 28779–88. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101420200. PMID 11373281.
- Granés F, Urena JM, Rocamora N, Vilaró S (April 2000). "Ezrin links syndecan-2 to the cytoskeleton". J. Cell Sci. 113 ( Pt 7) (7): 1267–76. doi:10.1242/jcs.113.7.1267. PMID 10704377.
Further reading
- Mahley RW, Ji ZS (1999). "Remnant lipoprotein metabolism: key pathways involving cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans and apolipoprotein E." J. Lipid Res. 40 (1): 1–16. doi:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)33334-4. PMID 9869645.
- Labarrere CA, Pitts D, Halbrook H, Faulk WP (1992). "Natural anticoagulant pathways in normal and transplanted human hearts". J. Heart Lung Transplant. 11 (2 Pt 1): 342–7. PMID 1315572.
- Marynen P, Zhang J, Cassiman JJ, Van den Berghe H, David G (1989). "Partial primary structure of the 48- and 90-kilodalton core proteins of cell surface-associated heparan sulfate proteoglycans of lung fibroblasts. Prediction of an integral membrane domain and evidence for multiple distinct core proteins at the cell surface of human lung fibroblasts". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (12): 7017–24. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)83534-7. PMID 2523388.
- Sage H, Vernon RB, Funk SE, Everitt EA, Angello J (1989). "SPARC, a secreted protein associated with cellular proliferation, inhibits cell spreading in vitro and exhibits Ca+2-dependent binding to the extracellular matrix". J. Cell Biol. 109 (1): 341–56. doi:10.1083/jcb.109.1.341. PMC 2115491. PMID 2745554.
- Lories V, De Boeck H, David G, Cassiman JJ, Van den Berghe H (1987). "Heparan sulfate proteoglycans of human lung fibroblasts. Structural heterogeneity of the core proteins of the hydrophobic cell-associated forms". J. Biol. Chem. 262 (2): 854–9. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)75865-7. PMID 2948951.
- Brown KJ, Parish CR (1994). "Histidine-rich glycoprotein and platelet factor 4 mask heparan sulfate proteoglycans recognized by acidic and basic fibroblast growth factor". Biochemistry. 33 (46): 13918–27. doi:10.1021/bi00250a047. PMID 7524669.
- Bolton P, Powell J, Rutter M, Buckle V, Yates JR, Ishikawa-Brush Y, Monaco AP (1995). "Autism, mental retardation, multiple exostoses and short stature in a female with 46,X,t(X;8)(p22.13;q22.1)". Psychiatr. Genet. 5 (2): 51–5. doi:10.1097/00041444-199522000-00001. PMID 7551962. S2CID 45132642.
- Barillari G, Gendelman R, Gallo RC, Ensoli B (1993). "The Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1, a growth factor for AIDS Kaposi sarcoma and cytokine-activated vascular cells, induces adhesion of the same cell types by using integrin receptors recognizing the RGD amino acid sequence". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90 (17): 7941–5. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90.7941B. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.17.7941. PMC 47263. PMID 7690138.
- Lyon M, Deakin JA, Mizuno K, Nakamura T, Gallagher JT (1994). "Interaction of hepatocyte growth factor with heparan sulfate. Elucidation of the major heparan sulfate structural determinants". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (15): 11216–23. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)78113-7. PMID 8157651.
- Albini A, Benelli R, Presta M, Rusnati M, Ziche M, Rubartelli A, Paglialunga G, Bussolino F, Noonan D (1996). "HIV-tat protein is a heparin-binding angiogenic growth factor". Oncogene. 12 (2): 289–97. PMID 8570206.
- Soussi-Yanicostas N, Hardelin JP, Arroyo-Jimenez MM, Ardouin O, Legouis R, Levilliers J, Traincard F, Betton JM, Cabanié L, Petit C (1997). "Initial characterization of anosmin-1, a putative extracellular matrix protein synthesized by definite neuronal cell populations in the central nervous system". J. Cell Sci. 109 (7): 1749–57. doi:10.1242/jcs.109.7.1749. PMID 8832397.
- Christa L, Carnot F, Simon MT, Levavasseur F, Stinnakre MG, Lasserre C, Thepot D, Clement B, Devinoy E, Brechot C (1997). "HIP/PAP is an adhesive protein expressed in hepatocarcinoma, normal Paneth, and pancreatic cells". Am. J. Physiol. 271 (6 Pt 1): G993–1002. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.1996.271.6.G993. PMID 8997243.
- Rusnati M, Coltrini D, Oreste P, Zoppetti G, Albini A, Noonan D, d'Adda di Fagagna F, Giacca M, Presta M (1997). "Interaction of HIV-1 Tat protein with heparin. Role of the backbone structure, sulfation, and size". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (17): 11313–20. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.17.11313. PMID 9111037.
- Oh ES, Couchman JR, Woods A (1997). "Serine phosphorylation of syndecan-2 proteoglycan cytoplasmic domain". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 344 (1): 67–74. doi:10.1006/abbi.1997.0180. PMID 9244383.
- Ishikawa-Brush Y, Powell JF, Bolton P, Miller AP, Francis F, Willard HF, Lehrach H, Monaco AP (1997). "Autism and multiple exostoses associated with an X;8 translocation occurring within the GRPR gene and 3' to the SDC2 gene". Hum. Mol. Genet. 6 (8): 1241–50. doi:10.1093/hmg/6.8.1241. PMID 9259269.
- Chang HC, Samaniego F, Nair BC, Buonaguro L, Ensoli B (1997). "HIV-1 Tat protein exits from cells via a leaderless secretory pathway and binds to extracellular matrix-associated heparan sulfate proteoglycans through its basic region". AIDS. 11 (12): 1421–31. doi:10.1097/00002030-199712000-00006. PMID 9342064. S2CID 7648619.
- Grootjans JJ, Zimmermann P, Reekmans G, Smets A, Degeest G, Dürr J, David G (1998). "Syntenin, a PDZ protein that binds syndecan cytoplasmic domains". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (25): 13683–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.25.13683. PMC 28366. PMID 9391086.
- Cohen AR, Woods DF, Marfatia SM, Walther Z, Chishti AH, Anderson JM, Wood DF (1998). "Human CASK/LIN-2 binds syndecan-2 and protein 4.1 and localizes to the basolateral membrane of epithelial cells". J. Cell Biol. 142 (1): 129–38. doi:10.1083/jcb.142.1.129. PMC 2133028. PMID 9660868.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.