Tiron (chemical)
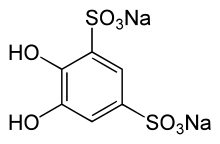
Tiron (trade name; systematic name disodium 4,5-dihydroxy-1,3-benzenedisulfonate) is a chemical compound used for its ability to form strong complexes with titanium and iron, as well as mixed compounds such as calcium titanium tiron.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Disodium 4,5-dihydroxybenzene-1,3-disulfonate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.220 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4Na2O8S2 | |
| Molar mass | 314.19 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Barzily, I; Yaalon, D. H; Avinur, P (1967). "The Mixed Compounds of Calcium and Titanium With Tiron. I". Israel Journal of Chemistry. 5 (6): 289–298. doi:10.1002/ijch.196700050.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.