Olneya
Olneya tesota is a perennial flowering tree of the family Fabaceae, legumes (peas, beans, etc.), which is commonly known as ironwood, desert ironwood, or palo fierro in Spanish. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Olneya. This tree is part of the western Sonoran Desert complex in the Southwestern United States.
| Olneya | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| (unranked): | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Tribe: | |
| Genus: | Olneya A. Gray |
| Species: | O. tesota |
| Binomial name | |
| Olneya tesota | |
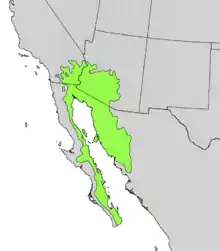 | |
| Natural range | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
Tesota Müll.Berol., W.G.Walpers, Ann. Bot. Syst. 4: 479 (1857) | |
Description
The desert ironwood grows as a bush or tree, reaching heights of about 10 metres (33 feet) and average trunk diameters of about 60 centimetres (24 inches). Exceptionally, in larger protected washes it can reach greater height and a more massive trunk.
In younger trees, the bark is gray, shiny, and smooth; in older trees the bark is broken open. The tree is evergreen, but can lose its leaves if temperatures fall below 2 °C (36 °F). In continual drought conditions the leaves will be lost.
The leaves are bluish-green and pinnately compound. They are arranged on a petiole, 15 cm (6 in) long, with 6–9 leaflets (or variously up to 15, with 7 opposite and one terminal), each measuring 0.7 to 2.5 cm (1⁄4 to 1 in). At the base of each pinnate leaf petiole grow two thorns, each about 1 cm (3⁄8 in) long.
Bloom time occurs in late April/May to June. Flowers are of 5 unequal petals, in colors of medium purple, magenta-red, or white to pale pink. Seedpods are 5–8 cm (2–3 in) long and light reddish brown when seedpods have ripened.
Two other species, Parkinsonia florida (blue palo verde) and Acacia constricta (catclaw acacia), have similar light red/brownish seedpods. Catclaw acacia's seedpods are shorter and J-shaped.
 View from below a specimen
View from below a specimen Tree in Sonoran Desert
Tree in Sonoran Desert
Taxonomy
The genus name of Olneya is in honour of Stephen Thayer Olney (1812–1878), who was an American manufacturer and botanist with expertise in the genus Carex.[3][4]
The genus was circumscribed by Asa Gray in Pl. Nov. Thurb. page 328 in 1854.[2]
Distribution and habitat
The species is native to the Southwestern United States and extreme northwestern Mexico in the Baja California Peninsula and the Sonoran Desert. Within Mexico its range includes the states of Baja California Sur and Baja California, on the Gulf of California side east of the cordillera ranges, and Sonora state west of the Sierra Madre Occidental cordillera, in the south approaching the northern border of northern Sinaloa state. In the Southwestern US its range includes the Colorado Desert of southeast Southern California, a part of the Sonoran Desert, and western and southern Arizona.[2] Olneya does not range into the higher-elevation, colder, southeast of Arizona's Sonoran Desert region, nor into the sky islands of the Madrean Sky Islands region.
Ecology
The pleasant-tasting sap is consumed by bees and hummingbirds. The silky-flycatcher or phainopepla pose a problem, for when they consume mistletoe berries and excrete them in the cracks of Olneya tesota, the mistletoe will parasitize its host.[5]
An indicator species
Olneya tesota is an indicator species of the Sonoran Desert region.[6] The Sonoran Desert has one other species with the identical north–south, and east–west range. The seasonally migrating lesser long-nosed bat follows the bloom season of various species from south to north and extends into the same regions of the Sonoran Desert as Olneya. The bat ranges from southern Baja California del Sur and north into the Southwestern US.[7]
In the north, both species define the Colorado Desert sub-region of the Sonoran Desert surrounding the northern end of the Gulf of California; further south in the Baja Peninsula the sub-division is defined as the Vizcaino Desert.
The winter and permanent range of the bat extend into the northern countries of Central America.
Uses
The seeds can be eaten by first being roasted.[8]
Olneya ironwood is very hard and heavy. Its density is greater than water and thus sinks; it does not float downstream in washes and must be moved by current motion.
Due to its considerable hardness, processing desert ironwood is difficult. Final treatment of the wood with solutions can also be difficult because of its high density. As a result, mass processing of this wood is difficult, and most of its commercial usages are artisanal, such as durable wooden sculptures as well as knife handles.
Culture
Ironwood Forest National Monument in south-central Arizona is named for O. tesota.
See also
References
- "Olneya tesota". Germplasm Resources Information Network. Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Retrieved 2009-10-13.
- "Olneya A.Gray | Plants of the World Online | Kew Science". Plants of the World Online. Retrieved 1 September 2022.
- Quattrocchi, Umberto (2016). CRC world dictionary of medicinal and poisonous plants : common names, scientific names, eponyms, synonyms, and etymology. CRC Press. ISBN 9781482250640.
- Burkhardt, Lotte (2022). Eine Enzyklopädie zu eponymischen Pflanzennamen [Encyclopedia of eponymic plant names] (pdf) (in German). Berlin: Botanic Garden and Botanical Museum, Freie Universität Berlin. doi:10.3372/epolist2022. ISBN 978-3-946292-41-8. Retrieved January 27, 2022.
- Peattie, Donald Culross (1953). A Natural History of Western Trees. New York: Bonanza Books. p. 587.
- Little Jr., Elbert L. (1976). "Map 103, Olneya tesota". Atlas of United States Trees. Vol. 3 (Minor Western Hardwoods). US Government Printing Office. LCCN 79-653298. OCLC 4053799.
- "Bat range, and article". Archived from the original on 2008-07-05. Retrieved 2010-01-22.
- Little, Elbert L. (1994) [1980]. The Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Trees: Western Region (Chanticleer Press ed.). Knopf. p. 498. ISBN 0394507614.
External links
- Calflora Database: Olneya tesota (desert ironwood, ironwood)
- USDA Plants Profile of Olneya tesota (desert ironwood)
- UC Photos gallery – Olneya tesota
- Lesser Long-nosed Bat Ranges – equal to Olneya tesota:
- Journey of the Nectar Bats
- Learner.org: Map of Lesser Long-nosed Bat range Archived 2012-03-06 at the Wayback Machine
- Learner.org: "Signs of Spring" Archived 2008-07-05 at the Wayback Machine – article.