United States Court of Appeals for the Tenth Circuit
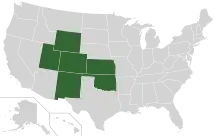
The United States Court of Appeals for the Tenth Circuit (in case citations, 10th Cir.) is a federal court with appellate jurisdiction over the district courts in the following districts:
- District of Colorado
- District of Kansas
- District of New Mexico
- Eastern District of Oklahoma
- Northern District of Oklahoma
- Western District of Oklahoma
- District of Utah
- District of Wyoming
| United States Court of Appeals for the Tenth Circuit | |
|---|---|
| (10th Cir.) | |
 | |
 | |
| Location | Byron White U.S. Courthouse |
| Appeals from | |
| Established | March 28, 1929 |
| Judges | 12 |
| Circuit Justice | Neil Gorsuch |
| Chief Judge | Jerome Holmes |
| www | |
These districts were part of the Eighth Circuit until 1929. The court is composed of nineteen active judges and is based at the Byron White U.S. Courthouse in Denver, Colorado. It is one of thirteen United States courts of appeals and has jurisdiction over 560,625 square miles,[1] or roughly one seventh of the country's land mass.
History

Congress created a new judicial circuit in 1929 to accommodate the increased caseload in the federal courts. Between 1866 and 1912, twelve new states had entered the Union and been incorporated into the Eighth and Ninth Circuits. The Eighth Circuit encompassed 13 states and had become the largest in the nation.[2]
Chief Justice William Howard Taft suggested the reorganization of the Eighth Circuit Court in response to widespread opposition in 1928 to a proposal to reorganize the nation's entire circuit structure. The original plan had sprung from an American Bar Association committee in 1925 and would have changed the composition of all but two circuits.[2]
The House of Representatives considered two proposals to divide the existing Eighth Circuit. A bill by Representative Walter Newton would separate the circuit's eastern and western states. An alternate proposal divided the northern from the southern states. With the judges and bar of the existing Eighth Circuit for Newton's bill and little opposition to dividing the circuit, lawmakers focused on providing for more judgeships and meeting places of the circuit courts of appeals in their deliberations.[2]
In 1929, Congress passed a law that placed the federal U.S. district courts in Minnesota, Iowa, North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Missouri, and Arkansas in the Eighth Circuit and created a Tenth Circuit that included Wyoming, Colorado, Utah, New Mexico, Kansas, and Oklahoma. Three additional judgeships were authorized and the sitting circuit judges were reassigned according to their residence. The Tenth Circuit was assigned a total of four judgeships.[3]
Current composition of the court
As of October 1, 2022:
| # | Title | Judge | Duty station | Born | Term of service | Appointed by | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active | Chief | Senior | ||||||
| 38 | Chief Judge | Jerome Holmes | Oklahoma City, OK | 1961 | 2006–present | 2022–present | — | G.W. Bush |
| 33 | Circuit Judge | Harris Hartz | Albuquerque, NM | 1947 | 2001–present | — | — | G.W. Bush |
| 36 | Circuit Judge | Timothy Tymkovich | Denver, CO | 1956 | 2003–present | 2015–2022 | — | G.W. Bush |
| 39 | Circuit Judge | Scott Matheson Jr. | Salt Lake City, UT | 1953 | 2010–present | — | — | Obama |
| 40 | Circuit Judge | Robert E. Bacharach | Oklahoma City, OK | 1959 | 2013–present | — | — | Obama |
| 41 | Circuit Judge | Gregory A. Phillips | Cheyenne, WY | 1960 | 2013–present | — | — | Obama |
| 42 | Circuit Judge | Carolyn B. McHugh | Salt Lake City, UT | 1957 | 2014–present | — | — | Obama |
| 43 | Circuit Judge | Nancy Moritz | Topeka, KS | 1960 | 2014–present | — | — | Obama |
| 44 | Circuit Judge | Allison H. Eid | Denver, CO | 1965 | 2017–present | — | — | Trump |
| 45 | Circuit Judge | Joel M. Carson III | Roswell, NM | 1971 | 2018–present | — | — | Trump |
| 46 | Circuit Judge | Veronica S. Rossman | Denver, CO | 1972 | 2021–present | — | — | Biden |
| 47 | Circuit Judge | vacant | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 21 | Senior Circuit Judge | Stephanie Kulp Seymour | Tulsa, OK | 1940 | 1979–2005 | 1994–2000 | 2005–present | Carter |
| 22 | Senior Circuit Judge | John Carbone Porfilio[4] | inactive | 1934 | 1985–1999 | — | 1999–present | Reagan |
| 23 | Senior Circuit Judge | Stephen H. Anderson | inactive | 1932 | 1985–2000 | — | 2000–present | Reagan |
| 25 | Senior Circuit Judge | Bobby Baldock | Roswell, NM | 1936 | 1985–2001 | — | 2001–present | Reagan |
| 26 | Senior Circuit Judge | Wade Brorby | inactive | 1934 | 1988–2001 | — | 2001–present | Reagan |
| 27 | Senior Circuit Judge | David M. Ebel | Denver, CO | 1940 | 1988–2006 | — | 2006–present | Reagan |
| 28 | Senior Circuit Judge | Paul Joseph Kelly Jr. | Santa Fe, NM | 1940 | 1992–2017 | — | 2017–present | G.H.W. Bush |
| 30 | Senior Circuit Judge | Mary Beck Briscoe | Lawrence, KS | 1947 | 1995–2021 | 2010–2015 | 2021–present | Clinton |
| 31 | Senior Circuit Judge | Carlos F. Lucero | Denver, CO | 1940 | 1995–2021 | — | 2021–present | Clinton |
| 32 | Senior Circuit Judge | Michael R. Murphy | Salt Lake City, UT | 1947 | 1995–2012 | — | 2012–present | Clinton |
| 34 | Senior Circuit Judge | Terrence L. O'Brien | Cheyenne, WY | 1943 | 2002–2013 | — | 2013–present | G.W. Bush |
Vacancies and pending nominations
| Seat | Prior judge's duty station | Seat last held by | Vacancy reason | Date of vacancy | Nominee | Date of nomination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | Lawrence, KS | Mary Beck Briscoe | Senior status | March 15, 2021 | Richard Federico | July 27, 2023 |
List of former judges
| # | Judge | State | Born–died | Active service | Chief Judge | Senior status | Appointed by | Reason for termination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Robert E. Lewis | CO | 1857–1941 | 1929–1940 | — | 1940–1941 | Harding / Operation of law[5] | death |
| 2 | John Hazelton Cotteral | OK | 1864–1933 | 1929–1933 | — | — | Coolidge / Operation of law[6] | death |
| 3 | Orie Leon Phillips | NM | 1885–1974 | 1929–1956 | 1948–1956 | 1956–1974 | Hoover | death |
| 4 | George Thomas McDermott | KS | 1886–1937 | 1929–1937 | — | — | Hoover | death |
| 5 | Sam G. Bratton | NM | 1888–1963 | 1933–1961 | 1956–1959 | 1961–1963 | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 6 | Robert L. Williams | OK | 1868–1948 | 1937–1939 | — | 1939–1948 | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 7 | Walter A. Huxman | KS | 1887–1972 | 1939–1957 | — | 1957–1972 | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 8 | Alfred P. Murrah | OK | 1904–1975 | 1940–1970 | 1959–1970 | 1970–1975 | F. Roosevelt | death |
| 9 | John Coleman Pickett | WY | 1896–1983 | 1949–1966 | — | 1966–1983 | Truman | death |
| 10 | David Thomas Lewis | UT | 1912–1983 | 1956–1977 | 1970–1977 | 1977–1983 | Eisenhower | death |
| 11 | Jean Sala Breitenstein | CO | 1900–1986 | 1957–1970 | — | 1970–1986 | Eisenhower | death |
| 12 | Delmas Carl Hill | KS | 1906–1989 | 1961–1977 | — | 1977–1989 | Kennedy | death |
| 13 | Oliver Seth | NM | 1915–1996 | 1962–1984 | 1977–1984 | 1984–1996 | Kennedy | death |
| 14 | John J. Hickey | WY | 1911–1970 | 1966–1970 | — | — | L. Johnson | death |
| 15 | William Judson Holloway Jr. | OK | 1923–2014 | 1968–1992 | 1984–1991 | 1992–2014 | L. Johnson | death |
| 16 | Robert Hugh McWilliams Jr. | CO | 1916–2013 | 1970–1984 | — | 1984–2013 | Nixon | death |
| 17 | James Emmett Barrett | WY | 1922–2011 | 1971–1987 | — | 1987–2011 | Nixon | death |
| 18 | William Edward Doyle | CO | 1911–1986 | 1971–1984 | — | 1984–1986 | Nixon | death |
| 19 | Monroe G. McKay | UT | 1928–2020 | 1977–1993 | 1991–1993 | 1993–2020 | Carter | death |
| 20 | James Kenneth Logan | KS | 1929–2018 | 1977–1994 | — | 1994–1998 | Carter | retirement |
| 24 | Deanell Reece Tacha | KS | 1946–present | 1985–2011 | 2001–2008 | 2011 | Reagan | retirement |
| 29 | Robert Harlan Henry | OK | 1953–present | 1994–2010 | 2008–2010 | — | Clinton | resignation |
| 35 | Michael W. McConnell | UT | 1955–present | 2002–2009 | — | — | G.W. Bush | resignation |
| 37 | Neil Gorsuch | CO | 1967–present | 2006–2017 | — | — | G.W. Bush | elevation to Supreme Court |
Chief judges
| Chief Judge | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Phillips | 1948–1956 | ||
| Bratton | 1956–1959 | ||
| Murrah | 1959–1970 | ||
| Lewis | 1970–1977 | ||
| Seth | 1977–1984 | ||
| Holloway, Jr. | 1984–1991 | ||
| McKay | 1991–1993 | ||
| Seymour | 1994–2000 | ||
| Tacha | 2001–2008 | ||
| Henry | 2008–2010 | ||
| Briscoe | 2010–2015 | ||
| Tymkovich | 2015–2022 | ||
| Holmes | 2022–present | ||
Chief judges have administrative responsibilities with respect to their circuits, and preside over any panel on which they serve, unless the circuit justice (the Supreme Court justice responsible for the circuit) is also on the panel. Unlike the Supreme Court, where one justice is specifically nominated to be chief, the office of chief judge rotates among the circuit judges.
To be chief, a judge must have been in active service on the court for at least one year, be under the age of 65, and have not previously served as chief judge. A vacancy is filled by the judge highest in seniority among the group of qualified judges, with seniority determined first by commission date, then by age. The chief judge serves for a term of seven years, or until age 70, whichever occurs first. If no judge qualifies to be chief, the youngest judge over the age of 65 who has served on the court for at least one year shall act as chief until another judge qualifies. If no judge has served on the court for more than a year, the most senior judge shall act as chief. Judges can forfeit or resign their chief judgeship or acting chief judgeship while retaining their active status as a circuit judge.[7]
When the office was created in 1948, the chief judge was the longest-serving judge who had not elected to retire, on what has since 1958 been known as senior status, or declined to serve as chief judge. After August 6, 1959, judges could not become or remain chief after turning 70 years old. The current rules have been in operation since October 1, 1982.[8]
Succession of seats
The court has twelve seats for active judges, numbered in the order in which they were initially filled. Judges who assume senior status enter a kind of retirement in which they remain on the bench, while vacating their seats, thus allowing the U.S. President to appoint new judges to fill their seats.
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
Notes
- Elizabeth Aguilera (November 20, 2006). "10th Circuit judge's oath a family affair". The Denver Post. Retrieved April 15, 2017.
- Establishment of the Tenth Judicial Circuit: "An Act To amend sections 116, 118, 126 of the Judicial Code, as amended, to divide the eighth judicial circuit of the United States, and to create a tenth judicial circuit." Federal Judiciary History. FJC.gov. Retrieved September 24, 2009.
- "Tenth Circuit Act of 1929". Official website of the Federal Judicial Center. Archived from the original on September 26, 2006. Retrieved October 20, 2006.
- Prior to January 8, 1996, Judge Porfilio was named John Porfilio Moore.
- Lewis was appointed to the bench of the United States Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit in 1921 by Warren G. Harding. 45 Stat. 1346 reassigned his seat to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Tenth Circuit.
- Cotteral was appointed to the bench of the United States Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit in 1928 by Calvin Coolidge. 45 Stat. 1346 reassigned his seat to the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Tenth Circuit.
- 28 U.S.C. § 45
- 62 Stat. 871, 72 Stat. 497, 96 Stat. 51
References
- "Standard Search". Federal Law Clerk Information System. Archived from the original on October 21, 2005. Retrieved June 16, 2005.
- primary but incomplete source for the duty stations
- "Instructions for Judicial Directory". Website of the University of Texas Law School. Archived from the original on November 11, 2005. Retrieved July 4, 2005.
- secondary source for the duty stations
- data is current to 2002
- "U. S. Court of Appeals for the Tenth Circuit". Official website of the Federal Judicial Center. Archived from the original on January 1, 2005. Retrieved June 16, 2005.
- source for the state, lifetime, term of active judgeship, term of chief judgeship, term of senior judgeship, appointer, termination reason, and seat information
