Tetraethylgermanium
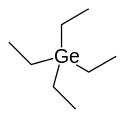
Tetraethylgermanium (IUPAC name: tetraethylgermane), abbreviated TEG, is an organogermanium compound with the formula (CH3CH2)4Ge. Tetraethylgermanium is an important chemical compound used in vapour deposition of germanium which is in a tetrahedral shape.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Tetraethylgermane | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| Abbreviations | TEG | ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.009.006 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID |
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UN number | 1993 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H20Ge | |||
| Molar mass | 188.878 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.998 g cm−3 | ||
| Boiling point | 163 to 165 °C (325 to 329 °F; 436 to 438 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  | |||
| Warning | |||
| H226, H302, H315, H319, H335 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P312, P321, P330, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P403+P233, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 35 °C (95 °F; 308 K) | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds |
| ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |||
Synthesis
Clemens Winkler first reported the compound in 1887 from diethylzinc and germanium tetrachloride, shortly after germanium was discovered in 1887.[1]
References
- Clemens Winkler (1887). "Mittheilungen über des Germanium. Zweite Abhandlung". J. Prak. Chemie. 36: 177–209. doi:10.1002/prac.18870360119. Retrieved 2008-08-20.
External links
- Tetraethylgermanium Datasheet commercial supplier
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.