Triafulvalene
Triafulvalene or cyclopropenylidenecyclopropene is a fulvalene hydrocarbon with chemical formula C6H4, composed of two linked cyclopropene rings. Triafulvalene has never been isolated,[1] since it can decompose via an isodesmic reaction.[2] However, this molecule is of theoretical significance for theoretical organic chemists,[3] and its structure, stability, and spectral properties are well-studied.
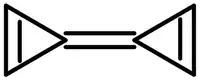 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
[1,1′-Bi(cyclopropylidene)]-2,2′-diene | |
| Other names
1,1′-Bi(cycloprop-2-en-1-ylidene) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4 | |
| Molar mass | 76.098 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
- Carey, Francis A.; Richard J. Sundberg (2007). Advanced Organic Chemistry: Part A: Structure and Mechanisms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 755–787. ISBN 978-0-387448-99-2.
- Neuenschwander, Markus (1986), "Synthetic and NMR spectroscopic investigations of fulvenes and fulvalenes" (PDF), Pure Appl. Chem., 58 (1): 55–66, doi:10.1351/pac198658010055, S2CID 55312999
- Scott, Anthony P.; Agranat, Israel; Biedermann, P. Ulrich; Riggs, Noel V.; Radom, Leo (1997). "Fulvalenes, Fulvenes, and Related Molecules: An ab Initio Study". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 62 (7): 2026–2038. doi:10.1021/jo962407l. ISSN 0022-3263. PMID 11671506.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.