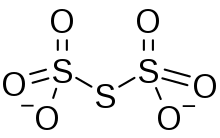
Trithionate
Trithionate is an oxyanion of sulfur with the chemical formula S
3O2−
6. It is the conjugate base of trithionic acid.[1] Dilute sodium hydroxide hydrolyzes S
4N
4 as follows, yielding sodium thiosulfate and sodium trithionate:
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,2,4,4-tetraoxido-1,5-dioxy-2,3,4-trisulfy-[5]catenate(2−) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| 3DMet | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| 142337 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| O6S3−2 | |
| Molar mass | 192.18 g·mol−1 |
| Conjugate acid | Trithionic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
2 S
4N
4 + 6 NaOH + 9 H
2O → Na
2S
2O
3 + 2 Na
2S
3O
6 + 8 NH
3
Certain sulfate-reducing bacteria have been known to use the compound in respiration.[2]
References
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Oltmann, L. F.; Stouthamer, A. H. (1975-10-27). "Reduction of tetrathionate, trithionate and thiosulphate, and oxidation of sulphide in proteus mirabilis". Archives of Microbiology. 105 (2): 135–142. doi:10.1007/BF00447128. ISSN 0302-8933. PMID 1106343. S2CID 1615795.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.