Vaginal ultrasonography
Vaginal ultrasonography is a medical ultrasonography that applies an ultrasound transducer (or "probe") in the vagina to visualize organs within the pelvic cavity. It is also called transvaginal ultrasonography because the ultrasound waves go across the vaginal wall to study tissues beyond it.[1]
Uses
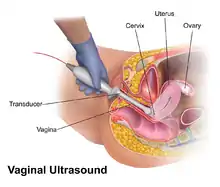
Vaginal ultrasonography is used both as a means of gynecologic ultrasonography and obstetric ultrasonography. It is preferred over abdominal ultrasonography in the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy.[2] It also can be used to evaluate patients with post-menopausal bleeding.[3] The finding on transvaginal ultrasound of a thin endometrial lining gives the physician a 99% negative predictive value that the patient does not have endometrial cancer.[3] If a patient had a prior endometrial sampling that was inconclusive, then a transvaginal ultrasound can be used to triage a women with post-menopausal bleeding.[3]
References
- Kumari, Sah Reena; Pritha, Basnet; Tara, Manandhar; Yadav, Prakash Chand; Shah, Sujeet Kumar (2022-05-31). "Comparison of Transvaginal Ultrasonography and Hysteroscopy for Evaluation of Postmenopausal Bleeding: A Cross Sectional Study". doi:10.5281/zenodo.6600349.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Kirk, E.; Bottomley, C.; Bourne, T. (2013). "Diagnosing ectopic pregnancy and current concepts in the management of pregnancy of unknown location". Human Reproduction Update. 20 (2): 250–61. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmt047. PMID 24101604.
- "The Role of Transvaginal Ultrasonography in Evaluating the Endometrium of Women With Postmenopausal Bleeding". www.acog.org. Retrieved 2023-10-12.