Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Park
Tatshenshini-Alsek Park or Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Wilderness Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada 9,580 km2 (3,700 sq mi). It was established in 1993 after an intensive campaign by Canadian and American conservation organizations to halt mining exploration and development in the area, and protect the area for its strong natural heritage and biodiversity values.
| Tatshenshini-Alsek Park | |
|---|---|
 Samuel Glacier | |
_location_map.svg.png.webp) Location of Tatshenshini-Alsek in British Columbia | |
| Location | Stikine Region, British Columbia, Canada |
| Nearest city | Whitehorse, Yukon |
| Coordinates | 59°52′03″N 138°00′49″W |
| Area | 9,580 km2 (3,700 sq mi) |
| Established | 1993 |
| Governing body | BC Parks |
| Website | bcparks |
| Part of | Kluane / Wrangell-St. Elias / Glacier Bay / Tatshenshini-Alsek |
| Criteria | Natural: (vii), (viii), (ix), (x) |
| Reference | 72ter |
| Inscription | 1979 (3rd Session) |
| Extensions | 1992, 1994 |
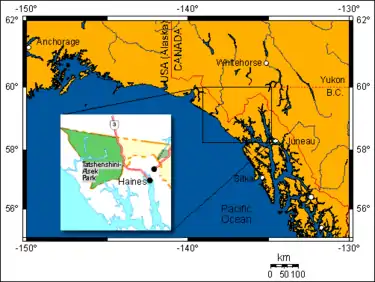
The park is located in the very northwestern corner of British Columbia, bordering the American state of Alaska and the Canadian Yukon Territory. Nestled between the Yukon's Kluane National Park and Reserve in the Yukon and Glacier Bay & Alaska's Wrangell–St. Elias National Parks and Preserves, the park includes all land in British Columbia west of the Haines Highway. It is part of the Kluane-Wrangell-St. Elias-Glacier Bay-Tatshenshini-Alsek park system, and in 1994 was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
History
Over the centuries, numerous indigenous peoples lived in this area, including the historic Tlingit and Southern Tutchone, who built fishing villages along the rivers. The eastern edge of the park follows an ancient trade route used by the Chilkat (a Tlingit people) to barter with the Tutchone.
In the mid-19th century, the sudden breakup of a natural dam on the Alsek River caused a severe flood. The dam had been formed by the advance of a glacier across the entire Alsek River channel; the obstructed river formed a large temporary lake upstream of the blockage. A wall of water 7 m (23 ft) high and 15 m (49 ft) wide swept an entire Tutchone village into the sea at Dry Bay, killing all the inhabitants.
Tatshenshini-Alsek was one of the last areas of British Columbia to be mapped and explored. In the 1960s the first geological exploration for minerals took place in the area. Significant copper deposits were found in the vicinity of Windy Craggy Mountain, in the middle of the Tatshenshini region. In the mid-1970s two companies began rafting the Tatshenshini (aka "the Tat", a term also used to refer to the region) and Alsek rivers for the first time. In the mid-1980s a proposal surfaced to develop Windy Craggy peak into a huge open-pit mine.
In 1991 Tatshenshini International was established, linking together the top 50 conservation organisations in North America. An extremely intensive campaign followed in Canada and in the United States, particularly the U.S. Congress and eventually the White House, when the active involvement of then Vice-President Al Gore was enlisted. Eventually, BC Premier Mike Harcourt responded by undertaking a review of the issues surrounding Tatshenshini-Alsek by the Commission on Resources and the Environment (CORE). BC government under Premier Harcourt decided in June 1993 to protect Tatshenshini-Alsek as a Class A park. The owners of the Windy-Craggy mineral claims were given a $103.8 million settlement.
In combination with the adjoining national parks, this completed protection of the world's largest international park complex. The International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) proposed the area for protection as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Kluane-Wrangell-St. Elias-Glacier Bay-Tatshenshini-Alsek transborder park system comprising Kluane, Wrangell-St Elias, Glacier Bay and Tatshenshini-Alsek parks, was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1994 for the spectacular glacier and icefield landscapes, in addition to the importance of its habitat for grizzly bears, caribou and Dall sheep.
In 1999, a party of sheep hunters found artifacts and remains of a young male at the foot of a glacier in the park; he was later called Kwäday Dän Ts’ìnchi, or "Long Ago Man Found". The well-preserved frozen body turned out to be between 300 and 550 years old. Representatives of Champagne and Aishihik First Nations were consulted for this find on their historic territory, and they named the young man. In addition, they agreed to scientific and DNA testing of the remains. Researchers recruited volunteers to see if people could be found who were genetically related to the "iceman". Some 241 volunteers were tested from the area Champagne and Aishihik First Nations, and related peoples in Yukon, British Columbia and Alaska. Seventeen living relatives, including two sisters, were found in the Champagne and Aishihik First Nations who are related through a mitochondrial DNA match of the direct female line.[2] Fifteen of these 17 identify as Wolf clan, suggesting the young man also belonged to that clan.[3] In the matrilineal kinship system, children are considered born into their mother's clan, and descent is figured through the mother's line.
Wildlife
The Alsek and Tatshenshini rivers flow through the park in glacier-carved U-shaped valleys. These valleys through the coastal mountains allow cool, moist ocean air into the cold interior. The quick change from ocean to interior environment, frequent floods, landslides and avalanches, a varied geology and great elevation changes have together created an exceptionally diverse range of habitat conditions.
Tatshenshini-Alsek Park supports a large grizzly bear population. A green area that cuts through a barrier of mountain and ice connects coastal and interior grizzly bear populations and provides a perfect habitat. The park is the only Canadian home of the glacier bear. This extremely rare blue-grey colour phase of the black bear is found only within the park and just over the border into the United States.
As well as bears, Tatshenshini-Alsek Park also supports Dall's sheep, and exceptional numbers of mountain goats, Kenai moose, grey wolves, eagles (bald and golden), falcons (peregrine and gyr), and trumpeter swans.
Along the coastline, sea lions and humpback whales can be seen.
The Alsek Ranges are located there, and Mount Fairweather, at 4,671 metres (15,325 ft), is the province's highest peak. The Tatshenshini-Alsek area lies in a region of high earthquake activity. Slippages along the Fairweather and Hubbard/Border Faults to the west and the Denali Fault to the north cause regular quakes.
Climate
The weather station, Blanchard River, is at the British Columbia border with Yukon, along Haines Highway. It has a subarctic climate (Köppen Dfc), bordering on tundra climate (Köppen ET).
| Climate data for Blanchard River, Yukon (1981-2010): 836 m (2,743 ft) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 5.5 (41.9) |
7.5 (45.5) |
8.5 (47.3) |
16.0 (60.8) |
24.0 (75.2) |
29.0 (84.2) |
29.0 (84.2) |
29.0 (84.2) |
21.5 (70.7) |
22.0 (71.6) |
8.0 (46.4) |
6.5 (43.7) |
29.0 (84.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −9.0 (15.8) |
−5.2 (22.6) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
3.3 (37.9) |
10.3 (50.5) |
15.8 (60.4) |
16.8 (62.2) |
15.9 (60.6) |
10.1 (50.2) |
2.8 (37.0) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
4.0 (39.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −14.6 (5.7) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
4.2 (39.6) |
9.1 (48.4) |
10.9 (51.6) |
9.9 (49.8) |
5.4 (41.7) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−11.0 (12.2) |
−1.6 (29.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −19.9 (−3.8) |
−16.8 (1.8) |
−14.2 (6.4) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
2.3 (36.1) |
4.8 (40.6) |
4.0 (39.2) |
0.6 (33.1) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−14.3 (6.3) |
−16.1 (3.0) |
−7.1 (19.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −46.0 (−50.8) |
−40.0 (−40.0) |
−37.0 (−34.6) |
−30.0 (−22.0) |
−15.0 (5.0) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
−11.5 (11.3) |
−26.5 (−15.7) |
−39.0 (−38.2) |
−41.0 (−41.8) |
−46.0 (−50.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 45.2 (1.78) |
39.0 (1.54) |
27.6 (1.09) |
19.3 (0.76) |
18.1 (0.71) |
38.4 (1.51) |
50.9 (2.00) |
47.4 (1.87) |
69.2 (2.72) |
60.7 (2.39) |
63.5 (2.50) |
73.5 (2.89) |
552.8 (21.76) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 45.0 (17.7) |
38.6 (15.2) |
27.3 (10.7) |
16.2 (6.4) |
2.4 (0.9) |
0.5 (0.2) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
2.6 (1.0) |
26.3 (10.4) |
57.8 (22.8) |
69.9 (27.5) |
286.6 (112.8) |
| Source: Environment Canada[4] | |||||||||||||
Pleasant Camp, British Columbia is on the southeastern edge of Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Park, near the Alaskan border. Pleasant Camp has a dry-summer subarctic climate (Köppen climate classification: Dsc).
| Climate data for Pleasant Camp, British Columbia (1981-2010): 274 m (899 ft) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 7.5 (45.5) |
11.5 (52.7) |
13.5 (56.3) |
20.0 (68.0) |
25.0 (77.0) |
30.5 (86.9) |
32.8 (91.0) |
34.0 (93.2) |
24.5 (76.1) |
18.0 (64.4) |
10.0 (50.0) |
6.5 (43.7) |
34.0 (93.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −5.0 (23.0) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
1.8 (35.2) |
7.4 (45.3) |
13.6 (56.5) |
18.3 (64.9) |
19.9 (67.8) |
18.3 (64.9) |
12.6 (54.7) |
5.6 (42.1) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
−3.7 (25.3) |
7.1 (44.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −7.9 (17.8) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
2.7 (36.9) |
7.8 (46.0) |
12.3 (54.1) |
14.5 (58.1) |
13.3 (55.9) |
8.7 (47.7) |
2.8 (37.0) |
−4.6 (23.7) |
−6.4 (20.5) |
3.0 (37.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −10.8 (12.6) |
−8.9 (16.0) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
2.0 (35.6) |
6.2 (43.2) |
9.1 (48.4) |
8.3 (46.9) |
4.7 (40.5) |
0.1 (32.2) |
−7.3 (18.9) |
−9.0 (15.8) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −32.0 (−25.6) |
−31.1 (−24.0) |
−27.0 (−16.6) |
−17.5 (0.5) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
−2.0 (28.4) |
0.5 (32.9) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
−19.0 (−2.2) |
−31.0 (−23.8) |
−32.2 (−26.0) |
−32.2 (−26.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 200.4 (7.89) |
139.1 (5.48) |
106.2 (4.18) |
69.7 (2.74) |
51.9 (2.04) |
37.4 (1.47) |
35.8 (1.41) |
72.4 (2.85) |
148.8 (5.86) |
188.1 (7.41) |
160.0 (6.30) |
217.3 (8.56) |
1,426.9 (56.18) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 165.4 (65.1) |
111.4 (43.9) |
82.6 (32.5) |
20.8 (8.2) |
2.6 (1.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.8 (0.3) |
35.0 (13.8) |
128.0 (50.4) |
177.4 (69.8) |
723.8 (285.0) |
| Source: Environment Canada[5] | |||||||||||||
See also
References
- "Tatshenshini-Alsek Park". Protected Planet. Retrieved 2020-09-17.
- "Scientists find 17 living relatives of 'iceman' discovered in B.C. glacier". CBC News. 25 April 2008. Retrieved 13 March 2012.
- Judith Lavoie, Canwest News Service, "Iceman's DNA Linked To Coastal Aboriginals (Canada)", Leader Post, 26 April 2008, accessed 5 October 2014
- "Blanchard River, Yukon". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010 (in English and French). Environment Canada. Retrieved September 2, 2023.
- "Pleasant Camp, BC". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010 (in English and French). Environment Canada. Retrieved September 2, 2023.